Ili-ishmani
Ili-ishmani (𒉌𒉌𒅖𒈠𒉌 i3-li2-isz-ma-ni) was a ruler of Elam around 2200 BCE. His name is purely Akkadian, and he was in charge of Elam at the time of Naram-Sin and/or Shar-Kali-Sharri, and probably their vassal.[3][4] His title of "Military Governor" (Shakkanakku in Akkadian, GIR.NITA in Sumerian) suggests that he was a dependent of the Akkadian kings, rather than an independent ruler.[5] Ili-ishmani rose from the position of scribe, already one of the top three positions in the land, to the position of Governor.[6]
| Ili-ishmani 𒉌𒉌𒅖𒈠𒉌 | |
|---|---|
| Military Governor of Elam | |
Axe blade with inscription "Ili-ishmani, scribe and shakkanakku of Elam". Louvre Museum Sb 14243.[1][2] | |
| Reign | c. 2200 BCE |
| Predecessor | Epirmupi |
| Successor | Awan Dynasty |
| Dynasty | Akkadian Governor of Elam |
His predecessor was probably Epirmupi.[7] After him, and the weakening of the Akkadian Empire, rule in Elam probably reverted to local rulers of the Awan Dynasty.[8]
Axe fragment
The fragment of an axe is known, which was dedicated by Ili-ishmani.[9][10] It reads:
Axe blade with inscription Ilishmani, scribe and shakkanakku of Elam (with transcription)𒉌𒉌𒅖𒈠𒉌 𒁾𒊬 𒄊𒀴 𒈠𒋾 𒉏𒆠
"i3-li2-isz-ma-ni / dub-sar / szagina / ma-ti / elam{ki}
"Ili-išmani, / scribe, / military governor (shakkanakku) / of the land / of Elam."
Seal inscription
A seal found in Lagash also has the inscription "Ili-ishmani Governor (Ensi) of Susa" (𒉌𒉌𒅖𒈠𒉌 𒑐𒋼𒋛 𒈹𒂞𒆠 Ili-ishmani ensi Shushanki).[14]
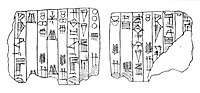 Seal found in Lagash, with the inscription "Ili-ishmani Governor of Susa" (𒉌𒉌𒅖𒈠𒉌 𒑐𒋼𒋛 𒈹𒂞𒆠 Ili-ishmani ensi Shushanki) on the reverse (columns 2 and 3)
Seal found in Lagash, with the inscription "Ili-ishmani Governor of Susa" (𒉌𒉌𒅖𒈠𒉌 𒑐𒋼𒋛 𒈹𒂞𒆠 Ili-ishmani ensi Shushanki) on the reverse (columns 2 and 3)
References
- "Site officiel du musée du Louvre". cartelfr.louvre.fr.
- Transcription and drawing in Lambert, Maurice (1979). "Journal asiatique" (in French). Société asiatique.: 13. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - Álvarez-Mon, Javier (2020). The Art of Elam CA. 4200–525 BC. Routledge. p. 216. ISBN 978-1-000-03485-1.
- Potts, D. T. (2016). The Archaeology of Elam: Formation and Transformation of an Ancient Iranian State. Cambridge University Press. p. 100. ISBN 978-1-107-09469-7.
- Potts, D. T. (2016). The Archaeology of Elam: Formation and Transformation of an Ancient Iranian State. Cambridge University Press. p. 100. ISBN 978-1-107-09469-7.
- "Journal asiatique" (in French). Société asiatique. 1979. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - Potts, D. T. (2016). The Archaeology of Elam: Formation and Transformation of an Ancient Iranian State. Cambridge University Press. p. 97. ISBN 978-1-107-09469-7.
- Foster, Benjamin R. (2015). The Age of Agade: Inventing Empire in Ancient Mesopotamia. Routledge. p. 274. ISBN 978-1-317-41552-7.
- Álvarez-Mon, Javier (2020). The Art of Elam CA. 4200–525 BC. Routledge. p. 148. ISBN 978-1-000-03485-1.
- "Site officiel du musée du Louvre". cartelfr.louvre.fr.
- "CDLI-Archival View". cdli.ucla.edu.
- "CDLI-Found Texts". cdli.ucla.edu.
- Transcription and drawing in Lambert, Maurice (1979). "Journal asiatique" (in French). Société asiatique.: 13. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - "Journal asiatique" (in French). Société asiatique. 1979: 12–13. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help)
| Preceded by Epirmupi |
Akkadian Governor of Elam 2200 BCE |
Succeeded by ----- (Awan Dynasty) |
.jpg)