GraphStream
GraphStream[2][3] is a graph handling Java library that focuses on the dynamics aspects of graphs. Its main focus is on the modeling of dynamic interaction networks of various sizes.
 | |
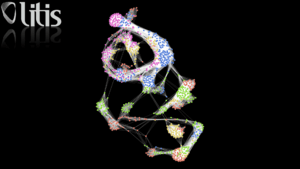 Modeling of Boids interactions with GraphStream | |
| Developer(s) | RI2C Team, LITIS[1] |
|---|---|
| Stable release | 1.1
/ November 11, 2011 |
| Operating system | Linux, Windows, macOS |
| Type | Dynamic Graph Library |
| License | GNU General Public License |
| Website | graphstream-project |
The goal of the library is to provide a way to represent graphs and work on it. To this end, GraphStream proposes several graph classes that allow to model directed and undirected graphs, 1-graphs or p-graphs (a.k.a. multigraphs, that are graphs that can have several edges between two nodes).
GraphStream allows to store any kind of data attribute on the graph elements: numbers, strings, or any object.
Moreover, in addition, GraphStream provides a way to handle the graph evolution in time. This means handling the way nodes and edges are added and removed, and the way data attributes may appear, disappear and evolve.
Stream
Dynamics of graphs is modeled as stream of graph events. These events can be about the structure of the graph (add and remove elements) or about the attributes of elements (graph, node and edge attributes).
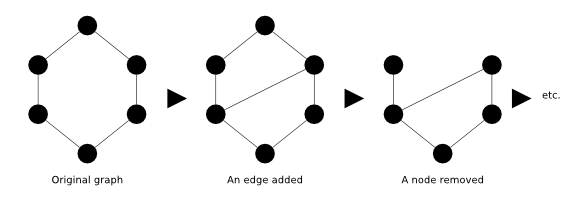
This is the list of events which can be found in GraphStream:[4]
- node/edge addition/deletion,
- clear graph,
- graph/node/edge attribute addition/change/deletion,
- begin step.
A stream is the connection between a source providing events and a sink. Sources can be anything able to produce events, for example a source reading a file, an algorithm generating a graph ...
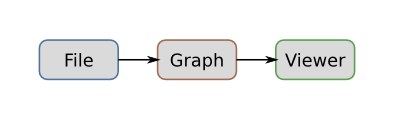
Visualization
GraphStream provides some features to display graphs. The rendering of elements can be customized by defining a CSS stylesheet for the graph being displayed. Viewer allows an automatic layout of nodes.
See also
- Graph (discrete mathematics)
- Graph drawing
- Graph theory
- Graph (data structure)
- Social network analysis software
References
- About GraphStream
- A. Dutot, F. Guinand, D. Olivier and Y. Pigné, 2007: GraphStream: A tool for bridging the gap between complex systems and dynamic graphs , in Emergent Properties in Natural and Artificial Complex Systems (EPNACS'07), Workshop of the 4th European Conference on Complex Systems (ECCS'07), Dresden, Germany
- A. Dutot, Y. Pigné, 2010: GraphStream workshop, in Emergent Properties in Natural and Artificial Complex Systems (EPNACS'10), a satellite meeting for ECCS'10 Archived 2011-02-07 at the Wayback Machine, Lisbon University Institute, LISBON, Portugal
- Getting started