Herzberg Castle
Herzberg Castle (German: Schloss Herzberg) is a German schloss in Herzberg am Harz in the district of Göttingen in the state of Lower Saxony. The present-day, quadrangular building has its origins in the 11th century as a medieval castle. After a fire in 1510 it was rebuilt as a schloss and is one of the few in Lower Saxony that was constructed as a timber-framed building. Because it belonged to the House of Welf for 700 years it is also known as the Welf Castle of Herzberg (Welfenschloss Herzberg).


Geography
Herzberg Castle stands on a wooded eminence (275 m above sea level (NN)) immediately above and west of the centre of the town of Herzberg am Harz, which lies on the southwestern edge of the Harz Mountains. A stretch of the River Sieber runs past the castle to the north.
Architecture

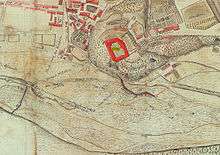
The present castle is an enclosed four-winged building with a rectangular courtyard (40 x 58 m) and was rebuilt after a serious fire in November 1510. Since the new castle was completed in 1528 its basements have been made of sandstone. One wing has an upper storey of stone, while the upper floors of the other three wings have been constructed using timber-framing. Its access through a gate tower and adjoining barbican has been retained. The old castle and the inner courtyard of the new one are entered after passing through the two-story gatehouse. The castle tower, known as the Clock Tower (Uhrturm), was built in the eastern corner. Its three upper storeys are made of timber.
History
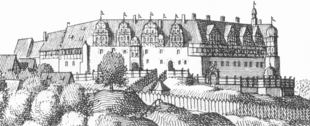
Originally the schloss was a medieval castle that was based on a hunting lodge built on the spot between 1024 and 1029. The castle was probably built at the behest of King, later Emperor, Lothair III, known as Lothair of Süpplingenburg.
In 1144, Herzberg Castle was given to the von Göttingen family of ministeriales from Bavaria by the House of Welf, who charged them with maintaining the castle and its surroundings. Previously, Count Hermann of Lutterberge had lived here, but he died in 1143 without any heirs who could inherit the fiefdom. The castle was first recorded in 1143 and, in 1158, it finally became a Welf allodial possession as the result of an exchange of property between Frederick Barbarossa and the Welf, Henry the Lion. Henry the Lion gave up estates inherited through his first wife, Clementia of Zähringen in Swabia. Since then the castle has been in Welf hands uninterruptedly for 708 years until the demise of the Kingdom of Hanover in 1866.
Empress Maria of Brabant, widow of Emperor Otto IV, made out a deed at the Hertsberg in 1218, thus the castle was an imperial residence for a short while. In 1279 the castle served as the residence for the widow of Duke Albert the Great. From 1337 to 1714 the castle was a ducal residence almost continuously.


In 1290 the castle became the residence of the Welf line of Brunswick-Grubenhagen, which was formed around this time. From 1486 the dukes of the Principality of Grubenhagen lived here until they died out in 1596. Thereafter the estate was transferred to the Welf line of Brunswick-Lüneburg.
There was a major fire at the castle in 1510. The lord of the castle, Duke Philip I, his wife, Catharine, and their son, Philip, were rescued at the last minute from the rapidly engulfing flames. The duke's shield bearer and the duchess's chambermaid died in the fire.
Duke George of Brunswick and Lüneburg lived in the castle until 1635 with his wife, the Landgravine Anne Eleanor of Hesse-Darmstadt. In 1629, the first Elector of Hanover was born here, Ernest Augustus, Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg.
In 1714 the schloss was given up as a residence and from 1882 it was the seat of the district court of Herzberg. In 1900 a museum was established in the castle. Although the castle had survived largely undamaged by fire over the centuries, it suffered severe damage at the end of the Second World War, which has since been repaired. On the night of 4 April 1945, there was a mighty explosion at a nearby ammunition dump, where 40,000 kg of explosives and 8,000 mines had been stored. This blew the roof off the castle and, in the wake of the explosion, the museum was destroyed and probably looted. In 1947, further damage was caused when some nearby military bunkers were blown up.
Today the castle houses a small cultural centre with a restaurant, a museum and the great hall, which is used for various cultural events. The museum portrays the history of the forestry industry in the Harz, the castle's history and that of the Welfs. Other exhibition areas present the history of Herzberg arms manufacture as well as the work of Herzberg organ maker Johann Andreas Engelhardt. In part of the permanent exhibition there is a facsimile of the Gospels of Henry the Lion, a masterpiece of Romanesque book illumination of the 12th century containing the four Gospel accounts.
Sources
- Ernst Andreas Friedrich: Wenn Steine reden könnten. Bd 4. Landbuch-Verlag, Hannover 1998, ISBN 3-7842-0558-5
- Hans Adolf Schultz: Burgen und Schlösser des Braunschweiger Landes, Braunschweig 1980, ISBN 3-87884-012-8
- Phillip Julius Rehtmeier: Historische Beschreibung S. 311, Braunschweig 1722
- Jürgen Wilke, Die Geschichte des Wappens der Stadt Herzberg/Harz S. 1-33 + Literaturverzeichnis, Göttingen 1998
- Wolfenbüttel Nds.StA. 1 Urk. 2
- Die Chronik Arnolds von Lübeck. Nach der Ausgabe der Monumenta Germaniae, übersetzt von Dr. J.C.M. Laurent, Berlin 1853
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Herzberg Castle. |
- Museum Schloss Herzberg Castle Museum (in German)
- Geological location of the castle and aerial photo (in German)
- Architectural details of Herzberg Castle at karstwanderweg.de (in German)