Gisr el-Mudir
Gisr el-Mudir (Arabic:جسر المدير, "bridge of the chief") also known as the Great Enclosure, is one of the oldest known stone structures in Egypt, located at Saqqara only a few hundred metres west of the Step Pyramid and the Buried Pyramid. The function of the space is not yet clear.
.png)
Description
The structure consists of a rectangular wall oriented north-south and measuring about 650 by 350 metres. The walls consist of two outer walls made of roughly hewn limestone about 15 metres apart; the space between them is filled with crushed stone, gravel and sand.[1] In the northwestern corner, the walls survive to a height of 4.5 to 5 metres (over 15 courses of stone). The style of construction suggests an original height of around 10 metres. In the south the state of preservation is clearly worse than in the north. Since the west wall of the structure is 30 metres shorter than the east, the south wall probably consisted of two parallel walls forming an entranceway. This pattern recurs in the larger funerary complex of Djoser's step pyramid.[2]
The walls were probably completed and in the enclosed area no remains of a construction have been found, so there cannot have been a pyramid or mastaba at the centre, since these constructions would have had to have been erected before the completion of an enclosure wall. A small building may have existed in the northwest corner of the space, since numerous limestone, pink granite, and basalt fragments were found there.[3] John Shae Perring demonstrated that a small hill which was once found in the centre of the enclosure was the leftover debris from the excavation of a tomb in the Greek period.[2]
Spoliation of stone for new construction afflicted Gisr el-Mudir much less than other buildings in the area, probably because of the poor quality of the stone used in its construction.
To the north and northeast of Gisr el-Mudir are the remnants of similar structures.
Discovery
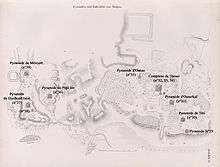
Already in the investigation of Saqqara by John Shae Perring in 1837, the outline of the enclosure was detected. It was also noted by Karl Richard Lepsius (1842–1846) and Jacques de Morgan (1897), but it was not excavated.
The first excavation was carried out in 1947 and 1948 by the then director of the Supreme Council of Antiquities Abdel Salam Hussein. His nickname "el-Mudir" (= "the chief") was the source of its modern name Gisr el-Mudir. The results of these excavations were not published.[2]
Systematic research was first undertaken in the 1990s by archaeologists of the National Museum of Scotland employing techniques like magnetometry and ground-penetrating radar.[3] Before these excavations, the structure was thought to be an unfinished pyramid complex from the Third Dynasty. However, pottery shards in the filling of the walls were found to date to the late Second or beginning of the Third Dynasty which leads some Egyptologists to believe this is evidence the structure may have been constructed at the end of the Second Dynasty.
The builder of the structure has not yet been determined. Rainer Stadelmann saw a connection between this enclosure and the two gallery tombs of the Second Dynasty located to the south of the Step Pyramid complex, which have been attributed to Hotepsekhemwy and Nebra or Ninetjer. In his opinion, the empty rectangular structure interacted with the graves similarly to how the valley areas interacted with the graves at Abydos.[4] Other scholars ascribe the structure to Khasekhemwy on account of similarities to his enclosure at Abydos, Shunet el-Zebib, and also because the erection of a stone building called Men-Netjeret is attributed to him in the Palermo Stone which seems to fit chronologically with the construction of Gisr el-Mudir.[2][5] The rectangular structure probably represents a transitional stage between the enclosures at Abydos and the Step Pyramid complex of Djoser.
References
- Illustration of the wall construction of Gisr el-Mudir Archived 2009-09-13 at the Wayback Machine
- Francesco Raffaele: Saqqara – Early Dynastic monuments (Dynasties 1-3)
- Ian J. Mathieson, Ana Tavares "Preliminary report of the National Museums of Scotland Saqqara Survey Project, 1990–91." The Journal of Egyptian Archaeology. Band 79, 1993, ISSN 0307-5133, S. 17–31.
- Mark Lehner. Geheimnis der Pyramiden. ECON, Düsseldorf 1997, pp. 82ff. Saqqara im Überblick.
- Ian Mathieson, Elizabeth Bettles, Joanne Clarke, Corinne Duhig, Salima Ikram, Louise Maguire, Sarah Quie, Ana Tavares: "The National Museums of Scotland Saqqara Survey Projekt 1993–1995." Journal of Egyptian Archaeology. 83, 1997, pp. 17–53, here p.36, 38ff., 53.
Bibliography
- Toby A. H. Wilkinson: Early Dynastic Egypt. Routledge, London 1999, ISBN 0-415-18633-1, pp. 210 ff.
External links
- Egypt State Information Service: Gisr el-Mudir
- Gisr el-Mudir on egyptphoto.ncf.ca
- Satellite photo of Gisr el-Mudir at Google Maps
- Article with images on Egyptian Monuments.
- The 'Great Enclosure' on ancient-egypt.org.