Mashiko, Tochigi
Mashiko (益子町, Mashiko-machi) is a town located in Tochigi Prefecture, Japan. As of 1 August 2020, the town had an estimated population of 21,841 in 7914 households[1], and a population density of 240 persons per km². The total area of the town is 89.40 square kilometres (34.52 sq mi).
Mashiko 益子町 | |
|---|---|
Town | |
Mashiko Town Office | |
Flag Seal | |
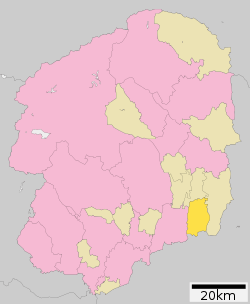 Location of Mashiko in Tochigi Prefecture | |
 Mashiko | |
| Coordinates: 36°28′2.4″N 140°05′36.1″E | |
| Country | Japan |
| Region | Kantō |
| Prefecture | Tochigi |
| District | Haga |
| Area | |
| • Total | 89.40 km2 (34.52 sq mi) |
| Population (August 2020) | |
| • Total | 21,841 |
| • Density | 240/km2 (630/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+9 (Japan Standard Time) |
| Symbols | |
| • Tree | Japanese red pine |
| • Flower | Yamayuri (Lilium auratum) |
| • Bird | Japanese bush warbler |
| Phone number | 0285-72-2111 |
| Address | 2030 Mashiko, Mashiko-machi, Haga-gun, Tochigi-ken 321-4293 |
| Website | Official website |

As of May 2015, the town had an estimated population of 23,400, and a population density of 240 persons per km2. Its total area is km2. Mashiko is known for its pottery, called Mashiko ware (益子焼).
Geography
Mashiko is located in the far southeast corner of Tochigi Prefecture.
Climate
Mashiko has a Humid continental climate (Köppen Cfa) characterized by warm summers and cold winters with heavy snowfall. The average annual temperature in Mashiko is 13.5 °C. The average annual rainfall is 1378 mm with September as the wettest month. The temperatures are highest on average in August, at around 25.7 °C, and lowest in January, at around 2.2 °C.[2]
Demographics
Per Japanese census data,[3] the population of Mashiko has remained relatively steadily over the past 40 years.
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1920 | 15,920 | — |
| 1930 | 17,034 | +7.0% |
| 1940 | 18,347 | +7.7% |
| 1950 | 24,542 | +33.8% |
| 1960 | 21,121 | −13.9% |
| 1970 | 19,844 | −6.0% |
| 1980 | 22,104 | +11.4% |
| 1990 | 24,317 | +10.0% |
| 2000 | 25,685 | +5.6% |
| 2010 | 24,351 | −5.2% |
History
Mashiko developed as a fortified temple town from the Nara period. During the Edo period, it was an exclave of Kurobane Domain from Nasu. After the Meiji restoration, Mashiko, Nanai and Tano villages were created within Haga District on April 1, 1889 with the creation of the modern municipalities system. Mashiko was elevated to town status on March 1, 1895. Mashiko annexed Nanai and Tano villages on June 1, 1954.
Government
Mashiko has a mayor-council form of government with a directly elected mayor and a unicameral town council of 16 members. Mashiko, together with the other municipalities in Haga District collectively contributes two members to the Tochigi Prefectural Assembly. In terms of national politics, the town is part of Tochigi 4th district of the lower house of the Diet of Japan.
Economy
The economy of Mashiko is heavily dependent on tourism from its ceramics crafts industry. The town is also a bedroom community for neighboring Mooka and Utsunomiya.
Education
Mashiko has four public primary schools and three public middle schools operated by the city government. The town has two public high schools operated by the Tochigi Prefectural Board of Education.. There are also 6 nurseries (Yawaragi, Nanai, Aoba, Midori, Mashiko and Tano) and 2 kindergartens (Nanai and Takara).
Transportation
Culture
.jpg)
Mashiko is known for its pottery, called mashikoyaki (益子焼). Early pottery in Mashiko dates back to the Jōmon and Yayoi periods. Mashikoyaki is often thought of as simple and rustic in style, with brown and maybe a little red glaze, but modern pottery made in Mashiko today is found in many styles, on account of the creative freedom brought to Mashiko by Shoji Hamada. Modern Mashikoyaki dates only to 1853, when a potter discovered that local clay here was ideal for ceramics. The style was popularized in 1930 when Hamada, later designated as a Living National Treasure, set up a kiln in Mashiko. Hamada′s student, Tatsuzō Shimaoka, was also designated as a Living National Treasure and worked in Mashiko from 1953 until his death in 2007.
Mashiko is a folkware kiln site that is unlike some of the other older kiln sites around Japan. The town is open to newcomers whether or not they are potters or of other professional backgrounds in arts, sciences and education. In Japan, craftsmen are usually born into their profession, but in Mashiko, anyone can become a potter. Following Shoji Hamada, people looking to return to a more traditional Japanese lifestyle settled in the area.[4] Twice a year, coinciding with the Golden Week Holidays in the first week of May, and again for the first week of November, there is a pottery and crafts festival where potters and craftsmen from Mashiko and surrounding areas come to the town and set up stalls.
Local attractions
- Saimyō-ji, Jizo-in, Entsu-ji - Buddhist temples containing several important cultural properties (as designated by the national and prefectural governments).
Sister cities

References
- "Mashiko Town official statistics" (in Japanese). Japan.
- Mashiko climate data
- Mashiko population statistics
- Holmes, Ann Sommer. The Transition of the Artisan-Potter to the Artist Potter in Mashiko, a folkware kiln site in Japan. New York University Press, 1982. p. 12.
- Baekeland, Frederick. Modern Japanese Ceramics in American Collections. New York: Japan Society, 1993. (ISBN 0-913304-38-7)
External links
![]()
- Official Website (in Japanese)
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Mashiko. |