HMS M15
HMS M15 was a First World War Royal Navy M15-class monitor. She was sunk off Gaza by UC-38 on 11 November 1917.
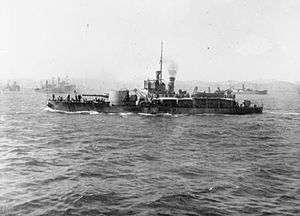 M15 at Mudros, 1916 | |
| History | |
|---|---|
| Name: | HMS M15 |
| Builder: | William Gray, Hartlepool. |
| Laid down: | 1 March 1915 |
| Launched: | 28 April 1915 |
| Fate: | Sunk by UC-38 on 11 November 1917. |
| General characteristics | |
| Class and type: | M15-class monitor |
| Displacement: | 540 tons |
| Length: | 177 ft 3 in (54.03 m) |
| Beam: | 31 ft (9.4 m) |
| Draught: | 6 ft 9 in (2.06 m) |
| Propulsion: |
|
| Speed: | 11 knots (20 km/h) |
| Complement: | 69 |
| Armament: |
|
Design
Intended as a shore bombardment vessel, M15's primary armament was a single 9.2 inch Mk X gun which had been held as a spare for the Drake-class cruiser and Cressy-class cruiser.[1] In addition to her 9.2-inch gun, she also possessed one 12-pounder and one six pound anti-aircraft gun. She was equipped with Triple Expansion steam engines rated to 800 horse power that allowed a top speed of eleven knots. The monitor's crew consisted of sixty nine officers and men.
Construction
HMS M15 was ordered in March, 1915, as part of the War Emergency Programme of ship construction. She was laid down at the William Gray shipyard at Hartlepool in March 1915, launched on 28 April 1915, and completed in June 1915.
First World War
M15 was towed to Malta in July, 1915, where she received her main armament. She then proceeded to Mudros, and later was involved in the defence of the Suez Canal.
After bombarding Gaza as part of the Third Battle of Gaza, on 11 November 1917, M15 and the destroyer HMS Staunch were torpedoed by UC-38. 26 men lost their lives in the sinking of M15.
Citations
- Randal Gray (ed). Conway's All the World's Fighting Ships, 1906–1921. Conway Maritime Press. p. 48. ISBN 0-85177-245-5.CS1 maint: extra text: authors list (link)
References
- Colledge, J. J.; Warlow, Ben (2006) [1969]. Ships of the Royal Navy: The Complete Record of all Fighting Ships of the Royal Navy (Rev. ed.). London: Chatham Publishing. ISBN 978-1-86176-281-8.
- Dittmar, F. J. & Colledge, J. J., "British Warships 1914-1919", (Ian Allan, London, 1972), ISBN 0-7110-0380-7