Mercaptobenzothiazole
2-Mercaptobenzothiazole (MBT) is an organosulfur compound with the formula C6H4NSCSH. The molecule consists of a benzene ring fused to a 2-mercaptothiazole ring. It is used in the sulfur vulcanization of rubber.[1]
thiazole-2-thiol_200.svg.png) | |
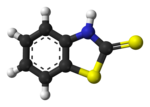 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1,3-Benzothiazole-2(3H)-thione | |
| Other names
Mercapto-2-benzothiazole; 2-MBT | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.216 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H5NS2 | |
| Molar mass | 167.24 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Solid |
| Melting point | 177–181 °C (351–358 °F; 450–454 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Synthesis and reactions
It is produced by the reaction of 2-aminothiophenol and carbon disulfide:
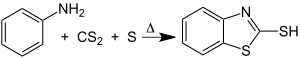
This method was developed by the discoverer of the compound. Other routes developed by Hoffmann included the reactions of carbon disulfide with 2-aminophenol and of sodium hydrosulfide with chlorobenzothiazole.[2] Further synthetic advances were reported in the 1920s that included demonstration that phenyldithiocarbamates pyrolyze to benzothiazole derivative.[3]
Oxidation gives the disulfide (MBTS). This can react with amines to give sulfenamide derivatives such as DCBS and 2-morpholinodithiobenzothiazole (MBSS). All of these compounds are important in sulphur vulcanization, where they act as accelerators.
disulfide.svg.png) Mercaptobenzothiazole disulfide (MBTS)
Mercaptobenzothiazole disulfide (MBTS)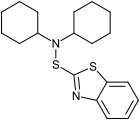 Dicyclohexyl-2-benzothiazolesulfenamide (DCBS)
Dicyclohexyl-2-benzothiazolesulfenamide (DCBS)
Uses
Using MBT, rubber vulcanizes with less sulfur and at milder temperatures, both factors give a stronger product. This effect was reported in 1921 by workers at Pirelli and in 1920 by Lorin B. Sebrell at Goodyear Tire & Rubber.[1]
In polymerization, it finds use as a radical polymerization inhibitor, chain transfer agent, reforming agent, and additive for photoinitiators.[4]
The compound has also been used in the past in the gold-mining industry for the froth flotation of gold from ore residue as part of the extraction process.[5]
This compound is used as cooling tower biocide.
Sodium salt is used as a biocide and preservative in adhesives (especially based on latex, starch, casein, and animal glues), paper, textiles. Often found together with sodium dimethyldithiocarbamate as e.g. Vancide 51. Zinc salt is used as a secondary accelerator in latex foam vulcanization.[6]
It can be added to oil-based hydraulic fluids, heat-transfer fluids (oils, antifreezes), cutting fluids and other mixtures as a corrosion inhibitor, effective for copper and copper alloys.[7]
It is also used in veterinary dermatology.[8] Here it is employed in topical preparations to treat acute moist dermatitis, "hot spots".[9]
In electroplating it is used as a brightener for copper sulfate baths, at about 50-100 milligrams/liter. Also can be added to silver cyanide baths.[7]
Safety
Studies have identified it as a potiential human carcinogen.[10][11] In 2016, it was identified by the World Health Organization as probably carcinogenic to humans.[12]
It causes allergic contact dermatitis.[13] The derivative morpholinylmercaptobenzothiazole is a reported allergen in protective gloves, including latex, nitrile, and neoprene gloves.[14]
It becomes air-borne as a result of wear on car tires, and is able to be inhaled.[15]
References
- Hans-Wilhelm Engels, Herrmann-Josef Weidenhaupt, Manfred Pieroth, Werner Hofmann, Karl-Hans Menting, Thomas Mergenhagen, Ralf Schmoll, Stefan Uhrlandt "Rubber, 4. Chemicals and Additives" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2004, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a23_365.pub2
- A. W. Hofmann (1887). "Zur Kenntniss des o-Amidophenylmercaptans". Chem. Ber. 20: 1788–1797. doi:10.1002/cber.188702001402.
- Sebrell, L. B.; Boord, C. E. (1923). "Preparation and properties of 1-mercaptobenzothiazole, its homologs and derivatives". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 45 (10): 2390–2399. doi:10.1021/ja01663a023.
- https://www.parchem.com/news-articles/2-Mercaptobenzothiazole-the-Hemi-Ultra-Vulcanization-Accelerator-N000170.aspx
- CABASSI, PAJ; et al. (November–December 1983). "The improved flotation of gold from the residues of Orange Free State ores" (PDF). Journal of the South African Institute of Mining and Metallurgy. 83 (11): 270–276. ISSN 0038-223X.
- Ash, Michael (2004). Handbook of Green Chemicals. ISBN 9781890595791.
- https://www.irowater.com/2-mercaptobenzothiazole-mbt-uses/
- "Mercaptobenzothiazole". drugs.com.
- https://dogcare.dailypuppy.com/mercaptobenzothiazole-uses-dogs-7559.html
- T. Sorahan (April 2009). "Cancer risks in chemical production workers exposed to 2-mercaptobenzothiazole". Occup Environ Med. 66 (4): 269–273. doi:10.1136/oem.2008.041400. PMID 19158128.
- National Toxicology Program scientists (May 1988). "NTP Toxicology and Carcinogenesis Studies of 2-Mercaptobenzothiazole (CAS No. 149-30-4) in F344/N Rats and B6C3F1 Mice (Gavage Studies)". Natl Toxicol Program Tech Rep Ser. 332: 1–172. PMID 12732904.
- Chris Graham (February 28, 2016). "Chemical found in babies' dummies and condoms 'probably causes cancer'". The Telegraph. Retrieved February 29, 2016.
- Gillian de Gannes; Sayali Tadwalkar; Aaron Wong & Nino Mebuke (2013), British Columbia Fails to Meet the North American Screening Standards: What are the Implications for Workers with Allergic Contact Dermatitis? (PDF), WorkSafeBC, archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-01-09
- Rose, R.F.; Lyons, P.; Horne, H.; Wilkinson, S.M. (2009), "A review of the materials and allergens in protective gloves", Contact Dermatitis, 61 (3): 129–137, doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.2009.01580.x, PMID 19780770
- Avagyan, R.; Sadiktsis, I.; Bergvall, C.; Westerholm, R. (2014), "Tire tread wear particles in ambient air—a previously unknown source of human exposure to the biocide 2-mercaptobenzothiazole", Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 21 (19): 11580–11586, doi:10.1007/s11356-014-3131-1