King (crater)
King is a prominent lunar impact crater that is located on the far side of the Moon, and can not be viewed directly from Earth. The crater was named after Arthur Scott King and Edward Skinner King in 1970.[1] Prior to that, this crater was known as Crater 211.[2] It forms a pair with Ibn Firnas, which is only slightly larger and is attached to the northeast rim of King. To the northwest is the crater Lobachevskiy, and Guyot is located an equal distance to the north-northwest.
 | |
| Coordinates | 5.0°N 120.5°E |
|---|---|
| Diameter | 76 km |
| Depth | Unknown |
| Colongitude | 241° at sunrise |
| Eponym | Arthur S. King and Edward S. King |
Description
The outer rim of King is roughly circular but with a slightly irregular appearance, particularly at the northern end. The crater displays little appearance of wear. The inner walls are terraced, particularly along the eastern side. Within the walls is a somewhat uneven interior floor. The interior is irregular and ridged, particularly in the eastern half. The elongated, Y-shaped central rise is part of a ridge that runs to the southern rim.
Due to its prominent rays, King is mapped as part of the Copernican System.[3]
Sita crater
A tiny crater near the east-southeastern inner wall has been officially given the Indian feminine name Sita by the IAU. It is located at selenographic coordinates 4.6° N, 120.8° E, and has a diameter of 2 kilometres.
Satellite craters
By convention these features are identified on lunar maps by placing the letter on the side of the crater midpoint that is closest to King.
| King | Latitude | Longitude | Diameter |
|---|---|---|---|
| J | 3.2° N | 121.8° E | 14 km |
| Y | 6.5° N | 119.8° E | 48 km |
King Y is to the north of King, and it is now a "pool" of impact melt, filled at the time of the King impact. The name "Al-Tusi" had been suggested for King Y, but this was not approved by the IAU. King J is a small crater to the southeast of King, and it is covered by King's ejecta blanket.
Mountain Peaks

Several mountain peaks (Montes) within King crater have been named. The names were approved by the IAU in 1976.
| Mons | Latitude | Longitude | Approximate Altitude[4] |
|---|---|---|---|
| André | 5.18° N | 120.56° E | 7000 m |
| Ardeshir | 5.03° N | 121.04° E | 5900 m |
| Dieter | 5.00° N | 120.30° E | 8000 m |
| Dilip | 5.58° N | 120.87° E | 5500 m |
| Ganau | 4.79° N | 120.59° E | 7900 m |
Views

 Oblique view from Apollo 12
Oblique view from Apollo 12 Closeup of the central peaks from Apollo 16
Closeup of the central peaks from Apollo 16 Oblique view of the "pool" (King Y) north of King from Apollo 16
Oblique view of the "pool" (King Y) north of King from Apollo 16 Closeup of the impact melt northeast of the crater, showing flow structures, from Apollo 16
Closeup of the impact melt northeast of the crater, showing flow structures, from Apollo 16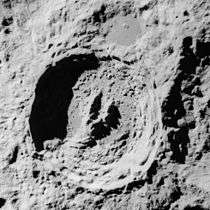 View of King during Apollo 16's trans-earth injection
View of King during Apollo 16's trans-earth injection
References
- King, Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature, International Astronomical Union (IAU) Working Group for Planetary System Nomenclature (WGPSN)
- Lunar Farside Chart (LFC-1A)
- The geologic history of the Moon, 1987, Wilhelms, Don E.; with sections by McCauley, John F.; Trask, Newell J. USGS Professional Paper: 1348. Plate 11: Copernican System (online)
- LTO65C1 King Lunar Topographic Orthophotomap, 1974
Further reading
- Andersson, L. E.; Whitaker, E. A. (1982). NASA Catalogue of Lunar Nomenclature. NASA RP-1097.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Bussey, B.; Spudis, P. (2004). The Clementine Atlas of the Moon. New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-81528-4.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Cocks, Elijah E.; Cocks, Josiah C. (1995). Who's Who on the Moon: A Biographical Dictionary of Lunar Nomenclature. Tudor Publishers. ISBN 978-0-936389-27-1.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- McDowell, Jonathan (July 15, 2007). "Lunar Nomenclature". Jonathan's Space Report. Retrieved 2007-10-24.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Menzel, D. H.; Minnaert, M.; Levin, B.; Dollfus, A.; Bell, B. (1971). "Report on Lunar Nomenclature by the Working Group of Commission 17 of the IAU". Space Science Reviews. 12 (2): 136–186. Bibcode:1971SSRv...12..136M. doi:10.1007/BF00171763.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Moore, Patrick (2001). On the Moon. Sterling Publishing Co. ISBN 978-0-304-35469-6.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Price, Fred W. (1988). The Moon Observer's Handbook. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-33500-3.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Rükl, Antonín (1990). Atlas of the Moon. Kalmbach Books. ISBN 978-0-913135-17-4.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Webb, Rev. T. W. (1962). Celestial Objects for Common Telescopes (6th revised ed.). Dover. ISBN 978-0-486-20917-3.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Whitaker, Ewen A. (1999). Mapping and Naming the Moon. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-62248-6.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Wlasuk, Peter T. (2000). Observing the Moon. Springer. ISBN 978-1-85233-193-1.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to King (crater). |
- LTO65C1 King Lunar Topographic Orthophotomap, 1974
- LTO65D2 Katchalsky Lunar Topographic Orthophotomap, 1975 (shows west side of King)
- King Crater Flyover by Lunar and Planetary Institute
- Figures 149 to 151 and Figures 152 to 160 in Chapter 5 of APOLLO OVER THE MOON: A View From Orbit (NASA SP-362, 1978) are various views of King Crater
- From LROC:
- King Crater's Unusual Melt Pond
- King crater ejecta deposits
- Anomalous mounds on the King crater floor
- Fault scarp with impact melt in King crater
- Making a Splash at King Crater
Related articles
- Wood, Chuck (2006-06-26). "King of the Farside". Lunar Photo of the Day. Archived from the original on 2007-02-23. Retrieved 2006-07-12.
- Wood, Chuck (September 29, 2010). "King for a Day". Lunar Photo of the Day. Retrieved August 5, 2017.