Hypotrich
The hypotrichs are a group of ciliated protozoa, common in fresh water, salt water, soil and moss. Hypotrichs possess compound ciliary organelles called "cirri," which are made up of thick tufts of cilia, sparsely distributed on the ventral surface of the cell. The multiple fused cilia which form a cirrus function together as a unit, enabling the organism to crawl along solid substrates such as submerged debris or sediments. Hypotrichs typically possess a large oral aperture, bordered on one side by a wreath or collar of membranelles (small membranous structures made up of fused cilia), forming an "adoral zone of membranelles," or AZM.[1][2][3]
| Hypotrich | |
|---|---|
| Uroleptus piscis | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Chromista |
| Infrakingdom: | Alveolata |
| Phylum: | Ciliophora |
| Class: | Spirotrichea |
| Subclass: | Hypotrichia Stein 1859 |
| Orders and Families | |
| |
Classification
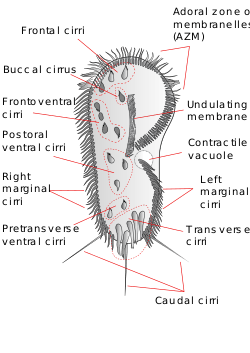
In older systems of classification, the term hypotrich comprised all ciliates possessing a relatively flattened body shape, strong cirri restricted to the ventral surface, and a large oral region (peristome) partially surrounded by an "adoral zone of membranelles".[2] From a phylogenetic point of view, this historic grouping--which included both euplotid ciliates (such as Euplotes and Aspidisca), and stichotrichian ciliates (such as Oxytricha and Urostyla)--is paraphyletic.[4] Any natural group, or clade, that contains both Euplotes and Oxytricha would also have to include many morphologically dissimilar spirotrich ciliates, such as the tintinnids and the oligotrichs.
.jpg)
.jpg)
In the classification system developed by Denis Lynn in collaboration with Eugene B. Small, the subclass Hypotrichia was restricted to euplotids and one small order of marine ciliates called Kiitrichida, while most of the traditional hypotrichs were placed in the subclass Stichotrichia.[5] However, some prominent researchers—notably, the Austrian ciliatologist Helmut Berger—rejected Lynn's nomenclature, and continued to assign non-euplotid "hypotrich" ciliates, such as oxytrichids and urostyloids, to some variant of Friedrich von Stein's original order Hypotricha.[6]
In their revised classification of the phylum Ciliophora, published in 2016, Gao et al. place the "stichotrichs" of Lynn & Small in the synonymous subclass Hypotrichia, and place all euplotid and discocephalid ciliates in the subclass Euplotia. The same high-level taxa are used, without ranks, by Adl et al. in their "Revised Classification of Eukaryotes" of 2012.
References
- Curds, Colin R. (1982). British and Other Freshwater Ciliated Protozoa. Bath: Cambridge University Press. pp. Vol. II, p. 368. ISBN 978-0-521-24257-8.
- Kudo, Richard R. (Richard Roksabro) (1954). Protozoology. MBLWHOI Library. Springfield, Ill., C. C. Thomas.
- Corliss, John O. (1979). The Ciliated Protozoa: Characterization, Classification, and Guide to the Literature. Pergamon Press. ISBN 9780080187525.
- Gao, Feng; Warren, Alan; Zhang, Qianqian; Gong, Jun; Miao, Miao; Sun, Ping; Xu, Dapeng; Huang, Jie; Yi, Zhenzhen (2016-04-29). "The All-Data-Based Evolutionary Hypothesis of Ciliated Protists with a Revised Classification of the Phylum Ciliophora (Eukaryota, Alveolata)". Scientific Reports. 6 (1): 24874. Bibcode:2016NatSR...624874G. doi:10.1038/srep24874. ISSN 2045-2322. PMC 4850378. PMID 27126745.
- "Classification of the Phylum Ciliophora, down to genus, revised by Denis Lynn (unpubl.)". www.uoguelph.ca. Archived from the original on 2017-07-15. Retrieved 2017-07-10.
- Monograph of the Urostyloidea (Ciliophora, Hypotricha) | Helmut Berger | Springer. Monographiae Biologicae. Springer. 2006. ISBN 9781402052729.