Leonurus sibiricus
Leonurus sibiricus, commonly called honeyweed or Siberian motherwort, is an herbaceous plant species native to China, Mongolia, and Siberia. It has verticillaster inflorescence. It is naturalized in many other parts of the world, including South, Central and North Americas.[1][2]
| Leonurus sibiricus | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Asterids |
| Order: | Lamiales |
| Family: | Lamiaceae |
| Genus: | Leonurus |
| Species: | L. sibiricus |
| Binomial name | |
| Leonurus sibiricus | |
Description
Leonurus sibiricus is an herbaceous annual or biennial with upright stems that grow from 20–80 cm (8–30 in) tall. Plants have long petioled basal leaves that are ovate-cordate in shape. The leaves have toothed margins and are incised with deeply cut lobes. Typically one or a few flowering stems are produced from short tap-roots. The lower stem leaves are deciduous and wither away as the plants begin blooming. The petioles of the leaves, midway up the stems are 2 cm (0.79 in) long. The flowers are produced in many flowered verticillasters, produced in whorls around the top half or more of the stem. The flowers are sessile with 8 mm (0.31 in) long calices that are tubular-campanulate in shape. The corolla is white or reddish to purple-red, with an upper lip that is oblong in shape and longer than the lower lip. When flowering is done, brown oblong shaped nutlets are produced in good number.[3] Blooming occurs from July into late September, but flowering can occur year-round when climate permits.[4][5]
This species' habitat within its natural range is stony or sandy grasslands or pine forests.[6]
Alkaloids
Alkaloids isolated from the plant include:[8]
- Cycloleonurinine
- Leoheterin
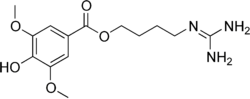
- Leonurine
- Leonurinine
- Leuronurine
- Prehispanolone[9]
- Preleoheterin
- Stachydrine[10]
References
- "Plants profile for Leonurus Sibiricus (honeyweed)". USDA PLANTS. Retrieved 2008-12-04.
- "Leonurus sibiricus". Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN). Agricultural Research Service (ARS), United States Department of Agriculture (USDA). Retrieved 2015-08-01.
- "Leonurus sibiricus in Flora of China @ efloras.org". www. efloras. org. Retrieved 2008-12-04.
- "Full text of "The flora of St. Croix and the Virgin Islands"". Archive.org. Retrieved 2010-01-18.
- "korea.PDF" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-06-04. Retrieved 2010-01-18.
- "Leonurus sibiricus in Flora of China @ efloras. org". www. efloras.org. Retrieved 2008-12-04.
- "The Leonurine and its preparation". An Hui New Star Pharmaceutical Development Co. 2008. Archived from the original on 2008-05-15. Retrieved 2008-08-28.
- "Leonurus sibiricus L. Labiatae Korean Name: Ik-mo-cho English Name: Motherwort Parts used. Herb. Traditional uses". webcache.googleusercontent.com. Retrieved 2008-12-04.
- "prehispanolone - PubChem Public Chemical Database". Pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. 2004-11-29. Retrieved 2010-01-18.
- "stachydrine - PubChem Public Chemical Database". Pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. 2004-11-29. Retrieved 2010-01-18.