Mazagão
Mazagão (Portuguese: Município de Mazagão, [mazɐˈgɐ̃w̃]) is a municipality located in the south of the state of Amapá in Brazil. Its population is 17,030 and its area is 13,131 square kilometres (5,070 sq mi).[1]
Mazagão | |
|---|---|
Municipality | |
| Município de Mazagão | |
 Flag  Seal | |
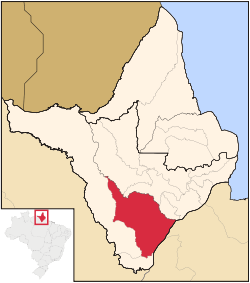 Mazagão in the state of Amapá | |
 Mazagão Mazagão in the state of Amapá | |
| Coordinates: 00°06′54″S 51°17′20″W | |
| Country | |
| Region | North |
| State | |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | João da Silva Costa (PPL) |
| Area | |
| • Land | 13,131 km2 (5,070 sq mi) |
| Population | |
| • Total | 17,032 |
| Time zone | UTC-3 (UTC-3) |
Name
The city was named after the Portuguese colony Mazagão in North Africa, now El Jadida, which the Portuguese abandoned in 1769 after some 250 years of occupation. Many of its inhabitants were evacuated to Brazil, where they founded a new settlement Nova Mazagão (0°12′59″S 51°25′55.6″W), now known as Mazagão Velho.[2] A total of 340 families arrived in the city of Belém in 1770 and in 1773 went to Nova Mazagão. One of the main theories on the origin of the name of Mazagaon - one of the original Seven Islands of Bombay and still a historic neighborhood of Mumbai, India - derives this name, too, from the Moroccan city, since both were under Portuguese rule in the same time.
Conservation
The municipality contains 44% of the 501,771 hectares (1,239,900 acres) Rio Cajari Extractive Reserve, created in 1990.[3] It contains 19% of the 806,184 hectares (1,992,120 acres) Rio Iratapuru Sustainable Development Reserve, created in 1997.[4] It contains part of the Jari Ecological Station.[5] It also contains 8.56% of the 2,369,400 hectares (5,855,000 acres) Amapá State Forest, a sustainable use conservation unit established in 2006.[6]
References
- "Mazagão" (in Portuguese). Macapá, Amapá, Brazil: Governo do Estado do Amapá. 2011. Archived from the original on 2014-08-27. Retrieved 2014-06-07.
- "Arqueologia de Mazagâo Velho". Site of the Department of Archaeology of the Federal University of Pernambuco, Brazil. Archived from the original on 2014-01-18. Retrieved 2013-02-20. (in Portuguese; the coordinates are under the image of the map of Brazil on the page; to see them pass your cursor over the image)
- RESEX do Rio Cajari (in Portuguese), ISA: Instituto Socioambiental, retrieved 2016-11-06
- RDS do Rio Iratapuru (in Portuguese), ISA: Instituto Socioambiental, retrieved 2016-11-05
- Figueiredo, João (13 March 1984), "DECRETO Nº 89.440, DE 13 DE MARÇO DE 1984", Brazilian Federal Senate (in Portuguese), Brazilian Government, retrieved 10 March 2016
- FES do Amapá (in Portuguese), ISA: Instituto Socioambiental, retrieved 2016-07-06