LNWR Class F
The London and North Western Railway (LNWR) Class F was a class of 2-8-0 steam locomotives in service between 1906 and 1928.
| LNWR Class F | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
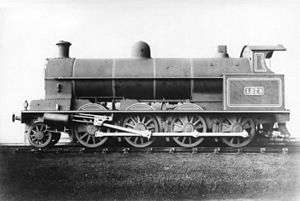 No. 1273 in photographic grey livery without tender | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
History

George Whale had rebuilt 26 of the Class B compound 0-8-0s with the simple addition of a leading pony truck between 1904-1908 to what would from 1911 become Class E. However, from 1906 rebuilds of Class Bs were given a larger 5'2" diameter boilers, and ten were so rebuilt. To these was added a pair of rebuilds of Class Es (Nos 1038 in 1907 and 647 in 1908).
From 1921, the LNWR started rebuilding the Class Fs into Class G1 superheated 0-8-0s, and by the grouping of 1923, six had been rebuilt. The remaining six were allocated the LMS numbers 9610-5. The LMS rebuilt a further four to G1s, between 1923-5. The remaining pair were withdrawn in 1927 and 1928 without being rebuilt. None was preserved.
List of locomotives
| LNWR no. | Origin | LMS no. | Fate | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 899 | Rebuilt from B 1907 | (9610) | Rebuilt to G1 1923 | [1] |
| 352 | Rebuilt from B 1907 | (9611) | Withdrawn 1927 | [1] |
| 2114 | Rebuilt from B 1908 | Rebuilt to G1 1922 | [1] | |
| 906 | Rebuilt from B 1907 | (9612) | Rebuilt to G1 1923 | [2] |
| 1036 | Rebuilt from B 1907 | Rebuilt to G1 1921 | [2] | |
| 1038 | Rebuilt from E 1907 | Rebuilt to G1 1921 | [2] | |
| 2570 | Rebuilt from B 1906 | Rebuilt to G1 1921 | [2] | |
| 1247 | Rebuilt from B 1906 | (9613) | Rebuilt to G1 1923 | [3] |
| 1273 | Rebuilt from B 1906 | 9614 | Withdrawn 1928 | [4] |
| 2573 | Rebuilt from B 1908 | Rebuilt to G1 1922 | [4] | |
| 647 | Rebuilt from E 1908 | (9615) | Rebuilt to G1 1925 | [5] |
| 1369 | Rebuilt from B 1907 | Rebuilt to G1 1922 | [6] |
LMS numbers in parentheses were not carried prior to rebuilding as G1 or withdrawal.
Notes
- Baxter 1979, p. 255.
- Baxter 1979, p. 256.
- Baxter 1979, p. 257.
- Baxter 1979, p. 258.
- Baxter 1979, p. 259.
- Baxter 1979, p. 260.
References
- Baxter, Bertram (1979). Baxter, David (ed.). British Locomotive Catalogue 1825-1923, volume 2B: London and North Western Railway and its constituent companies. Ashbourne: Moorland Publishing. ISBN 0-903485-84-2.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
Further reading
- Bob Essery & David Jenkinson An Illustrated Review of LMS Locomotives Vol. 2 Absorbed Pre-Group Classes Western and Central Divisions
- Edward Talbot, The London & North Western Railway Eight-Coupled Goods Engines
- Willie Yeadon, Yeadon's Compendium of LNWR Locomotives Vol 2 Goods Tender Engines