Iš (cuneiform)
The cuneiform sign iš is a common use sign in the Amarna letters and the Epic of Gilgamesh. It is used syllabically for iš; also for mel, mil, and a Sumerogramic usage for IŠ (Epic of Gilgamesh). Alphabetically as "iš", its most common usage, it can be used for "i" or "š". In Akkadian, the four vowels a, e, i, o, are all interchangeable, and the three different "s", can also be interchanged: s, ṣ, š.
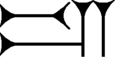

Cuneiform sign iš, line 10, EA 15, Obverse. (See line drawing below)
Epic of Gilgamesh use
For the Epic of Gilgamesh, the following usage is found in Tablets I-XII: iš-(134 times); mel-(1); mil-(8); IŠ-(18 times).[1]
Some common uses of "iš" in the Amarna letters
One of the most common uses of "iš" in the Amarna letters, is the use of the Akkadian language word "ištu",[2] which means "from", ("since"), in the English language. In the vassal city-state letters, in dialogue with the Pharaoh-in-Egypt, there is often mention of having listened to the correspondence – "words of the pharaoh", thus the words — "I have heard …", or "I have listened to …", the clay tablet "words" (correspondence), from the pharaoh. The common Akkadian word for "hear", or "listen", is "šemû".[3]
References
- Parpola, 197l. The Standard Babylonian Epic of Gilgamesh, Sign List, p. 159, Sign no. 212, iš/mel.
- Parpola, 197l. The Standard Babylonian Epic of Gilgamesh, Glossary, pp, 119-145; p. 128, "ištu", "from, since".
- Parpola, 197l. Glossary, pp, 119-145; p. 128, "šemû", "to hear, listen to".
- Held, Schmalstieg, Gertz, 1987. Beginning Hittite. Warren H. Held, Jr, William R. Schmalstieg, Janet E. Gertz, c. 1987, Slavica Publishers, Inc. w/ Glossaries, Sign List, Indexes, etc., 218 pages.
- Moran, William L. 1987, 1992. The Amarna Letters. Johns Hopkins University Press, 1987, 1992. 393 pages.(softcover, ISBN 0-8018-6715-0)
- Parpola, 197l. The Standard Babylonian Epic of Gilgamesh, Parpola, Simo, Neo-Assyrian Text Corpus Project, c 1997, Tablet I thru Tablet XII, Index of Names, Sign List, and Glossary-(pp. 119–145), 165 pages.
- Rainey, 1970. El Amarna Tablets, 359-379, Anson F. Rainey, (AOAT 8, Alter Orient Altes Testament 8)
