Marcus Claudius Fronto
Marcus Claudius Fronto (killed in battle AD 170) was a Roman senator and Consul, and a general in the Imperial Roman army during the reigns of emperors Antoninus Pius (r. 138-61), Marcus Aurelius (r. 161-80), and Lucius Verus (r. 161-69).
Sources
Despite his important military role under Marcus Aurelius, Fronto's existence is only known from two inscriptions, both of which contain a summary of his career:
- CIL III 01457, a dedication to Fronto (possibly on the base of a statue), when he was governor of Dacia in 168–170, by the citizens of Colonia Traiana Sarmizegetusa, a Roman colony, in which he is praised as "patron, bravest of men, most generous of governors" (patrono fortissimo viro amplissimo praeside)[1]
- CIL VI 41142, an epitaph engraved on the plinth of his statue, erected in his honour in the Forum of Trajan in Rome.[2]
The lack of mention of Fronto in surviving literary sources for this period is unsurprising, as they are extremely sparse and fragmentary.
Early life
Nothing is known about Fronto's early life except that his family originated in Asia Minor and that his father, Tiberius Claudius Fronto, was a Roman senator. Fronto was thus born into the ordo senatorius ("senatorial order"), the highly privileged and wealthy elite of some 600 families which filled most of the major civilian and military posts in the empire. Fronto pursued a typical senatorial cursus honorum (public-service career), a mix of civilian and military posts.
Political career
In the civic sphere, Fronto, in his early 20s, served a traditional term as one of the decemviri stlitibus judicandis ("Committee of Ten charged with adjudicating legal disputes"), a judicial body. He entered the Senate by the normal route, as one of 20 candidates elected by senators as quaestors each year (for which the minimum age was 25). He then served as curule aedile ab actis senatus (in charge of drafting senatorial decrees) and praetor. The culmination of his civilian career was election in 165 or 166[3] as Suffect Consul.
(NB: These posts were the old magistracies, one-year executive posts of the Roman Republic. In the imperial era, the posts survived due to the official fiction that the state remained a republic, but their function was limited to the administration of the City of Rome. Nevertheless, they remained crucial to career advancement, as they determined seniority in the Senate and eligibility to provincial governorships. The latter were reserved for senators of praetorian rank i.e. those who had held the post of praetor).
On his return from the Parthian War, Fronto served as one of the two curatores operum et locorum publicorum ("Directors of Public Works and Places"), charged with the maintenance of public buildings in Rome.[1]
Military career
In the military sphere, the normal path for senators' sons was to serve, in their early 20s, between the decemvirate and admission to the Senate, a stint of about 3 years as the ranking military tribune (the tribunus militum laticlavius), on the staff of a legatus legionis (legion commander) in order to gain military experience. It is probable that Fronto performed this service, but no record of it survives. Fronto's first recorded post as a general officer, held after his praetorship (i.e., probably in his early 30s), was as commander of the legion XI Claudia, under the emperor Antoninus Pius (r. 138-61).[2] This legion was permanently based, from AD 104, at Durostorum in Moesia Inferior on the lower Danube.
Parthian War (161–166)
During Marcus Aurelius' Parthian War (161-166), Fronto initially commanded the legion I Minervia, which in 162[3] he personally led on the long march to the Eastern front from its permanent base at Bonna on the river Rhine in Germania Superior.[2] During the course of this war, he won from the nominal commander-in-chief of the campaign, co-emperor Lucius Aurelius Verus, a string of the army's most prestigious awards for valour: the corona muralis ("mural crown" - a crown made of gold, in the shape of a wall with turrets for the first man to scale an enemy-held city wall: rarely awarded, since such a man hardly ever survived),[4] corona vallaris ("rampart crown"), corona aurea ("golden crown"), and four hastae purae (miniature gold spears); in addition, he was accorded 4 vexilla (honorific commander's standards, embroidered in gold thread).[1] In 163,[3] Fronto was promoted to field-marshal rank (legatus Augusti pro praetore--i.e., governor of an imperial province), in command of Roman forces in the Eastern provinces of Armenia, Osrhoene and Anthemusia.
In 165/6, Fronto, in his capacity as Consul, was entrusted with supervising the recruitment of Italian youth for Marcus Aurelius' two newly founded legions, II Italica and III Italica.[2]
Marcomannic Wars (166–170)
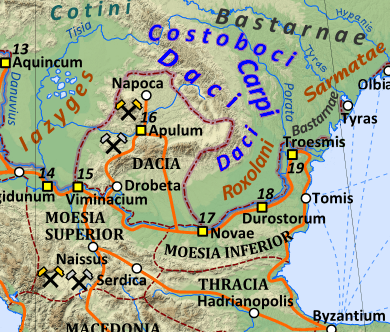
In 166-70, during the early stages of the Marcomannic Wars, known to the Romans as the "German and Sarmatian War" (bellum Germanicum et Sarmaticum), Fronto served as a field-marshal on the troubled Danube front. He was governor of Moesia Superior in 166-8,[3] facing the "Sarmatian salient" (i.e., the Hungarian Plain, lying between Roman-held Pannonia and Dacia, so called because it was ruled by the Iazyges, a Sarmatian tribe). In 168, he accompanied the co-emperors M. Aurelius and Lucius Verus to Sirmium as one of Verus' comites (literally: "companions"--i.e., senior staff-officers).[5] In 169, the emperors decided to return to Rome in order to escape the Antonine plague, a virulent smallpox epidemic which was ravaging the army (nevertheless, Verus died of the disease on the way). Fronto remained at the front. On the death (in battle or from plague) of Sextus Calpurnius Agricola, governor of neighbouring Tres Daciae province, Dacia Apulensis was added to his command and then the whole of Tres Daciae.[2][6] At this point, Fronto's "super-command" would probably have comprised 4 legions and around 60 auxiliary regiments, a grand total of over 50,000 troops.[7]
In this period, there was heavy fighting in Fronto's sector, although details are entirely lacking.[5] Fronto's adversaries were the Iazyges and neighbouring Germanic tribes, especially the Quadi, who threatened Dacia's western and northern borders. Fronto's epitaph records that he fought "a number of successful battles against the Germans and the Iazyges" (aliquot secunda proelia adversus Germanos et Iazyges).[2] However, in the campaigning season of 170, Fronto's luck ran out: "He fell, bravely fighting to his last breath for the Republic" (ad postremum pro re publica fortiter pugnans ceciderit).[2][8]
Memorial
In recognition of his services to the state, the Senate approved a motion tabled by the emperor to erect in Trajan's Forum (Rome) a statua armata of Fronto (literally: an "armed statue", a nude bronze sculpture of the subject, holding a spear: see Roman triumphal honours).[2]
Citations
References
- Corpus Inscriptionum Latinarum (CIL):
CIL III 1457
CIL VI 41442 - Prosopographia Imperii Romani (PIR) (Biographical Dictionary of the Roman Empire)
- Cambridge Ancient History 2nd Ed Vol XI (2000) Ch. 3: A.R. Birley: Hadrian and the Antonines
- Goldsworthy, Adrian (2003): Complete Roman Army
- Holder, Paul (2003): Auxiliary deployment in the Reign of Hadrian