Lamutskoye
Lamutskoye (Russian: Ламутское) is a rural locality (a selo) in Anadyrsky District of Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, Russia, located northwest of Markovo and 10 kilometers (6.2 mi) northeast of Chuvanskoye on the middle reaches of the Anadyr River.[11] As of the 2010 Census, its population was 173.[5][6]
Lamutskoye Ламутское | |
|---|---|
Location of Lamutskoye 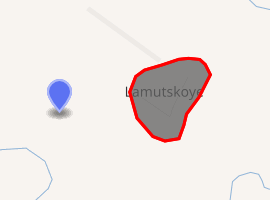
| |
 Lamutskoye Location of Lamutskoye 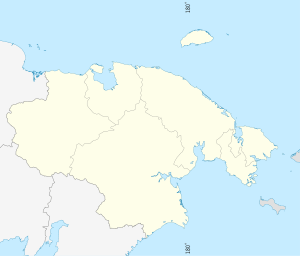 Lamutskoye Lamutskoye (Chukotka Autonomous Okrug) | |
| Coordinates: 65°32′N 168°50′E | |
| Country | Russia |
| Federal subject | Chukotka Autonomous Okrug[1] |
| Administrative district | Anadyrsky District[2] |
| Founded | 1936[3] or 1940[4] |
| Area | |
| • Total | 2 km2 (0.8 sq mi) |
| Population | |
| • Total | 173 |
| • Estimate | 138 |
| • Density | 87/km2 (220/sq mi) |
| • Municipal district | Anadyrsky Municipal District[8] |
| • Rural settlement | Lamutskoye Rural Settlement[8] |
| • Capital of | Lamutskoye Rural Settlement[8] |
| Time zone | UTC+12 (MSK+9 |
| Postal code(s)[10] | 689533 |
| Dialing code(s) | +7 42732 |
| OKTMO ID | 77603428101 |
Name and geography
The name of Lamutskoye is derived from the word Lamut—an archaic name for the Evens[12] (the dominant indigenous people in the area who migrated to western Chukotka from what is now the Sakha Republic of Russia[13]). It stands in the upper reaches of the Anadyr River, near the mouth of the Bolshoy Peledon River.[12]
History
Founded in 1936 (or, according to other sources, in 1940[4]) as a collective farm,[3] Lamutskoye served as a central hub for the Lamutsko-Yablonskaya nomadic reindeer breeders group, consisting of only eight itinerant families.[12] In 1960, along with Chuvanskoye and Markovo, the farm was merged to form the Markovsky State Farm.[3][12]
After the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991, small localities like Lamutskoye were extremely hard hit. In 2000, the monthly living wage across Chukotka was estimated at 3,800 rubles; however, the average wage in Lamutskoye was a meager 50–100 rubles.[14]
Administrative and municipal status
Within the framework of administrative divisions, Lamutskoye is subordinated to Anadyrsky District.[2] Within the framework of municipal divisions, Lamutskoye is a part of Lamutskoye Rural Settlement within Anadyrsky Municipal District.[8]
Culture and infrastructure
Lamutskoye is the starting point for the Ryilet festivities—the longest reindeer race in the world held each year over a 90-kilometer (56 mi) course between Lamutskoye and Chuvanskoye—in which racers compete for the Governor's Cup.[4][12]
Lamutskoye's infrastructure consists of a school, library, and the Palace of Culture, which conducts traditional feasts, races, and ceremonies connected with the reindeer herders.[4]
Demographics
As of 2010, the official census results showed a population of 173, of whom 98 were male and 75 female[5][6]—a significant reduction from the 2006 estimate of 230[3] and the 2005 estimate of 213 (according to a report prepared for the Kupol gold project,[15]). Of the 213 people living here in 2005, 212 were of indigenous origin.[15] The ethnic composition of Lamutskoye's population is as follows:
| Indigenous people | Number | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Chukchi |
111 |
52% |
| Lamut |
63 |
30% |
| Chuvan |
28 |
13% |
| Evenk |
6 |
2% |
| Yakut |
5 |
2% |
| Russian |
1 |
<1% |
| Total |
213 |
100% |
Source:[15]
Climate
Lamutskoye has a continental subarctic climate (Köppen climate classification Dfc) with bitterly cold, very long winters and short, very mild summers.[16]
| Climate data for Lamutskoye | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | −23.3 (−9.9) |
−23.8 (−10.8) |
−19.7 (−3.5) |
−10.2 (13.6) |
2.7 (36.9) |
16.1 (61.0) |
19.4 (66.9) |
15.5 (59.9) |
7.4 (45.3) |
−7.0 (19.4) |
−19.6 (−3.3) |
−24.7 (−12.5) |
−5.6 (21.9) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −28.5 (−19.3) |
−29.0 (−20.2) |
−25.5 (−13.9) |
−16.1 (3.0) |
−1.9 (28.6) |
9.8 (49.6) |
13.0 (55.4) |
9.6 (49.3) |
2.1 (35.8) |
−11.8 (10.8) |
−24.6 (−12.3) |
−29.8 (−21.6) |
−11.1 (12.1) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −33.6 (−28.5) |
−34.1 (−29.4) |
−31.3 (−24.3) |
−22.0 (−7.6) |
−6.5 (20.3) |
3.6 (38.5) |
6.6 (43.9) |
3.7 (38.7) |
−3.1 (26.4) |
−16.6 (2.1) |
−29.5 (−21.1) |
−34.8 (−30.6) |
−16.5 (2.4) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 27 (1.1) |
17 (0.7) |
13 (0.5) |
14 (0.6) |
12 (0.5) |
28 (1.1) |
48 (1.9) |
50 (2.0) |
28 (1.1) |
23 (0.9) |
30 (1.2) |
24 (0.9) |
314 (12.5) |
| Source: [17] | |||||||||||||
References
Notes
- Law #33-OZ
- Directive #517-rp
- Strogoff, p. 93
- Official website of Anadyrsky District. Lamutskoye Rural Settlement (in Russian)
- Russian Federal State Statistics Service (2011). "Всероссийская перепись населения 2010 года. Том 1" [2010 All-Russian Population Census, vol. 1]. Всероссийская перепись населения 2010 года [2010 All-Russia Population Census] (in Russian). Federal State Statistics Service.
- The results of the 2010 Census and the 2014 estimate are given for Lamutskoye Rural Settlement, a municipal formation of Anadyrsky Municipal District. According to Law #148-OZ, Lamutskoye is the only inhabited locality on the territory of Lamutskoye Rural Settlement.
- Office of the Federal State Statistics Service for Khabarovsk Krai, Magadan Oblast, Jewish Autonomous Oblast and Chukotka Autonomous Okrug. Численность населения Чукотского автономного округа по муниципальным образованиям на 1 января 2018 года Archived August 31, 2019, at the Wayback Machine (in Russian)
- Law #148-OZ
- "Об исчислении времени". Официальный интернет-портал правовой информации (in Russian). June 3, 2011. Retrieved January 19, 2019.
- Почта России. Информационно-вычислительный центр ОАСУ РПО. (Russian Post). Поиск объектов почтовой связи (Postal Objects Search) (in Russian)
- Chereshev, p. 12
- Electoral Commission of Chukotka Autonomous Okrug. Lamutskoye Archived October 29, 2013, at the Wayback Machine (in Russian)
- Dallman, Map 3.6
- Chereshev, p. 14
- Bema Gold Corporation, pp. 87–89
- McKnight and Hess, pp. 232–235
- "Weather Averages for Lamutskoye". www.climate-data.org. Retrieved July 1, 2012.
Sources
- Дума Чукотского автономного округа. Закон №33-ОЗ от 30 июня 1998 г. «Об административно-территориальном устройстве Чукотского автономного округа», в ред. Закона №55-ОЗ от 9 июня 2012 г. «О внесении изменений в Закон Чукотского автономного округа "Об административно-территориальном устройстве Чукотского автономного округа"». Вступил в силу по истечении десяти дней со дня его официального опубликования. Опубликован: "Ведомости", №7 (28), 14 мая 1999 г. (Duma of Chukotka Autonomous Okrug. Law #33-OZ of June 30, 1998 On the Administrative-Territorial Structure of Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, as amended by the Law #55-OZ of June 9, 2012 On Amending the Law of Chukotka Autonomous Okrug "On the Administrative-Territorial Structure of Chukotka Autonomous Okrug". Effective as of after ten days from the day of the official publication.). (in Russian)
- Дума Чукотского автономного округа. Закон №148-ОЗ от 24 ноября 2008 г. «О статусе, границах и административных центрах муниципальных образований на территории Анадырского муниципального района Чукотского автономного округа», в ред. Закона №24-ОЗ от 1 апреля 2011 г. «О внесении изменений в Приложение 2 к Закону Чукотского автономного округа "О статусе, границах и административных центрах муниципальных образований на территории Анадырского муниципального района Чукотского автономного округа"». Вступил в силу через десять дней со дня официального опубликования. Опубликован: "Ведомости", №46/1 (373/1), 28 ноября 2008 г. (Duma of Chukotka Autonomous Okrug. Law #148-OZ of November 24, 2008 On the Status, Borders, and Administrative Centers of the Municipal Formations on the Territory of Anadyrsky Municipal District of Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, as amended by the Law #24-OZ of April 1, 2011 On Amending Appendix 2 of the Law of Chukotka Autonomous Okrug "On the Status, Borders, and Administrative Centers of the Municipal Formations on the Territory of Anadyrsky Municipal District of Chukotka Autonomous Okrug". Effective as of the day which is ten days after the official publication date.). (in Russian)
- E. Chereshev and A. Shestakov. Anadyr River Watershed, Rapid Assessment Report. Institute of biological Problems of the North, Wild Salmon Center, June 2003.
- W. K. Dallmann. Indigenous Peoples of the north of the Russian Federation, Map 3.6, Chukotskiy Avtonomyy Okrug. 1997.
- Bema Gold Corporation. Environmental Impact Assessment, Kupol Gold Project, Far East Russia, June 2005.
- McKnight, Tom L; Hess, Darrel (2000). "Climate Zones and Types". Physical Geography: A Landscape Appreciation. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall. ISBN 0-13-020263-0.
- M. Strogoff, P.-C. Brochet, and D. Auzias. Petit Futé: Chukotka. "Avant-Garde" Publishing House, 2006.