Kordeckiego street in Bydgoszcz
Kordeckiego street is located in downtown district of Bydgoszcz, Poland. It has been laid in the 1850s. Many frontages on this street offer architectural interests: some of the buildings are registered on the Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship Heritage List.
| Bydgoszcz | |
|---|---|
 View of facades at the crossing with Swiętej Trojcy street | |
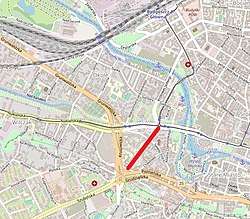 Kordeckiego Street highlighted on Bydgoszcz map | |
| Native name | Polish: Ulica o. Augustyna Kordeckiego w Bydgoszczy |
| Namesake | Augustyn Kordecki |
| Owner | City of Bydgoszcz |
| Length | 450 mGoogle maps (1,480 ft) |
| Width | ca. 10m |
| Area | Downtown district |
| Location | Bydgoszcz |
| Construction | |
| Construction start | Early 1850s[1] |
Location
Kordeckiego street runs on a south-west to north-east path: from Plac Poznański in the south to Focha Street in the north, crossing Swiętej Trojcy street on the way.
History
Kordeckiego street is registered on a 1855 address book of Bromberg[1] and appears partially on a 1876 city map under the calling Cichorien straße.[2] The extension of the street in first years of the 20th century led to a change in the house numbering of the buildings.
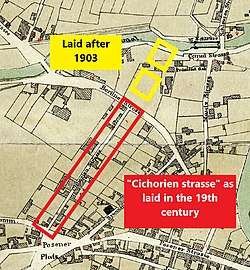
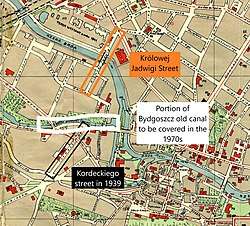
In 1974-1975, after the filling of a portion of Old Bydgoszcz Canal,[3] Kordeckiego street gained connection with Królowej Jadwigi Street at the crossing with Focha street in the north.
Since 2016-2017, municipal authorities launched a move towards renovating buildings in its control.[4]
Through history, this street bore the following names:[5]
- From inception in the 1850s to 1902, Cichorien straße (German for Chicory street);
- 1903-1920, (von) Hippel straße, from Theodor Gottlieb von Hippel the Younger (1775-1843), a friend of E. T. A. Hoffmann, who died in Bromberg;
- 1920-1939, Kordeckiego street;
- 1939-1945, (von) Hippel straße;
- 1945-1950, Kordeckiego street;
- 1950-1991 Jana Olszewskiego street, from Jan Olszewski, councilor a from Bydgoszcz,member of trade unions and also activist of the Polish Communist Party;
- Since 1991, Kordeckiego street.
Current name refers to Abbot Augustyn Kordecki (1603-1673), a prior of the Jasna Góra Monastery during the period of the Deluge.
Main areas and edifices
Tenements located north of Świętej Trójcy street crossing (i.e. No. 4,5,6,8,10,12) have all been erected after the extension of the street at the beginning of the 20th century.
Tenement at 4 Kordeckiego
1910[6]
Late Art Nouveau
The first landlord of the house was Adolf Müller, a painter.[7]
The facade bears late Art Nouveau characteristics. Its main feature is the avant-corps overhanging the main door: it carries openings with wrought iron railings and a loggia crowned by a tented roof-like top. One can also highlight the preserved wood-carved entry door with a large transom window.
 Main elevation
Main elevation Street door
Street door
Villa Korth, at 5 Kordeckiego
1910-1912[6]
Bernard Korth was the commissionner of this villa at the very place where he had his factory of Industrial machine for water supply and drainage systems, industrial elevators and cleaning machines. The plot then occupied the entire corner between the villa and Świętej Trójcy street.[7] Korth had also a branch on Kanal straße, today's western tip of Focha street. Bernhard's son, Bruno, took over the business in the 1920s till the start of WII.
The villa features neo-renaissance elements and echoes similar buildings in nearby Swiętej Trojcy street (No. 8 and 21). One can notice the heavy bossage on the facades ridges, the flower-shaped wrought iron decoration of the fence pillars, the roof lantern and the dormer tented roof topped by a finial.
 View from the street
View from the street Villa Korth at the beginning of the 20th century
Villa Korth at the beginning of the 20th century Flower-shaped wrought iron decoration of the fencing
Flower-shaped wrought iron decoration of the fencing
Tenement at 6 Kordeckiego
1912[6]
Late Art Nouveau, early Modern architecture
Adolf Müller, the painter living at then Hippel straße 4, was also the first owner of this tenement at its inception.[7]
The architectural elements composing the elevation show a transition to early modernism style: a predominance of straight vertical lines and very few details recall the gone Art Nouveau style (e.g. the ornamented balconies).
 Main elevation from the street
Main elevation from the street Adorned wrought iron balcony
Adorned wrought iron balcony
Tenement at 8 Kordeckiego
1910[6]
The house, initially located at Hippel straße 2, was owned by Artur Zemisch who ran a construction company and lived there.[7] He was also the landlord of the tenement at 30 Swiętej Trojcy street.
Although stripped of architectural details, the facade still features two balanced avant-corps bearing canted bay windows. The ground floor is adorned with dark marble and surrounds a portal decorated with Art Nouveau stuccoed motifs.
 Main frontage
Main frontage Main door and portal
Main door and portal
Tenement at 9 Kordeckiego, corner with 27 Swiętej Trojcy street
1905[6]
German Historicism
The house, initially at Berliner straße 6b, was owned by a smith, Anton Hertzke.[8] It was bought in the early 1910s by Carl ßeilke, a factory manager.[9] His widow lived there till 1926.[10] The building has experienced a thorough overhaul in 2016-2017.[11]
The tenement boasts two facades on the street of equivalent features: round top windows on the ground floor, the upper floors are all brick covered, with cartouches and long pilasters. Top wall dormers have ogee shapes. The corner of the building carries a thin bay window, much like a bartizan, crowned by an onion dome roof with a finial.
 View of the building from street crossing
View of the building from street crossing Detail of the finial
Detail of the finial.jpg) Facade on Kordeckiego
Facade on Kordeckiego Facade on Swiętej Trojcy street
Facade on Swiętej Trojcy street
Tenement at 10 Kordeckiego
1912[6]
First registered landlord was Johann Sikorski, running a restaurant at abutting No.12.[7] He did not live in this tenement.
The frontage displays a few Art Nouveau details, such as the decorated cartouches around the openings, the floral motifs on lintels or the round-shaped transom window above the main door.
 Main frontage
Main frontage
 Main door
Main door
Tenement at 11 Kordeckiego
1900s[12]
The building was initially owned by Carl August Franke, an affluent entrepreneur of Bromberg.[12]
The symmetrical facade is characterized by pedimented windows at each floor and the absence of any superfluous details.
 Main elevation
Main elevation
Tenement at 12 Kordeckiego, corner with Swiętej Trojcy street
1898[6]
The plot belonged to Johann Sikorski,[12] a restaurateur who had the tenement erected at the end of the 19th century. Initially at Hippelstraße 1,[13] the building had been the property of the Sikorski family till the end of the 1930s.
The tenement boasts Art Nouveau details, especially in the use of cartouches, pediments and friezes. The facade on Kordieckiego street is the most ornamented, the other one having lost its decoration. Both elevation have oriel windows with a balcony and are topped with an ogee shaped wall dormer.
 View from streets intersection
View from streets intersection.jpg) Facade on Kordeckiego street
Facade on Kordeckiego street
Buildings that follow are located in the historical part of the street, then named Cichorein straße with its own house numbering.
Emil ßohl tenement at 13 Kordeckiego
1905[6]
Eclecticism, elements of Art Nouveau
Emil ßohl, the first landlord, ran there a business selling alcohol-free beverages.[14] His special was the champagne-weiße (white champagne without alcohol).[15] At the time, the building was registered at 1 Cichorien straße.
Although the main frontage displays a neo-classical style, one can be surprised to discover a gorgeous Art Nouveau decor beneath the oriel window, featuring women figures, apple tree and other floral motifs.
.jpg) Main frontage
Main frontage Art Nouveau motifs
Art Nouveau motifs Art Nouveau motifs
Art Nouveau motifs
Tenement at No.14, corner with 29 Swiętej Trojcy street
Registered on Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship Heritage List, No.722476 Reg A/1389, October 6, 2008[16]
1910[6]
The house, initially at Berliner straße 7, was co-owned by Heinrich Kori, a Berlin engineer, and the widow of Rudolph Kori, a lawyer in Leipzig.[17] In 1910, the building moved to the hands of the Wedell brothers, Carl (a geometer) and Paul (a merchant):[18] it remained in the Wedell family until the outbreak of World War II.
The tenement boasts two facades of magnificent Art Nouveau architectural style, recently renovated in 2016. One can underline the corner bay window, overhanging the entrance, ornamented with stuccos depicting two blooming trees. On both facades, a multitude of adorned motifs recall the late Secession style, echoing the Grawunder brothers' tenements erected at Dworcowa Street 45/47 during the same period.
 View from streets intersection
View from streets intersection Decoration detail
Decoration detail.jpg) Gable motifs
Gable motifs.jpg) Cartouche
Cartouche.jpg) Elevation on Świętej Trojcy street
Elevation on Świętej Trojcy street
Tenement at No.15
1875-1900[6]
One of the oldest buildings in the street, with an owner dating back to 1878 (Mr Lehman, a rentier)[19] at this place then registered as 2 Cichorien straße.
The tenement has been restored in 2016-2017.
 Main frontage
Main frontage
Tenement at No.16
1910[6]
Few elements are known about the commissionner of this building: the first owner was Mr Herman, who did not live there.[20]
Nice Art Nouveau facade, with some elements to be emphasized: cartouches on the canter bay window topped by a small terrace and a splendid portal flanked by truncated columns, adorned with a stuccoed kneeling figure and a large transom windowtransom light.
 Main frontage
Main frontage Portal and door
Portal and door
Tenement at No.18
Registered on Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship Heritage List, No. A/1599, October 13, 2011[16]
1910[6]
Prior to this building, at the turn of the 20th century, stood there a house owned by Friedrich Hoffmeister, a bailiff.[21] A pharmacist, Franz Brüche, bought it back and had the current tenement erected.[7]
Renovated in 2018, the frontage is balanced by two canter bay windows topped by a terrace. The main door is gorgeously ornamented with stucco elements, as well as the facade gable extending over it. A dentil runs on top of the elevation.
Villa at No.19
1912,[6] by Alfred Schleusener
Alfred Schleusener, a Bromberg architect, designed the project in 1908. It recalls some of his realisations in the city (Alfred Schleusener Tenement, 7 20 Stycznia 1920 Street).[22]
Renovated in mid-2016, the villa decoration uses stucco motifs: from the columns flanking the door to the cartouches between windows to the festoons on the wall gable. Wood for the balcony or wrought iron on the railing are also utilised.
.jpg) View from the street
View from the street.jpg) Detail of the facade
Detail of the facade Portal and door
Portal and door
Building of the UTP, at No.20
Registered on Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship Heritage List, No.601368 A/337/1-2, September 30, 1992[16]
1880s,[6] by Carl Meyer
The building was erected at the end of the 19th century as the seat of dual primary schools for girls and boys, nicknamed Hippelschule after Hippel straße. Carl Meyer designed it, together with the adjacent sport hall at 22. During interwar period, the school, then named Holy Trinity, still taught girls and boys. It became co-educational school No. 10 in 1925.[23] At the end of WWII, the building had been housing a vocational school for several years before being handed over to the care of the University of Technology and Life Sciences in Bydgoszcz (Polish: Uniwersytet Technologiczno-Przyrodniczy-UTP) in the 1950s.[24]
The building has an elongated rectangle footprint, with wings extending in the back side. The three-floor edifice is covered with a gable hip roof and two ridge turrets topped by a finial. The front elevation displays two avant-corps where are located the entrances. Those have decorated lancet arched portals. Facades are adorned with friezes and cornices made of dark glazed brick[25]
 Hippelschule ca 1906
Hippelschule ca 1906 Main frontage on the street
Main frontage on the street Ridge turret and finial
Ridge turret and finial Portal and entrance
Portal and entrance
Gym house at No.22
Registered on Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship Heritage List, No.601369 A/337/1-2, September 30, 1992[16]
1900-1902s,[6] by Carl Meyer
Carl Meyer designed this gym hall following the same style as the one developed at N.20. This architecture recalls other gym buildings from this period in the city (e.g. at Gimnazjalna street or 4 Konarskiego Street).
Like at No.20, the neo-gothic edifice is garnished using glazed bricks, gothic-shaped windows and a ridge turret topped by a finial.
 View from the street
View from the street View from the street
View from the street Entrance from the UTP side
Entrance from the UTP side
Building at No.23
1912[6]
Emil Zemisch, a relative of Artur living at No.8, was the first landlord of this building.[7] He too ran a construction business till the outbreak of WWI.
Renovated in 2017, the edifice features Art Nouveau style, in particular in the details adorning the main door, the ground floor and top gable œil-de-bœufs or the stucco motifs on the bay window.
 Frontage from the street
Frontage from the street
 Main door
Main door
Mauß tenement at No.24
1870s[6]
In the late 1870s, the plot initially welcomed a barn.[19] Oscar and Heinrich Mauß commissionned this tenement in the early 1880s, [26] located then at 15 Cichorien straße for renting purposes. In 1937, Bydgoszcz architect Jan Kossowski moved his studio to this address, where he also lived with his family.
The tenement has been nicely restored in 2018.[27]
 Main frontage
Main frontage
Neubauer tenement at No.25
1890s[6]
Eclecticism & forms of Neo-Baroque
First landlord was August Neubauer, a rentier.[28] His son Reinhold, a barbier, lived there at the beginning of the 20th century[21] and his wife Mathilde survived him till the outbreak of WWI.[20]
The eclectic frontage is balanced on each side by a Neo-Baroque ensemble comprising windows flanked by a set of columns adorned at their footing with women figures. First floor openings are topped by pediments displaying feminine faces: stuccoed festoons with flowers embellish window sills.
 Main elevation
Main elevation Neo-baroque decoration
Neo-baroque decoration Adorned window
Adorned window Detail of a figure
Detail of a figure
Crescioli tenement at No.26
1870s[6]
This old building of Kordeckiego street have been owned from its erection to WWI by the Crescioli family: first landlord was Anacleto[19] followed by his widow Bertha.[20] Their relative, Livia, moved to 18 Swiętej Trojcy street after the 1st World War.[29]
The 2016 restoration underlined the frieze of the first floor as well as the window pediments of the second level, topped by a corbel table and delicate motifs.
 Main elevation
Main elevation Window decoration
Window decoration
Tenement at No.30
1890s[6]
The first landlord of this building, located at the time at Cichorein straße 12b, was Albert Trudnowski, a butcher living in the periphery of Bromberg.[30] The Trudnowski family kept ownership till the end of the 1920s.[29]
The balanced facade reflects an eclectic harmony of the architectural details.
 Elevation from the street
Elevation from the street Main door
Main door
Tenement at No.31
1875-1900[6]
One of the oldest buildings in the street, its first owner was Johann Brauer, a shoemaker; his wife was a midwife.[19] In the 1910s, the edifice was bought by Herbert Spadk, a merchand, for renting purposes.[29]
 Main facade
Main facade View from the street
View from the street
Tenement at No.32
1890s[6]
Similarly to the house at No.30, Albert Trudnowski was the first landlord of this building, located at the time at Cichorein straße 12a.[30] The Trudnowski family kept ownership till the end of the 1920s.[29]
The elevation style mirrors the abutting facade at No.30 in the use of architectural motifs.
 Main frontage
Main frontage
Tenement at 1 Plac Poznański, corner with Kordeckiego
1912[6]
The plot was a garden when the street has been laid in the 1870s.[19] The landlord at the time of the erection of the current building was Eduard Gawe, a metal craftsman.[7]
The edifice did not suffer major changes since its inception. Once can notice the set a piled balconies on both facades, the canter oriel window at the tenement corner and the series of mansard dormers topped by minute metal tented roof.
 The tenement ca 1932
The tenement ca 1932 View from the square
View from the square Facade on Kordeckiego
Facade on Kordeckiego
Tenement at 2 Plac Poznański, corner with Kordeckiego
1912[6]
Late Eclecticism
Like for buildings at No.30 and 32, Albert Trudnowski was the first landlord of this house, located at the time at Cichorein straße 11.[30] The tenement belonged to the Trudnowski family till the end of the 1920s.[29]
Both balanced elevations display typical eclectic architectural details: pediments or cartouche-like lintel on windows and a table corbel above a dentil running all the way on the top.
 View from the street
View from the street Facade on Kordeckiego
Facade on Kordeckiego Detail of the corbel
Detail of the corbel
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Kordeckiego Street in Bydgoszcz. |
References
- Allgemeiner Wohnungs-Anzeiger fur Bromberg 1855. Bromberg: Verlag von M. Aronsohn's Buchhandlung. 1855. p. 50.
- 1876 Plan der Stadt Bromberg
- Błażejewski, Krzysztof (11 June 2014). "W tym roku minęło 40 lat od ukończenia ronda Grunwaldzkiego. Na gruzach budowli o 200 lat starszej". expressbydgoski.pl. expressbydgoski. Retrieved 21 October 2017.
- key (7 December 2016). "Nieco zapomniana ulica pięknieje. Kiedyś jeździły nią tramwaje". bydgoszcz.wyborcza.pl. bydgoszcz.wyborcza. Retrieved 17 August 2019.
- Czachorowski, Antoni (1997). Atlas historyczny miast polskich, Tom II Kujawy. Zeszyt I Bydgoszcz. Toruń: Uniwersytet Mikołaja Kopernika.
- Zarządzenie NR439/2015. Bydgoszcz: Miasto Bydgoszczy. 7 August 2015. pp. 38–39.
- Adressbuch nebst allgemeinem Geschäfts-Anzeiger von Bromberg und dessen Vororten für das Jahr 1911: auf Grund amtlicher und privater Unterlagen. Bromberg: Dittmann. 1911. pp. 252, 288, 344, 402, 455, 501.
- "Straßen". Adressbuch nebst allgemeinem Geschäfts-Anzeiger von Bromberg und dessen Vororten auf das Jahr 1904 auf Grund amtlicher und privater Unterlagen. Bromberg: Dittmann. 1904. pp. 17, 219.
- "Names". Adressbuch nebst allgemeinem Geschäfts-Anzeiger von Bromberg und dessen auf Grund amtlicher und privater Unterlagen. Bromberg: Ditmmann. 1917. p. 217.
- "Ulicy". Książka Adresowa Miasta Bydgoszczy. Bydgoszcz. 1926. p. 179.
- key (18 July 2017). "Ładniej na ul. Świętej Trójcy. Dwie kamienice odnowione". bydgoszcz.wyborcza.pl. bydgoszcz.wyborcza. Retrieved 16 August 2019.
- Adressbuch nebst allgemeinem Geschäfts-Anzeiger von Bromberg mit Vorvorten für 1906 : auf Grund amtlicher und privater Unterlagen. Bromberg: Dittmann. 1906. p. 51.
- "Straßen". Adressbuch nebst allgemeinem Geschäfts-Anzeiger von Bromberg und dessen auf Grund amtlicher und privater Unterlagen. Bromberg: Dittmann. 1903. p. 44.
- Adressbuch nebst allgemeinem Geschäfts-Anzeiger von Bromberg mit Vorvorten für 1907: auf Grund amtlicher und privater Unterlagen. Bromberg: Dittmann. 1907. p. 362.
- As mentioned in an advertising in the 1907 Bromberg address book
- zabytek-kujawsko-pomorskie-data dostępu=28.02.2014
- "Names". Adressbuch nebst allgemeinem Geschäfts-Anzeiger von Bromberg und dessen Vororten auf das Jahr 1900 auf Grund amtlicher und privater Unterlagen. Bromberg: Dittmann. 1900. pp. 14, 406.
- "Straßen". Adressbuch nebst allgemeinem Geschäfts-Anzeiger von Bromberg und dessen Vororten auf das Jahr 1910 auf Grund amtlicher und privater Unterlagen. Bromberg: Dittmann. 1910. pp. 79, 339, 483.
- Wohnungs-Anzeiger nebst Adress- und Geschäfts-Handbuch für Bromberg und Umgebung : auf das Jahr 1878. Bromberg: Mittlersche Buchhandlung. 1878. pp. XI, 12, 18.
- Adressbuch nebst allgemeinem Geschäfts-Anzeiger von Bromberg mit Vorvorten für 1915: auf Grund amtlicher und privater Unterlagen. Bromberg: Dittmann. 1915. pp. 93, 251.
- Adressbuch nebst allgemeinem Geschäfts-Anzeiger von Bromberg und dessen Vororten auf das Jahr 1905: auf Grund amtlicher und privater Unterlagen. Bromberg: Dittmann. 1905. pp. 80, 147.
- dss (6 June 2016). "Kamienica w centrum odzyska blask. Projekt znanego architekta". bydgoszcz.wyborcza.pl. bydgoszcz.wyborcza. Retrieved 17 August 2019.
- Biskup, Marian (1999). Historia Bydgoszczy. Tom II. Część pierwsza 1920-1939. Bydgoszcz: Bydgoskie Towarzystwo Naukowe. pp. 651–700. ISBN 83-901329-0-7.
- Michalski, Stanisław (1988). Bydgoszcz wczoraj i dziś 1945-1980. Bydgoszcz: Państwowe Wydawnictwo Naukowe Warszawa-Poznań. ISBN 83-01-05465-4.
- Parucka, Krystyna (2008). Zabytki Bydgoszczy – minikatalog. Bydgoszcz: "Tifen"-Krystyna Parucka. ISBN 9788392719106.
- Wohnungs-Anzeiger nebst Adress- und Geschäfts-Handbuch für Bromberg und Umgebung : auf das Jahr 1882. Bromberg: Mittlersche Buchhandlung. 1882. p. 72.
- key (28 March 2018). "Kolejny wyremontowany dom w Bydgoszczy. Ale piękne zdobienia". bydgoszcz.wyborcza.pl. bydgoszcz.wyborcza. Retrieved 17 August 2019.
- Wohnungs-Anzeiger nebst Adress- und Geschäfts-Handbuch für Bromberg und Umgebung : auf das Jahr 1892. Bromberg: Dittmann. 1891. p. 150.
- Książka Adresowa Miasta Bydgoszczy : wydana w roku 1926. Bydgoszcz: Władysław Weber. 1926. pp. 47, 79.
- Adressbuch nebst allgemeinem Geschäfts-Anzeiger von Bromberg und dessen Vororten auf das Jahr 1900 : auf Grund amtlicher und privater Unterlagen. Bromberg: Dittmann. 1900. p. 209.
Bibliography
- Mackiewicz, Zygmunt (2004). Historia szkolnictwa wyższego w Bydgoszczy (in Polish). Bydgoszcz: Bydgoskie Towarzystwo Naukowe. pp. 35–46. ISBN 83-917322-7-4.




