Kambalny
Kambalny (Russian: Камбальный) is a stratovolcano located in the southern part of Kamchatka Peninsula, Russia. It is the southernmost active volcano of Kamchatka.[4] It has erupted mafic rocks.[5] It has a summit crater as well as five cinder cones on its flanks which are the source of lava flows.
| Kambalny | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Highest point | |
| Elevation | 2,156 m (7,073 ft) [1] |
| Prominence | 1,970 m (6,460 ft) [2][3] |
| Listing | Ultra |
| Coordinates | 51°18′20″N 156°52′31″E [1] |
| Geography | |
 Kambalny Location on Kamchatka Peninsula, Russia 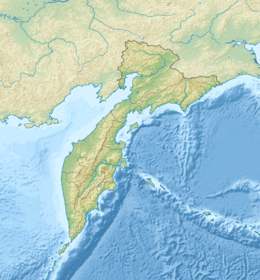 Kambalny Kambalny (Kamchatka Krai) | |
| Location | Kamchatka, Russia |
| Parent range | Eastern Range |
| Geology | |
| Age of rock | Holocene |
| Mountain type | Stratovolcano |
| Last eruption | 2017 |
The volcano probably formed during the early Holocene[4] and aside from the summit crater also features an explosion crater on the southwestern side of the summit.[6] Three large collapses of the edifice occurred around 6300 BP; between the first two volcanic activity restored the cone, while the third occurred on the ridge on which Kambalny was constructed. The longest of these landslides travelled 20 kilometres (12 mi).[5] The total volume of these landslides, 5–10 cubic kilometres (1.2–2.4 cu mi), is the largest of all Holocene landslides, but it was buried at Kambalny proper by later volcanic activity. The collapse scar in the ridge is still visible and was the site of later landslides when Kambalny volcano was active.[5]
Kambalny is part of a group of volcanoes from the late Pleistocene and the Holocene that surround the Kurile Lake caldera. Other volcanoes in that group are Diky Greben, Ilyinsky, Koshelev and Zheltovsky.[7] Kambalny itself is constructed on a ridge which formed in the Quaternary during the uplift of the central part of a trough.[8] This trough is also the site of the Pleistocene Pauzhetka Caldera and Kambalny formed on this caldera rim.[9] The position of Kambalny is also controlled by the margin between the Kurile island arc and the South Kamchatka block.[10]
The cone rises about 1,800 metres (5,900 ft) above the surrounding terrain.[11] The Pauzhetsky geothermal field is associated with the Kambalny volcanic ridge,[12] and Kambalny may be the heat source for this system.[13] The geothermal energy output at Kambalny is about 320 megawatts (320,000,000 W).[14] Fumarolic activity along with the emission of CO
2, H
2S and CH
4 occur in the area of Kambalny.[15] These fumaroles have left efflorescences that are derived from compounds leached from rocks and which have yielded novel minerals.[16] The geothermal field is subdivided into three sectors, Severo-Kambalny ("North-Kambalny"), Central'no Kambalny ("Central Kambalny") and Yuzhno-Kambalny ("South-Kambalny").[16]
Recent eruption history
The last eruption from Kambalny occurred March 24, 2017[17] when ash emission was observed that continued for six days.[6] The ash originated in a funnel in the western crater flank; it formed mud streams[18] and appears to have originated in a phreatic eruption.[19] The last known volcanic activity prior to 2017 was in 1769. Future volcanic activity from the volcano may be a threat to the Mutnovsky geothermal operations.[20] Further, additional large collapses of the edifice are possible, which may endanger hunters, fishermen and tourists.[21] As of June 2012, the volcano has no associated seismic station.[22]
Other eruptions took place 8,000, 7,500, 600 and possibly 200 years ago.[6] The ash erupted during a phreatic eruption 564–686 years BP is a marker ash that has been found as far as Paramushir island in the northern portion of the Kuril Islands.[23] Tephras younger than this date have been identified as well.[24]
References
- Ivanov, Anton; Shoba, Serghei; Krasilnikov, Pavel (December 2014). "A pedogeographical view of volcanic soils under cold humid conditions: the Commander Islands". Geoderma. 235–236: 50. Bibcode:2014Geode.235...48I. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2014.06.031.
- "Russia: Kamchatka and the Russian Pacific Islands Ultra-Prominence Page" Peaklist.org. The prominence value given here (1,970 m) is based on a summit elevation of 2,161 m. Retrieved 2011-11-26.
- "Vulkan Kambalny, Russia" Peakbagger.com. The prominence value given here (1,970 m) is based on a summit elevation of 2,161 m. Retrieved 2011-11-26.
- Ponomareva, Melekestsev & Dirksen 2006, p. 132.
- Ponomareva, Melekestsev & Dirksen 2006, p. 133.
- Gordeev et al. 2018, p. 1257.
- Ponomareva, V.V.; Kyle, P.R.; Melekestsev, I.V.; Rinkleff, P.G.; Dirksen, O.V.; Sulerzhitsky, L.D.; Zaretskaia, N.E.; Rourke, R. (September 2004). "The 7600 (14C) year BP Kurile Lake caldera-forming eruption, Kamchatka, Russia: stratigraphy and field relationships" (PDF). Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research. 136 (3–4): 199–222. Bibcode:2004JVGR..136..199P. doi:10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2004.05.013.
- Averiev, V. V.; Ivanov, V. V.; Piip, B. I. (December 1960). "Problems of using volcanic thermae of the Kurile-Kamchatka island arc for power". Bulletin Volcanologique. 23 (1): 261–262. Bibcode:1960BVol...23..257A. doi:10.1007/BF02596653.
- Bindeman, I.N.; Leonov, V.L.; Izbekov, P.E.; Ponomareva, V.V.; Watts, K.E.; Shipley, N.K.; Perepelov, A.B.; Bazanova, L.I.; Jicha, B.R.; Singer, B.S.; Schmitt, A.K.; Portnyagin, M.V.; Chen, C.H. (January 2010). "Large-volume silicic volcanism in Kamchatka: Ar–Ar and U–Pb ages, isotopic, and geochemical characteristics of major pre-Holocene caldera-forming eruptions". Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research. 189 (1–2): 57–80. Bibcode:2010JVGR..189...57B. doi:10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2009.10.009.
- "Chapter 1 Recent tectonics of the crust and volcanism in Kamchatka". Bulletin Volcanologique. 42 (1–4): 15. March 1979. Bibcode:1979BVol...42....9.. doi:10.1007/BF02597042.
- Malahoff, Alexander (1969-01-01). "Magnetic Studies over Volcanoes". In Hart, Pembroke J. (ed.). The Earth's Crust and Upper Mantle. Geophysical Monograph Series. American Geophysical Union. pp. 436–446. doi:10.1029/gm013p0436. ISBN 9781118668979.
- Kiryukhin, Alexey V; Yampolsky, Vladimir A (August 2004). "Modeling study of the Pauzhetsky geothermal field, Kamchatka, Russia". Geothermics. 33 (4): 423. doi:10.1016/j.geothermics.2003.09.010.
- Koborov, A.D. (April 2005). "Reservoir Temperatures by Means of Mineralogic-Geochemical Geothermometer" (PDF). International Geothermal Association. World Geothermal Congress 2005. Retrieved 6 November 2016.
- Kiryukhin, Alexey V. (January 2001). "GEOTHERMAL ENERGY TRANSPORT IN RECENT VOLCANISM AREAS (KAMCHATKA AND KURILE ISLANDS ) : SOME EXAMPLES AND CONCEPTUAL MODEL" (PDF). pangea.stanford.edu. Twenty-Sixth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering. Retrieved 6 November 2016.
- Ivanov, V. V. (December 1959). "Present-day hydrothermal activity within the Kurile-Kamchatka Island arc and its relation to volcanicity". Bulletin Volcanologique. 20 (1): 141. Bibcode:1959BVol...20..137I. doi:10.1007/BF02596575.
- Ismagilova et al. 2018, p. 3.
- "Volcano Discovery Volcano Ash Advisory". Volcano Discovery. Retrieved 25 March 2017.
- Gordeev et al. 2018, p. 1258.
- Gordeev et al. 2018, p. 1259.
- IVANOV, Victor; TANIGUCHI, Hiromitsu; DVIGALO, Victor; GOTO, Akio (2000-03-01). "Explosive Volcanism of Kamchatka". Northeast Asian Studies. 4: 174. ISSN 1343-9332.
- Ponomareva, Melekestsev & Dirksen 2006, p. 136.
- Girina, O. A. (2012-07-01). "On precursor of Kamchatkan volcanoes eruptions based on data from satellite monitoring" (PDF). Journal of Volcanology and Seismology. 6 (3): 144. doi:10.1134/S0742046312030049. ISSN 0742-0463.
- Nakamura, Y.; Nishimura, Y.; Hirakawa, K.; Tanioka, Y.; Pinegina, T.; Kravchunovskaya, E. (2009-12-01). "Chronology of tsunami and tephra on Paramushir Island, northern Kuril Islands". AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts. 53: S53A–1462. Bibcode:2009AGUFM.S53A1462N.
- Global Volcanism Program
Other references
- "Kambalny Volcano" VolcanoLive.com
Sources
- Gordeev, E. I.; Girina, O. A.; Gorbach, N. V.; Manevich, A. G.; Melnikov, D. V.; Anikin, L. P.; Manevich, T. M.; Dubrovskaya, I. K.; Chirkov, S. A.; Kartashova, E. V. (9 November 2018). "First Historical Eruption of Kambalny Volcano" (PDF). Doklady Earth Sciences. 482 (2): 1257–1259. doi:10.1134/S1028334X18100045.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Ismagilova, Rezeda M.; Nuzhdaev, Anton A.; Shilovskikh, Vladimir V.; Belakovsky, Dmitry I.; Siidra, Oleg I.; Zhitova, Elena S. (2018). "Ammoniovoltaite, (NH4)2Fe2+5Fe3+3Al(SO4)12(H2O)18, a new mineral from the Severo-Kambalny geothermal field, Kamchatka, Russia". Mineralogical Magazine. 82 (5): 1057–1077. doi:10.1180/minmag.2017.081.083. ISSN 0026-461X.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Ponomareva, Vera V.; Melekestsev, Ivan V.; Dirksen, Oleg V. (November 2006). "Sector collapses and large landslides on Late Pleistocene–Holocene volcanoes in Kamchatka, Russia" (PDF). Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research. 158 (1–2): 117–138. Bibcode:2006JVGR..158..117P. doi:10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2006.04.016.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)