Kalyptorhynchia
Kalyptorhynchia is a suborder of rhabdocoel flatworms. It contains almost 600 species and has a cosmopolitan distribution.[1]
| Kalyptorhynchia | |
|---|---|
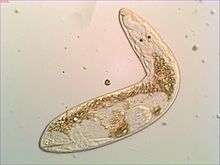 | |
| Gyratrix hermaphroditus. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Platyhelminthes |
| Class: | Rhabditophora |
| Order: | Rhabdocoela |
| Suborder: | Kalyptorhynchia Graff, 1905 |
| Infraorders | |
| |
Description
All kalyptorhynchs have an anterior muscular proboscis which is used to capture prey. The proboscis is located inside an invagination of the epidermis called the proboscis-sheath that is closed by a sphincter at the tip of the body.[1] Another synapomorphy supporting the group is the incorporation of the axonemes within the cell body of sperm cells during spermiogenesis.[2]
Classification
Kalyptorhynchs are traditionally classified into two infraorders: Eukalyptorhynchia, with a cone-shaped proboscis, and Schizorhynchia, with a proboscis formed by two opposite parallel muscular sheets.[1] However, molecular studies have shown that Eukalyptorhynchia is not a monophyletic group and further studies are necessary to improve the knowledge about the relationships of the different kalyptorhynch clades.[1][2]
References
- Smith, Julian P. S., III; Litvaitis, Marian K.; Gobert, Stefan; Uyeno, Theodore; Artois, Tom (2015). "Evolution and Functional Morphology of the Proboscis in Kalyptorhynchia (Platyhelminthes)". Integrative and Comparative Biology. 55 (2): 205–216. doi:10.1093/icb/icv056. ISSN 1540-7063. PMC 4612338. PMID 26002347.
- Willems, Wim R.; Wallberg, Andreas; Jondelius, Ulf; Littlewood, David T. J.; Backeljau, Thierry; Schockaert, Ernest R.; Artois, Tom J. (2006). "Filling a gap in the phylogeny of flatworms: relationships within the Rhabdocoela (Platyhelminthes), inferred from 18S ribosomal DNA sequences". Zoologica Scripta. 35 (1): 1–17. doi:10.1111/j.1463-6409.2005.00216.x. hdl:1942/1609. ISSN 0300-3256.