Maryland Route 328
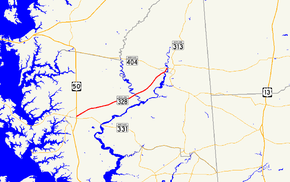
Maryland Route 328 (MD 328) is a state highway in the U.S. state of Maryland. The state highway runs 15.24 mi (24.53 km) from U.S. Route 50 (US 50) in Easton east to just north of MD 404 in West Denton. MD 328 connects Easton with Denton, passing through eastern Talbot County and a neck of land in Caroline County between the Choptank River and Tuckahoe Creek. MD 328 was constructed in Talbot County in the late 1910s between downtown Easton and a point west of Matthews. The state highway was constructed in Caroline County in the late 1920s and early 1930s, and was originally designated MD 457. The gap between the two highways was filled in the late 1940s and included a modern bridge over Tuckahoe Creek. MD 328's western terminus was moved to US 50 in the early 1960s. In West Denton, the highway was relocated and extended north to present MD 404 in the early 1980s.
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 | ||||
| Route information | ||||
| Maintained by MDSHA | ||||
| Length | 15.24 mi[1] (24.53 km) | |||
| Existed | 1927–present | |||
| Tourist routes | ||||
| Major junctions | ||||
| West end | ||||
| East end | River Road in West Denton | |||
| Location | ||||
| Counties | Talbot, Caroline | |||
| Highway system | ||||
| ||||
Route description
_at_Lewistown_Road_and_Kingston_Landing_Road_in_Matthews%2C_Talbot_County%2C_Maryland.jpg)
MD 328 begins at an intersection with US 50 (Ocean Gateway) in Easton. The roadway continues west on the opposite side of the intersection as Goldsborough Street toward downtown Easton. MD 328 heads northeast as Matthewstown Road, a two-lane undivided road that passes by residential subdivisions before entering farmland. After the intersection with Black Dog Alley, the state highway crosses Galloway Creek, Wootenaux Creek, and two unnamed tributaries of Kings Creek. MD 328 passes Ewing Airport, then crosses Beaverdam Branch before intersecting Lewistown Road in the hamlet of Matthews. A short distance east of Matthews, the state highway crosses Tuckahoe Creek on a bridge dedicated to Frederick Douglass.[1][2]
MD 328 continues into Caroline County as New Bridge Road, passing through farmland until the highway reaches West Denton. River Landing Road, the old alignment of MD 328 that approaches the Choptank River riverfront, splits to the northeast, while the state highway continues north past the Neck Meetinghouse and Yard to an intersection with MD 404 Business (Meeting House Road), which provides access to downtown Denton. MD 328 passes the other end of River Landing Road before reaching an intersection with the Denton bypass, MD 404 (Shore Highway). The state highway ends just north of the intersection with MD 404; River Road continues north as a county highway toward Ridgely.[1][2]
MD 328 is a part of the National Highway System as a principal arterial from US 50 in Easton to Black Dog Alley near Easton.[1][3]
History
The first section of MD 328 was paved from Easton to a point just east of Wootenaux Creek by 1919.[4] In addition, another section of present-day MD 328 was paved from MD 404 (now MD 404 Business) in West Denton southwest about 2 mi (3.2 km) by 1921.[5] The Talbot County portion of the highway was extended to just west of Beaverdam Branch, about 2 mi (3.2 km) west of Matthews, by 1923.[6] The Caroline County portion of the highway was extended southwest to Tuckahoe Creek in two sections in 1933 and 1935 and was designated MD 457.[7][8][9]
After World War II, construction began to fill the 5-mile (8.0 km) gap between the eastern end of MD 328 and the western end of MD 457.[10] The new bridge over Tuckahoe Creek and the remainder of the highway were completed in 1947 and by 1948 the MD 328 designation was applied to the whole highway from Easton to Denton.[11][12][13] By 1963, the western terminus had been rolled back from downtown Easton to US 50.[14] In West Denton, MD 328 was moved to a new alignment in 1981 since the old alignment had been overpassed by MD 404's new bridge over the Choptank River in 1980.[15][16] MD 328 was extended to its present terminus in 1985 ahead of the opening of the Denton bypass in 1987.[17][18] A new bridge over Tuckahoe Creek was built immediately downstream from the former MD 328 bridge. The new bridge opened to traffic in October 2012.[19]
Junction list
| County | Location | mi [1] | km | Destinations | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Talbot | Easton | 0.00 | 0.00 | Western terminus | |
| Caroline | West Denton | 14.67 | 23.61 | ||
| 15.16 | 24.40 | ||||
| 15.24 | 24.53 | River Road north – Ridgely | Eastern terminus | ||
| 1.000 mi = 1.609 km; 1.000 km = 0.621 mi | |||||
See also

References
- Highway Information Services Division (December 31, 2013). Highway Location Reference. Maryland State Highway Administration. Retrieved 2010-09-10.
- Talbot County (PDF).
- Caroline County (PDF).
- Google (2010-09-10). "Maryland Route 328" (Map). Google Maps. Google. Retrieved 2010-09-10.
- National Highway System: Maryland (PDF) (Map). Federal Highway Administration. October 1, 2012. Retrieved 2015-02-09.
- Zouck, Frank H.; Uhl, G. Clinton; Mudd, John F. (January 1920). Annual Reports of the State Roads Commission of Maryland (1916–1919 ed.). Baltimore: Maryland State Roads Commission. p. 48. Retrieved 2010-09-10.
- Maryland Geological Survey (1921). Map of Maryland: Showing State Road System and State Aid Roads (Map). Baltimore: Maryland Geological Survey.
- Maryland Geological Survey (1923). Map of Maryland: Showing State Road System and State Aid Roads (Map). Baltimore: Maryland Geological Survey.
- Byron, William D.; Lacy, Robert (December 28, 1934). Report of the State Roads Commission of Maryland (1931–1934 ed.). Baltimore: Maryland State Roads Commission. pp. 324–325. Retrieved 2010-09-10.
- Tabler, H.E.; Wilkinson, C. Nice; Luthardt, Frank F. (December 4, 1936). Report of the State Roads Commission of Maryland (1935–1936 ed.). Baltimore: Maryland State Roads Commission. pp. 222–223. Retrieved 2010-09-10.
- Maryland State Roads Commission (1939). General Highway Map: State of Maryland (Map). Baltimore: Maryland State Roads Commission.
- Reindollar, Robert M.; Webb, P. Watson; McCain, Russell H. (February 1, 1947). Report of the State Roads Commission of Maryland (1945–1946 ed.). Baltimore: Maryland State Roads Commission. pp. 89–90. Retrieved 2010-09-10.
- Federal Highway Administration (2012). "NBI Structure Number: 100000050012010". National Bridge Inventory. Federal Highway Administration.
- Reindollar, Robert M.; George, Joseph M.; McCain, Russell H. (February 15, 1949). Report of the State Roads Commission of Maryland (1947–1948 ed.). Baltimore: Maryland State Roads Commission. p. 106. Retrieved 2010-09-10.
- Maryland State Roads Commission (1948). Maryland: Official Highway Map (Map). Baltimore: Maryland State Roads Commission.
- Maryland State Roads Commission (1963). Maryland: Official Highway Map (Map). Baltimore: Maryland State Roads Commission.
- Maryland State Highway Administration (1981). Maryland: Official Highway Map (Map) (1981–1982 ed.). Baltimore: Maryland State Highway Administration.
- Federal Highway Administration (2012). "NBI Structure Number: 100000050016010". National Bridge Inventory. Federal Highway Administration.
- Maryland State Highway Administration (1985). Maryland: Official Highway Map (Map) (1985–1986 ed.). Baltimore: Maryland State Highway Administration.
- Maryland State Highway Administration (1987). Maryland: Official Highway Map (Map). Baltimore: Maryland State Highway Administration.
- "Project Information: MD 0328 NEW BRIDGE ROAD BRIDGE 5012 OVER TUCKAHOE CREEK". Maryland State Highway Administration. Retrieved 2010-09-13.
