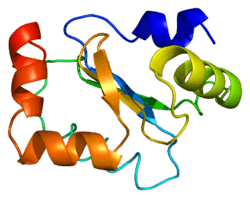
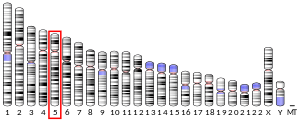
GLRX
Glutaredoxin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GLRX gene.[5][6]
Interactions
GLRX has been shown to interact with Wilson disease protein[7] and ATP7A.[7]
gollark: @golalark?
gollark: If you're running it without signature verification you can just load the omnidisk with one of the all-permissions-granted no-disk-ID-check UUIDs.
gollark: The omnidisk again, somehow?
gollark: I would do that anyway.
gollark: How do you go around obfuscating it, anyway?
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000173221 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000021591 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Padilla CA, Bajalica S, Lagercrantz J, Holmgren A (Feb 1997). "The gene for human glutaredoxin (GLRX) is localized to human chromosome 5q14". Genomics. 32 (3): 455–7. doi:10.1006/geno.1996.0141. PMID 8838810.
- "Entrez Gene: GLRX glutaredoxin (thioltransferase)".
- Lim, Chris M; Cater Michael A; Mercer Julian F B; La Fontaine Sharon (Sep 2006). "Copper-dependent interaction of glutaredoxin with the N termini of the copper-ATPases (ATP7A and ATP7B) defective in Menkes and Wilson diseases". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 348 (2): 428–36. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.07.067. hdl:10536/DRO/DU:30003772. ISSN 0006-291X. PMID 16884690.
Further reading
- Lou MF (2003). "Redox regulation in the lens". Progress in Retinal and Eye Research. 22 (5): 657–82. doi:10.1016/S1350-9462(03)00050-8. PMID 12892645.
- Sykes MC, Mowbray AL, Jo H (2007). "Reversible glutathiolation of caspase-3 by glutaredoxin as a novel redox signaling mechanism in tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced cell death". Circ. Res. 100 (2): 152–4. doi:10.1161/01.RES.0000258171.08020.72. PMID 17272816.
- Padilla CA, Martínez-Galisteo E, Bárcena JA, et al. (1995). "Purification from placenta, amino acid sequence, structure comparisons and cDNA cloning of human glutaredoxin". Eur. J. Biochem. 227 (1–2): 27–34. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1995.tb20356.x. PMID 7851394.
- Bandyopadhyay S, Gronostajski RM (1994). "Identification of a conserved oxidation-sensitive cysteine residue in the NFI family of DNA-binding proteins". J. Biol. Chem. 269 (47): 29949–55. PMID 7961993.
- Fernando MR, Sumimoto H, Nanri H, et al. (1994). "Cloning and sequencing of the cDNA encoding human glutaredoxin". Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1218 (2): 229–31. doi:10.1016/0167-4781(94)90019-1. PMID 8018729.
- Papov VV, Gravina SA, Mieyal JJ, Biemann K (1994). "The primary structure and properties of thioltransferase (glutaredoxin) from human red blood cells". Protein Sci. 3 (3): 428–34. doi:10.1002/pro.5560030307. PMC 2142694. PMID 8019414.
- Padilla CA, Spyrou G, Holmgren A (1996). "High-level expression of fully active human glutaredoxin (thioltransferase) in E. coli and characterization of Cys7 to Ser mutant protein". FEBS Lett. 378 (1): 69–73. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(95)01413-6. PMID 8549805.
- Park JB, Levine M (1996). "Purification, cloning and expression of dehydroascorbic acid-reducing activity from human neutrophils: identification as glutaredoxin". Biochem. J. 315. ( Pt 3) (3): 931–8. doi:10.1042/bj3150931. PMC 1217296. PMID 8645179.
- Davis DA, Newcomb FM, Starke DW, et al. (1997). "Thioltransferase (glutaredoxin) is detected within HIV-1 and can regulate the activity of glutathionylated HIV-1 protease in vitro". J. Biol. Chem. 272 (41): 25935–40. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.41.25935. PMID 9325327.
- Park JB, Levine M (1997). "The human glutaredoxin gene: determination of its organization, transcription start point, and promoter analysis". Gene. 197 (1–2): 189–93. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(97)00262-X. PMID 9332366.
- Bandyopadhyay S, Starke DW, Mieyal JJ, Gronostajski RM (1998). "Thioltransferase (glutaredoxin) reactivates the DNA-binding activity of oxidation-inactivated nuclear factor I." J. Biol. Chem. 273 (1): 392–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.1.392. PMID 9417094.
- Sun C, Berardi MJ, Bushweller JH (1998). "The NMR solution structure of human glutaredoxin in the fully reduced form". J. Mol. Biol. 280 (4): 687–701. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.156.1182. doi:10.1006/jmbi.1998.1913. PMID 9677297.
- Yang Y, Jao S, Nanduri S, et al. (1999). "Reactivity of the human thioltransferase (glutaredoxin) C7S, C25S, C78S, C82S mutant and NMR solution structure of its glutathionyl mixed disulfide intermediate reflect catalytic specificity". Biochemistry. 37 (49): 17145–56. doi:10.1021/bi9806504. PMID 9860827.
- Balijepalli S, Tirumalai PS, Swamy KV, et al. (1999). "Rat brain thioltransferase: regional distribution, immunological characterization, and localization by fluorescent in situ hybridization". J. Neurochem. 72 (3): 1170–8. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.1999.0721170.x. PMID 10037490.
- Barrett WC, DeGnore JP, König S, et al. (1999). "Regulation of PTP1B via glutathionylation of the active site cysteine 215". Biochemistry. 38 (20): 6699–705. doi:10.1021/bi990240v. PMID 10350489.
- García-Pardo L, Granados MD, Gaytán F, et al. (1999). "Immunolocalization of glutaredoxin in the human corpus luteum". Mol. Hum. Reprod. 5 (10): 914–9. doi:10.1093/molehr/5.10.914. PMID 10508218.
- Mallis RJ, Poland BW, Chatterjee TK, et al. (2000). "Crystal structure of S-glutathiolated carbonic anhydrase III". FEBS Lett. 482 (3): 237–41. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(00)02022-6. PMID 11024467.
- Balijepalli S, Boyd MR, Ravindranath V (2001). "Human brain thioltransferase: constitutive expression and localization by fluorescence in situ hybridization". Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 85 (1–2): 123–32. doi:10.1016/S0169-328X(00)00206-0. PMID 11146114.
- Qiao F, Xing K, Liu A, et al. (2001). "Human lens thioltransferase: cloning, purification, and function". Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 42 (3): 743–51. PMID 11222536.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.