Lake Hazen
Lake Hazen is often called the northernmost lake of Canada, in the northern part of Ellesmere Island, Nunavut, but detailed maps show several smaller lakes up to more than 100 km (62 mi) farther north on Canada's northernmost island. Turnabout Lake is immediately northeast of the northern end of Hazen lake. Still further north are the Upper and Lower Dumbell Lakes, with Upper Dumbell Lake 5.2 km (3 mi) southwest of Alert, Canada's northernmost settlement on the coast of Lincoln Sea, Arctic Ocean.[3]
| Lake Hazen | |
|---|---|
 NASA image | |
 Lake Hazen  Lake Hazen | |
| Location | 118 km (73 mi) southwest of Alert, Nunavut |
| Coordinates | 81°48′N 71°00′W |
| Primary inflows | Glaciers of the Eureka Uplands: Henrietta Nesmith Glacier Gilmour Glaciers |
| Primary outflows | Ruggles River |
| Catchment area | 4,900 km2 (1,900 sq mi) |
| Basin countries | Canada |
| Max. length | 74 km (46 mi)[1] |
| Max. width | 12 km (7 mi)[1] |
| Surface area | 537.5 km2 (207.5 sq mi)[1] |
| Max. depth | 267 m (876 ft)[2] |
| Water volume | 51.4×109 m3 (41.7×106 acre⋅ft)[2] |
| Shore length1 | 185 km (115 mi) |
| Surface elevation | 158 m (518 ft)[1] |
| Islands | St. John's Island |
| Settlements | Hazen Camp |
| 1 Shore length is not a well-defined measure. | |
The northeastern end of Lake Hazen is 118 km (73 mi) southwest of Alert. Lake Hazen is the largest lake north of the Arctic Circle by volume. By surface area, it is third largest, after Lake Taymyr in Russia and Lake Inari in Finland. Lake Hazen is 74 km (46 mi) long and up to 12 km (7 mi) wide, with an area of 537.5 km2 (207.5 sq mi).[1] It stretches in a southwest-northeast direction from 81°40′N 72°58′W to 81°56′N 68°55′W. The lake is up to 269 m (883 ft) deep and has an estimated volume of 51.4 km3.[2] The shoreline is 185 km (115 mi) long and 158 m (518 ft) above sea level. It has several islands, the largest of them being Johns Island, which is 7 km (4.3 mi) long and less than 1 km (0.62 mi) wide, also extending in a southwest-northeast direction like the lake itself. Other islands include Gatter Island, Clay Island (both close to the northeastern shore), Whisler Island, and Dyas Island (both close to the southern shore). The lake is covered by ice about ten months a year. It is fed by glaciers (most importantly Henrietta Nesmith and the Gilmour Glaciers) from the surrounding Eureka Uplands—Palaeozoic rocks north of the lake, rising up to 2,500 m (8,200 ft) above sea level—and drained by 15 km (9.3 mi) long Ruggles River, which flows into Chandler Fjord on the northern east coast of Ellesmere Land. The lake is flanked by the Arctic Cordillera.
The area around the lake is a thermal oasis within a polar desert, with summer temperatures up to 20 °C (68 °F).[2]
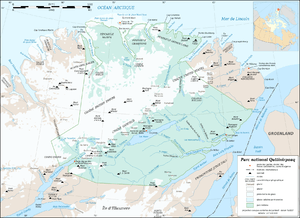
The lake is part of Quttinirpaaq National Park.
Artifacts of Thule civilization were discovered near Lake Hazen in 2004.[4] Thule preceded the Inuit. In 1882, Adolphus Greely discovered the lake during his 1881–1883 expedition. Greely's base camp for the exploration was Fort Conger at the northeastern shore of Ellesmere Island, at 81°44′N 64°44′W, which was established as part of the first International Polar Year. Greely named the lake in honour of General William Babcock Hazen, who had organized the expedition.[1] Camp Hazen was established on the northern shore of the lake in 1957 during the International Geophysical Year (IGY), and has been used by various scientific parties since then.
Lake Hazen is populated by two morphotypes of Arctic char, a larger and a smaller. Studies in the 1990s indicated neither char morphotype is anadromous, but Inuit traditional knowledge states otherwise.[5]
Named Inflows
All named rivers and creeks are listed in a clockwise manner, starting in the south:
At the southwestern end (from south to north):
- Very River
- Adams River
On the northwest coast (from southwest to northeast):
- Turnstone River
- Henrietta River
- Ptarmigan Creek
- Blister Creek
- Skeleton Creek
- Snow Goose River
- Abbé River
- Cuesta Creek
- Mesa Creek
- Gilman River
At the northeast end (from north to south):
- Turnabout River
- Salor Creek
On the southeast coast (only in the southwest, near the southwest end of the lake):
- Cobb River
- Traverse River
Tourism
Hikers can start their hiking trips at Lake Hazen itself, or from Tanquary Fiord warden station at Tanquary Fiord Airport 70 km (43 mi) southwest of the lake.
References
- Mark Nuttal: Encyclopedia of the Artctic. Routledge, 2012, ISBN 9781136786808, S. 835-836 (excerpt, p. 835, at Google Books)
- G. KÖCK, D. MUIR, F. YANG, X. WANG, C. TALBOT, N. GANTNER, D. MOSER: Bathymetry and Sediment Geochemistry of Lake Hazen (Quttinirpaaq National Park, Ellesmere Island, Nunavut). Arctic, Vol. 65, No. 1 (MARCH 2012), pp. 56-66 (JSTOR)
- "Description of Lake Hazen". University of Guelph. Archived from the original on 2011-05-18. Retrieved 2008-02-10.
- Greg Younger-Lewis (October 29, 2004). "Ambitious plan proposed for Quttinirpaaq National Park". nunatsiaq. Archived from the original on November 14, 2006. Retrieved 2008-02-10.
- Douglas Clark, “Assessing the Health of the Lake Hazen Ecosystem, Ellesmere Island, Northwest Territories,” Parks Canada, 1997. Archived from the original on 2007-09-28. Retrieved 2020-05-14. “Two morphotypes of Arctic char are present in Lake Hazen: a large, cannibalistic form, and a small, presumably benthic-feeding form (Reist et al. 1995). Taken together, the results of both radiotelemetry studies in 1995–6 (Babaluk et al. in prep.) and, more conclusively, strontium uptake by char (Halden et al. 1996) suggest that neither form is anadromous. However, this is in contradiction to Inuit traditional knowledge, which holds that the char in Lake Hazen do go to sea (Ellesmere Island National Park Reserve Advisory Board, March 5, 1997). A comprehensive demographic analysis of the char population of Lake Hazen is in progress (J. Reist, pers. comm.). Fecundity information is still required.”