Ministry of Defence (Vietnam)
The Ministry of Defence (Vietnamese: Bộ Quốc phòng) is the governmental ministry of the Socialist Republic of Vietnam that manages, coordinates and supervises military affairs, including all military units, paramilitary units, and similar agencies in the country. The major office of the Ministry of Defence is located within the ancient Hanoi Citadel. The ministry is operated under the Constitution of the Socialist Republic of Vietnam as well as other various laws. The Ministry publishes the newspaper Quân Đội Nhân Dân together with the Central Military Commission of the Communist Party of Vietnam.
.jpg) | |
| Agency overview | |
|---|---|
| Jurisdiction | Government of Vietnam |
| Headquarters | 7 Nguyễn Tri Phương, Ba Đình, Hanoi |
| Employees | 450,000 military[1] |
| Annual budget | ₫ 27,024 billion (2008)[2] |
| Agency executives |
|
| Website | Official Website |
Organisation

Command structure
According to the 1992 Constitution of the Socialist Republic of Vietnam, the Ministry of Defence holds the supreme command of the Vietnam People's Army and other paramilitary units.[3] The command organisation of the ministry is composed of the central office, the General Staff (Bộ Tổng tham mưu), the General Political Department of the People's Army (Tổng cục chính trị) and other general departments, departments.
The General Staff is the commanding and co-ordinating institution of the Vietnam People's Army and other paramilitary units, it is currently directed by the Chief of the General Staff and Deputy Minister of Defence, Col. Gen. Đỗ Bá Tỵ who would be also acting minister during the absence of the minister in office. The General Political Department, presently headed by Col. Gen. Ngô Xuân Lịch, takes charge of political, moral and other activities in the military forces related to the Communist Party of Vietnam, the Department of Politics also operates the system of military court and procuracy.
The General Political Department is under the leadership activities of the Secretariat and often operations under the directly authority of the Central Military Commission. Other general departments (Tổng cục) of the ministry are General Department of Engineering (Tổng cục Kỹ thuật), General Department of Logistics (Tổng cục Hậu cần), General Department of Military Industries and Manufacture (Tổng cục Công nghiệp quốc phòng) and General Department of Military Intelligence (Tổng cục Tình báo quốc phòng or Tổng cục 2). Directly under the ministry are also the Search and Rescue Operations Department (Cục Cứu hộ, cứu nạn) and Department of Foreign Relations (Cục Đối ngoại).
The command structure of the ministry is coordinated by the Central Office (Văn phòng Bộ) which acts at the same time as office of the Central Party Committee of the military forces (Quân ủy Trung ương).[4]
The following is the structure of the central organisation of the Ministry of Defence:[5]
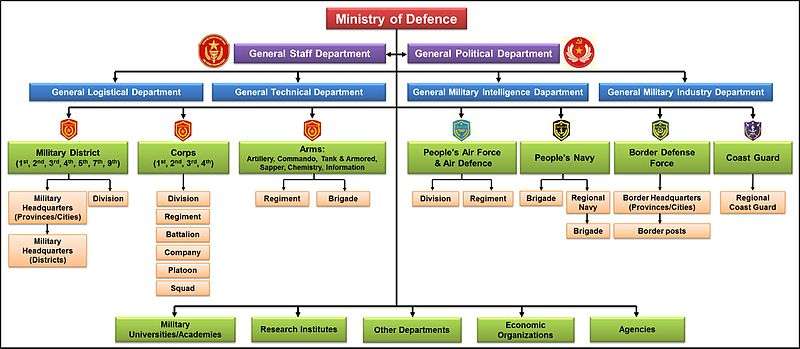
Components
.jpg)
The Ministry of Defence is the supreme command of the People's Army of Vietnam which contains several arms and army corps, the Vietnam People's Ground Forces, the Vietnamese People's Navy, the Vietnamese People's Air Force and Air Defence, the Vietnam Border Defence Force and the Vietnam Coast Guard. To organise the military activities and units, the territory of Vietnam is divided into 7 military regions and the Capital High Command which contains the region of Hanoi.[5]
The principal and core military force of Vietnam is the Vietnam People's Army (VPA)[6] with a regular force of 450,000 soldiers and officers and the reserve force of about 5 million.[1] The land-based units of the VPA consists of four army corps (quân đoàn): 1st, 2nd, 3rd and 4th; six arms (binh chủng): Artillery, Tank and Armoured Warfare, Sappers, Signals, Engineers and Chemical; seven military regions (quân khu) and one command (bộ tư lệnh): 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th, 5th Military Region, 7th Military Region, 9th Military Region and the High Command of the Capital City of Hanoi.[7] The border guard, coast guard, air force-air defence and the navy are organised as arms of the VPA, the navy in particular is divided in five naval regions (vùng hải quân) (from 1st to 5th).[8]
Besides, the Ministry of Defence also manages a system of academies, universities and research institutes with a total number of 21 academies (học viện), universities (trường đại học) and one college (trường cao đẳng). The principal academy of the ministry if the Vietnam Academy of Defence (Học viện Quốc phòng), it is the only institution for training strategical officers.[9] The Ministry of Defence has its own branch of economic organisations[10] which contains the Viettel Mobile, one of the leading mobile network operator in Vietnam.
Budget
The annual budget of the Ministry of Defence occupies approximately 2% of the GDP of Vietnam. The major portion of the budget is used for maintenance of officers, NCOs, soldiers and their readiness for action. Following are the ministry's budgets of recent years:[2]
| Year | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 |
| GDP of Vietnam | 839,211 | 973,791 | 1,143,442 | 1,490,000 |
| Ministry's budget | 16,278 | 20,577 | 28,922 | 27,024 |
| % per GDP | 1,872% | 2,194% | 2,529% | 1,813% |
| Unit: billion VND | ||||
List of Ministers
References
Notes
- Ministry of Defence (2009), White book, p. 67
- Ministry of Defence (2009), White book, p. 38
- Ministry of Defence (2009), White book, p. 52
- Ministry of Defence (2009), White book, pp. 55–56
- Ministry of Defence (2009), White book, p. 109
- Ministry of Defence (2009), White book, p. 61
- Ministry of Defence (2009), White book, p. 69
- Ministry of Defence (2009), White book, p. 72
- Ministry of Defence (2009), White book, p. 77
- Ministry of Defence (2009), White book, p. 81
Bibliography
- Ministry of Defence of Vietnam (2009). White book of Defence of Vietnam (in Vietnamese). Hanoi: World Publishing House.
- Ministry of Defense, Socialist Republic of Vietnam, Vietnam's National Defense in the Early Years of the 21st Century, Ha Noi, 2004.
