Intercostobrachial nerve
The intercostobrachial nerves are cutaneous branches of the intercostal nerves.
| Intercostobrachial nerve | |
|---|---|
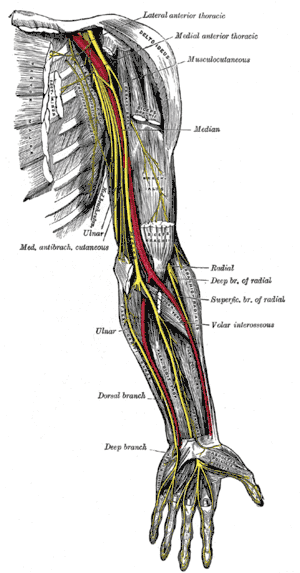 Nerves of the left upper extremity. (Intercostobrachial nerve visible near top center.) | |
| Details | |
| From | intercostal nerves #2 and #3 |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nervi intercostobrachiales |
| TA | A14.2.04.012 |
| FMA | 75486 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
Second intercostal nerve
The lateral cutaneous branch of the second intercostal nerve does not divide, like the others, into an anterior and a posterior branch; it is named the intercostobrachial nerve. It pierces the Intercostalis externus and the Serratus anterior, crosses the axilla to the medial side of the arm, and joins with a filament from the medial brachial cutaneous nerve. It then pierces the fascia, and supplies the skin of the upper half of the medial and posterior part of the arm, communicating with the posterior brachial cutaneous branch of the radial nerve. It is often the source of referred cardiac pain.
The intercostabrachial nerve is also sometimes divided in axillary node clearance (ANC), such as that done for breast cancer surgery which requires the removal of the axillary nodes. Sensation to the cutaneous region supplied by the nerve is affected.
The size of the intercostobrachial nerve is in inverse relationship to that of the medial brachial cutaneous nerve.
Third intercostal nerve
A second intercostobrachial nerve is frequently given off from the lateral cutaneous branch of the third intercostal; it supplies filaments to the axilla and medial side of the arm.
See also
- Cutaneous innervation of the upper limbs
Additional images
- Cutaneous nerves of right upper extremity.
- Diagram of segmental distribution of the cutaneous nerves of the right upper extremity.
 Innervation
Innervation
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 946 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- Anatomy photo:05:st-0505 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Axillary Region: Nerves"
- Hand kinesiology at the University of Kansas Medical Center