MG132
MG132 is a potent, reversible, and cell-permeable proteasome inhibitor [1] (Ki = 4 nM). It belongs to the class of synthetic peptide aldehydes.[2][3] It reduces the degradation of ubiquitin-conjugated proteins in mammalian cells and permeable strains of yeast by the 26S complex without affecting its ATPase or isopeptidase activities. MG132 activates c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK1), which initiates apoptosis. MG132 also inhibits NF-κB activation with an IC50 of 3 μM and prevents β-secretase cleavage.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
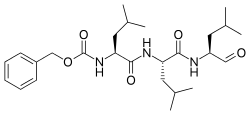
| IUPAC name
Benzyl N-[(2S)-4-methyl-1-[[(2S)-4-methyl-1-[[(2S)-4-methyl-1-oxopentan-2-yl]amino]-1-oxopentan-2-yl]amino]-1-oxopentan-2-yl]carbamate | |
| Other names
N-Benzyloxycarbonyl-L-leucyl-L-leucyl-L-leucinal Z-Leu-Leu-Leu-al | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C26H41N3O5 | |
| Molar mass | 475.630 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Solubility | 100 mM in EtOH and DMSO |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Molecular Mechanism
There are several inhibitors that can readily enter cell and selectively inhibit degradative pathway. It includes peptide aldehydes, such as Cbz-leu-leu-leucinal (MG132), Cbz-leu-leu-norvalinal (MG115) and acetyl-leu-leu-norleucinal (ALLN).[1] These are substrate analogues and potent transition-state inhibitors of chymotrpsin like activity of proteasome machinery.[4][5] The peptide aldehydes are also known to inhibit certain lysosomal cysteine proteases and the calpains hence MG132 may not be exclusive inhibitor of proteasomal pathway.[4]
References
- Lee, Do Hee; Goldberg, Alfred L (October 1998). "Proteasome inhibitors: valuable new tools for cell biologists". Trends in Cell Biology. 8 (10): 397–403. doi:10.1016/S0962-8924(98)01346-4.
- Ito A, Takahashi R, Muira C, Baba Y (1975). "Synthetic Study of Peptide Aldehydes". Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin. 12 (23): 3106–3113. doi:10.1248/cpb.23.3106.
- Hayashi M, Saito Y, Kawashima S (31 January 1992). "Calpain activation is essential for membrane fusion of erythrocytes in the presence of exogenous Ca2+". Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 182 (2): 939–946. doi:10.1016/0006-291x(92)91822-8. PMID 1734892.
- Rock, Kenneth L.; Gramm, Colette; Rothstein, Lisa; Clark, Karen; Stein, Ross; Dick, Lawrence; Hwang, Daniel; Goldberg, Alfred L. (September 1994). "Inhibitors of the proteasome block the degradation of most cell proteins and the generation of peptides presented on MHC class I molecules". Cell. 78 (5): 761–771. doi:10.1016/s0092-8674(94)90462-6. ISSN 0092-8674.
- Lee, Do Hee; Goldberg, Alfred L. (1 November 1996). "Selective Inhibitors of the Proteasome-dependent and Vacuolar Pathways of Protein Degradation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae". Journal of Biological Chemistry. 271 (44): 27280–27284. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.44.27280. ISSN 0021-9258.