Isthmian-Atlantic moist forests
The Isthmian-Atlantic moist forests (NT0129) are a Central American tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion located in Nicaragua, Costa Rica and Panama.[4]
| Isthmian-Atlantic moist forests (NT0129) | |
|---|---|
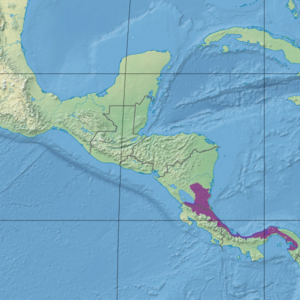 Ecoregion territory (in purple) | |
| Ecology | |
| Realm | Neotropical |
| Biome | Tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests |
| Geography | |
| Area | 58,792 km2 (22,700 sq mi) |
| Countries | Nicaragua, Costa Rica and Panama |
| Conservation | |
| Conservation status | Vulnerable [1][2] |
| Protected | 20,545 km² (36%)[3] |
Geography
The ecoregion extends from Panama in the east along the Caribbean coast of Costa Rica into the southeast of Nicaragua. In Panama the ecoregion extends across the isthmus of Panama from the Caribbean to the Gulf of Panama.[5] The Isthmian-Atlantic moist forests lie in the neotropical realm and the tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests biome.[5] At the junction of Central and South America, this Atlantic component of this rainforest is located along the Atlantic lowlands of this region, at approximately 500 meters elevation. Due to the connection of North and South America via Central America, this rainforest contains flora and fauna from both regions in the Mesoamerican Biological Corridor.
In the east the ecoregion merges into the Chocó-Darién moist forests ecoregion, which extends down the Pacific coast of Colombia. There are sections of Panamanian dry forests and South American Pacific mangroves along the Gulf of Panama shore, and of Mesoamerican Gulf-Caribbean mangroves along the Caribbean shore.[6] In central Panama the ecoregion transitions to the south into Isthmian-Pacific moist forests. Further west in Panama and in Costa Rica the ecoregion transitions to the south into Talamancan montane forests, and in the northern part of Costa Rica transitions into Costa Rican seasonal moist forests.[6] The northwest of the ecoregion transitions into Central American dry forests to the east of Lake Nicaragua, and into Central American Atlantic moist forests to the north. The ecoregion contains patches of Eastern Panamanian montane forests at the higher levels.[6]
Geology
Due to relatively recent volcanic activity in Central America, the bedrock in the Isthmian-Atlantic moist forests is mostly basalt, a black igneous rock. The soil of the forests is subject to leeching. This and the trees feeding from the soil makes it poor for farming or other agricultural purposes.
Climate
The average temperature for the Isthmian-Atlantic Rainforests is 24° Celsius or above. The coolest months tend to be from November to January, and the warmest from March to May. The topography affects the region’s climate as well; the seasons come to each slope of the hills at slightly different times.
The average rainfall for the area can range from 2,500 mm to over 5,000 mm per annum. This translates to an average temperature of 75° Fahrenheit, with an estimated rainfall of 100 inches to more than 200 inches a year. On the Caribbean slope, the side facing the Atlantic Ocean, the rainy season lasts from mid to late April and continues until December and possibly January. A dry spell tends to occur towards the end of summer. On most days during this time period, it may rain for two to three hours then become sunny again.
Flora
The layout of the forests is typical of tropical rainforests. Tall evergreen buttressed trees that can grow up to 40 meters make up the canopy. There is also a large diversity in the selection of epiphyte flora, plants that grow on other plants but are not parasites, in that region. In the understory and canopy are slow-growing trees such as the Almendro tree and the Cream nut tree.
The Isthmian-Atlantic moist forests also contain many types of rainforests, including lowland evergreen forests, coastal mangrove forests, and seasonal swamp forests. The latter occurs near the coast and especially where the rainforest turns into mangrove forests on the coast or in low-lying areas in Panama or Nicaragua.
The Almendro tree is native to Central America. The trunk forks repeatedly as it grows, resulting in the effect of a rounded crown. The crown is covered with bunches of purple flowers soon after the rainy season. The tree is classified as ‘hardwood’, and covered by a smooth pink-gold bark. Each fruit can weigh between 18-26 grams and contains a single seed in a thick wooden pod covered in sweet green pulp. About 20 fruits per square metre of crown can be produced by one tree in a good year.
The Monkey Pot tree is a native species of the Americas. It produces small purple flowers and woody fruit. When fruit is ripe, the bottom of the pod will open and release the seeds.
Fauna
There are few species native only to the Isthmian-Atlantic moist forests. About 80-95% of the mammal species in Costa Rica also occur in Panama, Nicaragua, and outside the rainforest in parts of Honduras and Colombia. However, it is the only home to the snowy cotinga, the sulphur-rumped tanager, the stripe-cheeked woodpecker, and the streak-crowned antvireo. Additionally, the Caribbean slope is a major migratory route for birds. 30% of the birds in that region migrate through the Neotropical realm annually, especially on the foothills. Four species of marine turtles nest on the coastal beaches at the edge of these rainforests, and the Atlantic lowlands have the highest concentration of butterfly species in the world, including some of the rarest species of butterfly. The rainforest is also home to animals such as the Honduran white bat and the common chunk-headed snake (Imantodes cenchoa).
The common chunk-headed snake is also called the blunthead snake. It tree-dwelling. Although slightly venomous, the venom is mostly restricted the back teeth to aid the tree snake in eating prey such as small lizards.
The sulphur-rumped tanager (Heterospingus rubrifrons) finds its only home in the Isthmian-Atlantic moist forests of Costa Rica. It belongs in the family Thraupidae, and generally makes its home in subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests. Despite its very small numbers, it is classified as Least Concern by the IUCN.
Human impact and management
Despite the fact that this rainforest is among the least represented in the Costa Rican and Nicaraguan environmental protection boards, about 130,000 hectares of this rainforest are currently protected and economical stresses such as the Global Forest Coalition suggest that there will be little expansion of these commercial areas in the near future. Additionally, in Nicaragua, 40,000 hectares of the forest have been sanctioned as the Indio Maíz Biological Reserve. La Amistad National Park has also been created in Panama. Fortunately the topography of the region has saved some of the rainforest from the attention of humans as the machines used to log the trees could not reach the tops of the slopes of Nicaragua and Panama. In Costa Rica, however, the forest is easily accessed.
Much of the original rainforest has now become land for commercial or subsistence agriculture, so there are few expanses of the original ecosystem remaining. Humans are still logging and clearing the area. Flat areas with alluvial soil are being used for banana farming, while hilly areas with less fertile soil are being logged and converted into pastures for the cattle to graze in.
The Tortuguero National Park is now a way for poachers to access the second largest green sea turtle nesting beach in the world. The expansion of society has also had a negative effect on the rainforest. The growing communities extract more resources from the rainforest each year, and the improving health and road systems encourage more people to come to the area. People are also capturing wildlife for pets. For example, baby parrots are being shipped to pet stores, which results in declining parrot numbers.
External link
- "Isthmian-Atlantic moist forests". Terrestrial Ecoregions. World Wildlife Fund.
References
- "Isthmian-Atlantic moist forests". Terrestrial Ecoregions. World Wildlife Fund. Retrieved 2013-09-22.
- World Wildlife Fund, ed. (2001). "Isthmian-Atlantic moist forests". WildWorld Ecoregion Profile. National Geographic Society. Archived from the original on 2010-03-08.
- Eric Dinerstein, David Olson, et al. (2017). An Ecoregion-Based Approach to Protecting Half the Terrestrial Realm, BioScience, Volume 67, Issue 6, June 2017, Pages 534–545; Supplemental material 2 table S1b.
- http://www.eoearth.org/article/Isthmian-Atlantic_moist_forests
- Isthmian-Atlantic moist forests - Myers, WWF Abstract.
- WildFinder – WWF.
Sources
- "Isthmian-Atlantic moist forests", Global Species, Myers Enterprises II, retrieved 2017-06-14
- WildFinder, WWF: World Wildlife Fund, retrieved 2017-06-14