Lowboy (trailer)
A lowboy (low-loader in British English, low-bed in western Canada and South Africa or float in Australia and eastern Canada) is a semi-trailer with two drops in deck height: one right after the gooseneck and one right before the wheels. This allows the deck to be extremely low compared with other trailers. It offers the ability to carry legal loads up to 12 ft (3.66 m) tall, which other trailers cannot. Lowboys are used to haul heavy equipment such as bulldozers, industrial equipment etc.

History
The first lowboy trailer was invented in the 1920s; it featured a riveted gooseneck and solid rubber tires. The first detachable gooseneck trailer, referred to as an RGN (Removable goose neck), was invented in 1958.[1]
Types
The lowboy trailer comes in several types, for a wide range of tasks. Some types are:
- Fixed gooseneck (FGN): allows a longer deck length and has the lightest weight. These are lower trailers than normal, with low-profile tires, usually with drop ramps in the rear to facilitate loading of equipment, but are not actually considered "lowboys". The neck is arched in such a way, that it when lowered, it becomes a ramp thus allowing the front tires of equipment to be pulled onto the deck.[2]
- Fixed-neck: the neck is fixed to trailers; offers the lightest weight, but sacrifices the ability to detach and load over the front
- Hydraulic detachable gooseneck (hydraulic RGN or HRGN)): fastest and easiest to detach, at the expense of weight and deck length. It is the most common and versatile of lowboy trailers; the gooseneck is detached using large hydraulic cylinders to raise and lower the trailer and a small cylinder shores the neck to the truck, removing the neck so a large piece of equipment can be driven over the front onto the deck of the trailer for transport. The hydraulics can be run from the truck auxiliary or from a pony motor mounted in the neck of the trailer.[3]
- Mechanically-detachable gooseneck (mechanical RGN or MRGN): while usually lighter than the hydraulic detachable gooseneck, users sacrifice ease and speed of detaching. Used for long specialty hauls.[4]
- Mechanical folding gooseneck (MFGN): The deck folds down to ground level to provide a ramp for from trailer loading.[5]
Features
Lowboy trailer features include:
Suspension types
- Spring ride: lowest cost; however, it has a rougher ride and adds more stress to the trailer
- Air-ride: smoother ride, adding to the life of the trailer frame. Air rides can also be adjusted for a higher or lower deck height.
- Hydraulic suspension: an oil-filled system, allowing wide variation of axle movement
- Independent suspension: a double wishbone, hydraulic suspension, which offers more stability, greater steering angle and more travel
Structural types
- Main structural steel type: mill rolled beams save money; although being around 4,000–6,000 lb (1,814–2,722 kg) heavier, they also reverse camber after a few years due to the much-lower strength of the main beams.
- T1 or A514 beams save weight and allow more versatile engineering of the trailer; they are cut to the highest-strength shape possible and welded together.
Gallery
- Two MAN SE ballast tractors pulling and one Mercedes pushing a 100,000 kg (220,000 lb) transformer on 10-axle lowboy
 A lowboy trailer carrying a Link-Belt lattice crawler crane.
A lowboy trailer carrying a Link-Belt lattice crawler crane. Another view of a lowboy
Another view of a lowboy Lowboy with a Volvo tracked excavator
Lowboy with a Volvo tracked excavator
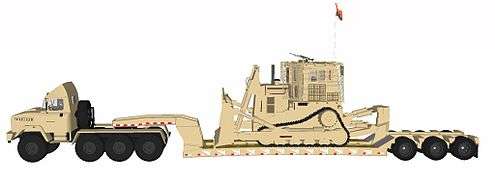 Military lowboy trailer
Military lowboy trailer Steam locomotive on lowboy
Steam locomotive on lowboy
See also
- Dolly (trailer)
- Flatbed trolley
- Flatbed truck
- Flatcar
- Heavy Equipment Transport System (HETS)
- Long combination vehicle
- Oliver Danson North
References
- RGN trailers- Accessed 2012-04-06
- Fixed goose neck trailer- Retrieved 2012-04-06
- - Hydraulic Detachable Gooseneck
- Mechanical removable gooseneck Archived 2012-01-03 at the Wayback Machine- Retrieved 2012-04-06
- Mechanical folding gooseneck- Retrieved 2012-04-06
External links

