Ibn Ustadh-Hurmuz
Abu Ali Hasan ibn Ustadh-Hurmuz (Arabic: أبو علي حسن بن أستاذ هرمز), commonly known after his father as Ibn Ustadh-Hurmuz (ابن أستاذ هرمز) (died 1011) was a Daylamite[1] military officer of the Buyids, and an important figure in the Buyid state during the late 10th century.
Biography
Origins
He was the son of Ustadh-Hurmuz, a prominent Buyid chamberlain (hajib), who, after the death of the Buyid king Adud al-Dawla, began serving the latter's eldest son Sharaf al-Dawla, who was the ruler of Fars, and fought for complete control of the Buyid Empire against his younger brother Samsam al-Dawla, who was the ruler of Iraq. During this period, Ustadh-Hurmuz was appointed by Sharaf al-Dawla as the governor of Oman. However, wishing to change his allegiance to Sharaf al-Dawla's brother, he was forced to retire in 984.
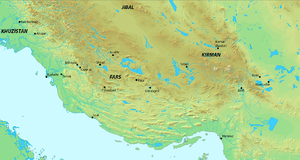
Service under the Buyids of Fars
During this period, Ibn Ustadh-Hurmuz was about 23 years old and was already in the service of Samsam al-Dawla; but in 987, Samsam al-Dawla was defeated and captured by Sharaf al-Dawla, who shortly annexed Iraq. He, however, died himself one year later, and was succeeded by his younger brother Baha' al-Dawla in Iraq, while Samsam al-Dawla managed to escape from captivity and fled to Fars, where he managed to conquer the entire region, and was joined by Ibn Ustadh-Hurmuz including other of his former officers such as Fuladh ibn Manadhar. In 995, Ibn Ustadh-Hurmuz became the leader of his Daylamite kinsmen in the Buyid army,[1] thus giving him a powerful position in the Buyid Empire. Two years later, he captured Ahvaz, but in the following year, Samsam al-Dawla was killed during a revolt by the sons of the deceased former Buyid ruler Izz al-Dawla.
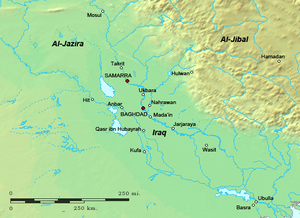
Service under the Buyids of Iraq
Ibn Ustadh-Hurmuz quickly used the opportunity to transfer his allegiance to Baha' al-Dawla,[2][3] who became the new ruler of Fars. In 1001, Ibn Ustadh-Hurmuz was appointed as the governor of Ahvaz, and one year later, became the governor of Iraq, where he made order by solving disputes between different religious sects, and by defeating bandits who had caused chaos in the region.
He also managed to defeat the former governor of Iraq, Abu Ja'far al-Hajjaj, who was supported by Kurds and Shayban Arabs.[4] He also defended Iraq against incursions from Batihah and the Hasanwayhid ruler Badr ibn Hasanwayh. Furthermore, Ibn Ustadh-Hurmuz managed to suppress the rebellion of the Uqaylid ruler Qirwash, who had briefly taken control of a few Buyid cities and had changed his allegiance to the Fatimid Caliphate.[5] Ibn Ustadh-Hurmuz later died in 1010/1, and was succeeded by the Buyid vizier Fakhr al-Mulk as the governor of Iraq.[1] Ibn Ustadh-Hurmuz's father, however, outlived the latter, and lived until 1015.
References
- Kennedy 2004, p. 237.
- Kennedy 2004, p. 236.
- Kabir 1964, p. 80.
- Kennedy 2004, p. 251.
- Kennedy 2004, p. 297.
Sources
- Cahen, Cl. (1971). "Ḥasan b. Ustād̲h̲-Hurmuz". In Lewis, B.; Ménage, V. L.; Pellat, Ch. & Schacht, J. (eds.). The Encyclopaedia of Islam, New Edition, Volume III: H–Iram. Leiden: E. J. Brill. OCLC 495469525.
- Donohue, John J. (2003). The Buwayhid Dynasty in Iraq 334 H./945 to 403 H./1012: Shaping Institutions for the Future. Leiden and Boston: Brill. ISBN 90-04-12860-3.
- Kennedy, Hugh (2004). The Prophet and the Age of the Caliphates: The Islamic Near East from the 6th to the 11th Century (Second ed.). Harlow: Longman. ISBN 978-0-582-40525-7.
- Kabir, Mafizullah (1964). The Buwayhid Dynasty of Baghdad, 334/946-447/1055. Retrieved 3 February 2014.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
| Preceded by Abu Ja'far al-Hajjaj |
Buyid governor of Iraq 1002 - 1010/1 |
Succeeded by Fakhr al-Mulk |