Maryland Line (CSA)
The Maryland Line in the Army of the Confederate States of America was made up of volunteers from Maryland who, despite their home state remaining in the Union, fought for the Confederate States of America during the American Civil War. Of approximately 25,000 Marylanders who volunteered, most fought in the Army of Northern Virginia, and it was not until late in 1863 that a Maryland Line in the CSA was formally created. However, by this late stage in the war, few men wished to leave the units they had fought alongside for more than two years, and the exiles' dream of an independent Maryland Line in the Confederate army would never be fully realized.

History
Like other border states such as Kentucky and Missouri, Maryland found itself in a difficult position as war approached, with opinion heavily divided between supporters of North and South. The western and northern parts of the state, especially those Marylanders of German origin, tended to favor remaining in the Union, whilst the low-lying Chesapeake Bay area had a slave economy and tended to support the Confederacy if not outright secession.[2]
However, Maryland would remain part of the Union during the United States Civil War, because of President Abraham Lincoln's swift action to suppress dissent in Maryland. The belated assistance of Governor Hicks also played an important role, as Hicks, initially indecisive, eventually co-operated with federal officials to stop further violence and prevent a move to secession.
Baltimore Riots of April 1861

By April 1861 it had become clear that war was inevitable, and it was around this time that a number of Marylanders began to resign their commissions in the US Army, among them, George H. Steuart, then a junior officer, who resigned his captain's commission to join the Confederacy.[3]
On April 19 Baltimore was disrupted by riots, during which Southern sympathizers attacked Union troops passing through the city by rail, causing what were arguably the first casualties of the Civil War. Major General George H. Steuart, commander of the Maryland Militia ordered his militia to assemble, armed and uniformed, to repel the Federal soldiers,[4] as Steuart himself was strongly sympathetic to the Confederacy, along with most of his senior officers. Perhaps knowing this, and no doubt aware that public opinion in Baltimore was divided, Governor Thomas Holliday Hicks did not order out the militia.[5]
Steuart's eldest son commanded one of the city militias during the disturbances of April 1861 and, in a letter to his father, the younger Steuart wrote:
I found nothing but disgust in my observations along the route and in the place I came to - a large majority of the population are insane on the one idea of loyalty to the Union and the legislature is so diminished and unreliable that I rejoiced to hear that they intended to adjourn...it seems that we are doomed to be trodden on by these troops who have taken military possession of our State, and seem determined to commit all the outrages of an invading army. [6]
Occupation of Maryland
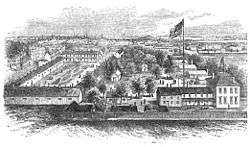
The political situation remained uncertain until May 13, 1861 when Union troops occupied the state, restoring order and preventing a vote in favor of Southern secession, and by late summer Maryland was firmly in the hands of Union soldiers. Arrests of Confederate sympathizers soon followed, and many of those who had declared their support for the Confederacy were forced to leave the state. Among them were militia General George H. Steuart, who fled to Charlottesville, Virginia, after which much of his family's property was confiscated by the Federal Government.[7] Steuart's family home in Baltimore, Old Steuart Hall, was seized by the Union Army and Jarvis Hospital was soon erected on the grounds of the estate, to care for wounded Federal soldiers.[8]
Flight to the South

However, although the state would remain in the Union throughout the war, many members of the newly formed Maryland Line in the Confederate army would be drawn from Steuart's militia.[9] Marylanders sympathetic to the South were easily able to cross the Potomac River to join and fight for the Confederacy. Exiles organized a Maryland Line in the Army of Northern Virginia which consisted of one infantry regiment, one infantry battalion, two cavalry battalions and four battalions of artillery. According to the best extant records, up to 25,000 Marylanders went south to fight for the Confederacy. Many members of the Maryland Line would be drawn from former members of the state militia.[9] During the events of April 1861 in Baltimore, around 15,000 Marylanders had volunteered to serve under the command of Colonel Isaac Trimble for the defense of the city, but following the occupation of Baltimore on May 13 by Union General Benjamin Butler, these new units were forbidden to assemble and effectively ceased to exist.[10]
By early May around 500 Marylanders had begun to assemble at Harper's Ferry, Virginia, under the command of Captain Bradley Tyler Johnson, forming 8 companies of Maryland infantry. Johnson preferred not to join the newly forming Virginia regiments, arguing that Marylanders should fight under their own flag. However, other former members of the Maryland militia did not agree; many members of the elite Maryland Guard and Independent Greys from Baltimore went to Richmond, where they were mustered into the service of Virginia.[10]
About 60,000 Maryland men served in all branches of the Union military. However, many of the Union troops were said to enlist on the promise of home garrison duty.
Lee's Invasion of the North
In September 1862 General Robert E. Lee launched his Maryland Campaign, taking the war to the Union for the first time. Southerners were optimistic that Marylanders would rise up and join the Southern columns, but they were to be disappointed. Upon entering Maryland, the Confederates found little support; rather, they were met with reactions that ranged from a cool lack of enthusiasm, to, in many cases, open hostility. Lee was disappointed at the state's resistance, a condition that he had not anticipated as many of the fiercely pro-Southern Marylanders had already traveled south at the beginning of the war to join the Confederate Army in Virginia. Only a "few score" of men joined Lee's columns in Maryland.[11]
Formation of the Maryland Line
On June 22, 1863, the Confederate Secretary of State for war, James A. Seddon, finally authorized the formation of a formal "Maryland Line" in the Confederate Army.[10]
On October 22, 1863 the 1st Maryland Infantry Batallion was detached from the brigade of General George H. Steuart and assigned to the newly formed Maryland Line, travelling by rail to Hanover Junction, Virginia, where they met the 1st Maryland Cavalry, CSA, the Baltimore Light Artillery, CSA, the 1st Maryland Artillery, CSA, and the 4th Maryland Artillery, CSA. At this time all Marylanders serving in the Army of Northern Virginia were invited to join the newly formed Maryland Line. Few however did so, as the men were by now reluctant to break up units which had already fought together for over two years.[12]
The cavalry battalion of the Maryland Line, commanded by Col Bradley T. Johnson, joined the Army of Northern Virginia during the Overland Campaign. The Line suffered losses in the Battle of Haw's Shop on May 27, 1864. The Marylanders also participated in the actions related to the Battle of Cold Harbor. They later participated in Jubal Early's campaigns in the Shenandoah Valley. The infantry battalion was engaged at Cold Harbor. Eventually it was assigned to the corps of LTG Ambrose Powell Hill during the Siege of Petersburg. The artillery units also participated in the Virginia campaigns of 1864-1865.
Notable Commanders

- Arnold Elzey (1816–1871) was a Marylander who fought in both the United States Army and the Confederate Army, serving as a major general during the American Civil War. He was one of the few officers to receive an on-the-field promotion to general by President Jefferson Davis.

- Brigadier General George Hume Steuart (1828–1903). Steuart was an American military officer who served thirteen years in the United States Army, then resigned at the start of the American Civil War,[3] rising to the rank of brigadier general in the Army of Northern Virginia. Nicknamed "Maryland Steuart" to avoid verbal confusion with Virginia cavalryman J.E.B. Stuart, Steuart zealously promoted the secession of Maryland before and during the conflict. Wounded at Cross Keys[13] and then captured at the Battle of Spotsylvania Court House,[14] Steuart was exchanged in the summer of 1864, returning to a brigade command in the Army of Northern Virginia for the remainder of the war, serving in the division of MG George Pickett. Steuart was one of the officers who with Robert E. Lee surrendered to Ulysses S. Grant at Appomattox Court House.[15]
List of Units

Artillery
- 1st Maryland Artillery, CSA (a.k.a. Dement's Artillery)
- 2nd Maryland Artillery, CSA (a.k.a. Baltimore Light Artillery)
- 3rd Maryland Artillery, CSA (a.k.a. Ritter's Battery)
- 4th Maryland Artillery, CSA (a.k.a. Chesapeake Battery)
Cavalry
- 1st Maryland Cavalry, CSA
- 2nd Maryland Cavalry, CSA (a.k.a. Gilmor's Partisan Rangers)
Infantry
- 1st Maryland Infantry, CSA
- 2nd Maryland Infantry, CSA
See also
- Maryland in the American Civil War
- Maryland Civil War Confederate units
References
- Eicher, David J., The Longest Night: A Military History of the Civil War, Simon & Schuster, 2001, ISBN 0-684-84944-5.
- Field, Ron, et al., The Confederate Army 1861-65: Missouri, Kentucky & Maryland Osprey Publishing (2008), Retrieved March 4, 2010
- Glatthaar, Joseph T., General Lee's Army: From Victory to Collapse, Free Press (Simon & Schuster), 2008, ISBN 978-0-684-82787-2.
- Goldsborough, W. W., The Maryland Line in the Confederate Army, Guggenheimer Weil & Co (1900), ISBN 0-913419-00-1.
- Hanson, George Adolphus, Old Kent: The Eastern Shore of Maryland: Notes Illustrative of the Most Ancient Records Of Kent County, Maryland (1876), unknown publisher.
- McPherson, James M., Crossroads of Freedom: Antietam, The Battle That Changed the Course of the Civil War, Oxford University Press, 2002, ISBN 0-19-513521-0.
- Nelker, Gladys P., The Clan Steuart, Genealogical Publishing (1970).
- Papenfuse, Edward C. et al., Archives of Maryland, Historical List, new series, Vol. 1. Annapolis, MD: Maryland State Archives (1990).
- Pfanz, Harry W., Gettysburg - Culp's Hill and Cemetery Hill University of North Carolina Press, Chapel Hill, NC (1993).
- Richardson. Hester Dorey, Side-Lights on Maryland History: With Sketches of Early Maryland Families, Tidewater Publishing, 1967. ISBN 978-0-8063-0296-6.
- Steuart, George H., Letter to the National Intelligencer dated November 19, 1860, unpublished, Archive of the Maryland Historical Society.
- Steuart, William Calvert, Article in Sunday Sun Magazine, "The Steuart Hill Area's Colorful Past", Baltimore, February 10, 1963.
- White, Roger B, Article in The Maryland Gazette, "Steuart, Only Anne Arundel Rebel General", November 13, 1969.
- Young, Alfred C., Lee's Army during the Overland Campaign: A Numerical Study, Louisiana State University Press, Baton Rouge, 2013. ISBN 978-0-8071-5172-3
Notes
- Goldsborough, p.109.
- Field, Ron, et al., p.33, The Confederate Army 1861-65: Missouri, Kentucky & Maryland Osprey Publishing (2008), Retrieved March 4, 2010
- Cullum, George Washington, p.226, Biographical Register of the Officers and Graduates of the U.S. Military Retrieved Jan 16 2010
- Hartzler, Daniel D., p.13, A Band of Brothers: Photographic Epilogue to Marylanders in the Confederacy Retrieved March 1, 2010
- Brugger, Robert J., p.285, Maryland, A Middle Temperament: 1634-1980, Johns Hopkins University Press (1996) Retrieved Jan 15 2010
- Mitchell, Charles W., p.102, Maryland Voices of the Civil War. Retrieved February 26, 2010
- Brugger, Robert J., p.280, Maryland, A Middle Temperament: 1634-1980 Retrieved Feb 28 2010
- Nelker, p.120
- Goldsborough, p.9
- Field, Ron, et al., p.36, The Confederate Army 1861-65: Missouri, Kentucky & Maryland Osprey Publishing (2008), Retrieved March 4, 2010
- McPherson, p. 98; Glatthaar, p. 166; Eicher, p. 339.
- Maryland Civil War units at www.2ndmdinfantryus.org/csunits.html Retrieved February 20, 2010
- Goldsborough, p.56.
- Hoptak, John David (August 12, 2009), Happy 181st Birthday. . ., 48th Pennsylvania Infantry/Civil War Musings, Accessed January 7, 2009
- Pfantz, p.313
External links
- The Maryland line in the Confederate States Army. Published by Gale Cengage Learning, ISBN 9781432812676 Retrieved February 20, 2010
- Maryland Civil War units at www.2ndmdinfantryus.org/csunits.html Retrieved February 20, 2010
- Re-enactment society of the 1st Maryland Infantry Retrieved May 10, 2010