La Asunción
La Asunción (Spanish pronunciation: [la asunˈsjon]) is a city in Venezuela. The capital of Nueva Esparta state (made up of three islands[1]), it lies on the Isla Margarita in the Caribbean Sea, off the South American mainland. It is 6 miles (10 km) inland from Porlamar and is in a genuine colonial setting. It has an imposing backdrop of Santa Rosa Castle, also known as the Santa Rosa Fort, which was built to protect the city. The most important structures in the city are built around the Plaza Bolivar. The Catedral Nuestra Señora de La Asunción, dated to the 16th century, is one of the earliest churches in the country. According to the 2011 census, it has a population of 28,513 people.
La Asunción | |
|---|---|
City | |
  | |
Flag Seal | |
.svg.png) La Asunción | |
| Coordinates: 11°01′39″N 63°51′46″W | |
| Country | |
| State | Nueva Esparta |
| Municipality | Arismendi Municipality |
| Elevation | 67 m (220 ft) |
| Population (2011) | |
| • Total | 28,513 |
| Time zone | UTC-4:30 (VST) |
| Area code(s) | 0295 |
| Demonym | Asuntino/a |
| Climate | BSh |
La Asunción was founded in 1565 by Captain Pedro González Cervantes de Albornoz. It is situated in a fertile valley surrounded by green hills, right in the center of eastern Margarita, where a fresher climate exist. It is the seat of the regional government.
History
In 1562, the Spanish villages of Espiritu Santo migrated to this hamlet to escape the marauding pirates and the tyrant Lope de Aguirre Spanish invaders. However, the pirates did not spare them as later in 1566 the French pirates headed by Jean Bontemps completely razed the village which was further compounded by the English privateer John Hopkins. However, as it got re-established as a town, it was given the Coat of Arms and called a city. This was followed by the building of the Santa Rosa fort.[2]
La Asunción thus was founded in 1565 by Captain Pedro González Cervantes de Albornoz. Construction of the Santa Rosa de la Eminencia castle on a hill overlooking the city began on the orders of the governor, Juan Muñoz de Gadea, after the French buccaneer Marquis de Maintenon attacked the city in early 1676.[3] The work was started on 24 March 1677[4] and finished c. 1683, under the command of the field master Don Juan Fermin.[5] La Asunción was involved in the Venezuelan War of Independence, and noted General Juan Bautista Arismendi married his wife Luisa Cáceres de Arismendi on December 4, 1814 in the city at the age of 39. Abandoned in 1935, twenty years later due to a local initiative the castle achieved the status of a War Museum.[6] It was declared as a National Monument in 1965 by president Raúl Leoni.[4][6]
Geography

It is situated in a fertile valley surrounded by green hills in the Santa Lucia valley, in the center of eastern Isla Margarita. Porlamar is 6 miles (9.7 km) to the south. It was then a secluded location considering its inaccessibility to pirates in the olden days.[7] It is a fertile valley which is nurtured by the Cerro El Copey which rises in the mountains here. A bridge across the Río Asunción was built in 1609 which existed till 1970 and provided entry to the town from the north.[2]
Demographics
La Asunción under the Nueva Esparta State (NES) had a population of 10,375 in 1981 and the recent figure as of 30 October 2010 was 28,309.[8] The corresponding figure for the NES was 263,748 and 491,610.[9]
Government
It is the seat of the regional government and the municipality of Arismendi Municipality, Nueva Esparta.[10]
Cityscape
The city has two banks, a post office, two museums, and a private hospital with modern facilities.[2] The Palacio Municipal is located behind the cathedral and houses the offices of the state government. The Assemblea Legislativa is accommodated in the building which was earlier a franciscan monastery and which also subsequently served as a hospital and prison. A sundial fixed in 1612 at the initiative of a governor, is known as "Relox Equinoccia Inferior". which is still seen at this venue.[2] The Plaza of La Asuncion is in two parts, the southern part is named as Plaza Bolivar and the northern part is named Plaza Luisa Caceres, whose statue is installed there. An old double storied house has been converted into a souvenir shop with a coffee kiosk.[2] The birthplace of the independence hero Juan Bautista Arismendi, husband of Luisa Caceres de Arismendi has been refurbished.[2]
Transportation
Air
La Asunción is located 30 kilometers from Santiago Mariño Caribbean International Airport which offers scheduled flights to mainland Venezuela as well as charter flights to international destinations.
Sea
Ferry services are available from a terminal 40 kilometers to the southwest in Punta de Piedras. Conferry offers service to Puerto La Cruz, Guanta, and La Guaira, on mainland Venezuela as well as service to Coche Island.
Landmarks
Some of the prominent landmarks of La Asuncion are the cathedral of Nuestra Senora de la Asuncion, the Santa Rosa castle, the Museo Nueva Cádiz, the Casa de la Cultura and Cerro El Copey National Park.
Catedral Nuestra Señora de La Asunción


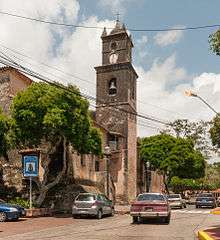
Built between 1570 and 1612, the Catedral Nuestra Señora de La Asunción is the oldest existing church in Venezuela.[11] Its construction was started in 1570 (much before the construction of the cathedral of Coro) and was never completed. A new church was built from 1609 which took 10 years to complete.[1][2][11] The church has a rectangular plan with massive walls as protection against pirate attacks. Supported on two lines of huge pillars which support the roof. There is a bell tower outside and which is also unique and the bells are now preserved in the plaza. One of the most important religious buildings on the Island, the Virgin of La Asunción is worshipped here. The cathedral has been declared a historical city monument. It has a plain façade and interior, but its left lateral tower, which dates to 1599, is the oldest in the country.[2][10] The important festival observed here is in mid August to celebrate Our Lady of Assumption when a procession is held and mass offered in the church.[2]
Castle of Santa Rosa de la Eminencia

.jpg)

The castle of Santa Rosa de la Eminencia was built in 1682 due to its prominent location on a hill; it acted as an observatory to watch for any invading forces approaching from the north, south, or east. A tunnel (a kilometer long dug during the original construction) from the fort connected to the governor's house, the church and the Convent of San Francisco. The fort guarded the eastern approach to the capital and was one of three forts that secured the island's strategic location to fend off the English, French, Dutch and other colonizers.[2][7][10] It was where Luisa Caceres de Arismendi, wife of the leading freedom fighter Juan Bautista Arismendi against Spanish imperialism, after capture by the Spanish on 27 September was imprisoned here one day before she became 17 years of age in 1816. She became a local heroine; in the prison cell of the fort, her first son was born and died prematurely due to lack of medical attention. She was imprisoned as her husband had escaped to the forests of Cerro El Copey and by capturing her they hoped that they could make the freedom fighter to surrender but the plan failed. After the death of the baby she was moved to Spain from where she escaped. She eventually joined her husband with whom she begot 11 children and the died at the age of 65. After her death she had the honour of being buried in the El Pantheon Nacional in Caracas one of the two women buried here. The cell where she was incarcerated in the castle has been preserved in its original form in which she lived. An inscription at the entrance to the cell reads "Luisa Caceres de Arismendi" for her virtue valour and martyrdom for her husband and country as prisoner in this jail when she was 16 years of age." The fort with strong sense of military purpose has exhibits of weapons of warfare, paintings of Simon Bolivar, knights in armor, and also iron balls which were tied to the legs of prisoners. Behind the kitchen there is abottle dungeon whose entrance is through a hole in the roof.[1][2][10] The fort provides an excellent view of the sea and Cerro Matasiete. It had a moat and a draw bridge which no longer exist.[2] The map on display in the museum is reported to be the best in the world.
Museum Nueva Cádiz
The Casa Capitular, the seat of the colonial government, and a city hall has been re-purposed as the Museo Nueva Cádiz (Museum New Cádiz) which features displays of pre-colonial artifacts and local handicrafts. Initially, as the seat of the government it had housed the offices in the first floor and a prison on the ground floor.[2][10] On May 4, 1810, the museum was the venue for Margarita's Declaration of Independence following the declaration made in Caracas on April 19, 1810. As the prison space was inadequate to accommodate the large number of prisoners, it was converted into a museum with a gallery and a biliary.
An interesting display in the museum is a sculpture of the tyrant ruler Lope de Aguirre who had terrorized the islanders during 1561; this event is featured in the film titled Aguirre, the Wrath of God produced by Werner Herzog with Klaus Kinski in the lead role.[2]
Casa de Juan Bautista Arismendi
Casa de Juan Bautista Arismendi honors Venezuela's war hero, Juan Bautista Arismendi.
Casa de la Cultura
The Casa de la Cultura is located opposite to the church and has a theater. A pre-Columbian pottery collection is on display here and replicas of the same could be bought in the nearby town of Santa Ana.[2]
Cerro El Copey National Park
Isla Margarita and particularly "Cerro El Copey National Park" are especially important with respect to the numbers of endemic species they harbor. The island was connected to mainland until the Pleistocene. As a result, there is a predominance of typical continental bird families like Tinamidae, Dendrocolaptidae, Formicaridae and Furnaridae, which are totally absent from the Antilles. Circa 31 mammal species are found on the island, four of which (the red-tailed squirrel Sciurus granatensis nesaeus, the eastern cottontail rabbit Sylvilagus floridanus margaritae, the white-tailed dear Odocoileus virginianus margaritae, and the capuchin monkey Cebus apella margaritae) are endemic subspecies, with the main populations located inside the national park. The Margarita capuchin monkey is considered to be the country's most threatened primate species and is critically endangered.
Gallery Images
 Colonial street in La Asuncion
Colonial street in La Asuncion Cerro el Copey National Park
Cerro el Copey National Park Santa Rosa Castle
Santa Rosa Castle Bolívar Square
Bolívar Square Luisa Cáceres de Arismendi Square
Luisa Cáceres de Arismendi Square 5 de Julio Boulevard
5 de Julio Boulevard
Notable residents

- Juan Fermín de Huidobro (1783-1853)- governor of Margarita
- Francisco Esteban Gómez (1783-1853) - military leader who died in La Asunción
- Modesta Bor
- Luis Beltrán Prieto Figueroa
- Juan Bautista Arismendi
- Luisa Cáceres de Arismendi
- José Enrique “Chelique” Sarabia - singer and songwriter[12]
References
- "History and Geography of Margarita". Freewebs.com. Retrieved 17 May 2013.
- Russell Maddicks (1 February 2011). Venezuela: The Bradt Travel Guide. Bradt Travel Guides. p. 175. ISBN 978-1-84162-299-6.
- "Castillo Santa Rosa de la Eminencia" (in Spanish). CorpoTur Margarita. Archived from the original on 9 January 2013. Retrieved 4 January 2013.
- "Fortaleza de Santa Rosa de La Eminencia" (in Spanish). Explorando Rutas. Archived from the original on 8 November 2012. Retrieved 4 January 2013.
- "History". Margarita Online. Retrieved 4 January 2013.
- "Castillo Santa Rosa de la Eminencia" (in Spanish). Conoce Margarita. Retrieved 4 January 2013.
- Showker, Kay (1 March 2006). Caribbean Ports Of Call Eastern And Southern Regions. Globe Pequot. pp. 377–. ISBN 978-0-7627-3885-4. Retrieved 16 May 2013.
- "Venezuela: Federal States, Major Cities, Urban Localities" (PDF). City Population.de. Archived from the original on 9 October 2012. Retrieved 17 May 2013.
- "Nueva Esparta state". City Population.de. Retrieved 17 May 2013.
- Susan Brushaber (1 October 1997). Venezuela Alive. Hunter Publishing, Inc. pp. 138–. ISBN 978-1-55650-800-4. Retrieved 17 May 2013.
- Wardrope, William (2003). Venezuela. Gareth Stevens Publishing. pp. 59–. ISBN 978-0-8368-2369-1. Retrieved 16 May 2013.
- Balderston, Daniel; Gonzalez, Mike; López, Ana M. (2000). Encyclopedia of Contemporary Latin American and Caribbean Cultures: A-D. Vol. 1. CRC Press. pp. 82–. ISBN 978-0-415-13188-9. Retrieved 16 May 2013.