Tonne
The tonne (/tʌn/ (![]()
| tonne | |
|---|---|
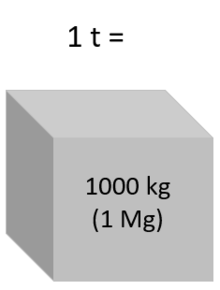 One tonne is equal to 1000 kilograms or 1 megagram | |
| General information | |
| Unit system | Non-SI unit accepted for use with SI |
| Unit of | Mass |
| Symbol | t |
| In SI base units: | 1 t = 1000 kg = 1 Mg |
Symbol and abbreviations
The BIPM symbol for the tonne is 't', adopted at the same time as the unit in 1879.[4] Its use is also official for the metric ton in the United States, having been adopted by the United States National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).[5] It is a symbol, not an abbreviation, and should not be followed by a period. Use of majuscule and minuscule letter case is significant, and use of other letter combinations is not permitted and would lead to ambiguity. For example, 'T', 'MT', 'mT', 'Mt', 'mt' are the SI symbols for the tesla, megatesla, millitesla, megatonne (one teragram), and millitonne (one kilogram) respectively. If describing TNT equivalent units of energy, one megatonne of TNT is equivalent to approximately 4.184 petajoules.
Origin and spelling
In French and English, tonne is the correct spelling. It is usually pronounced the same as ton (/tʌn/), but the final "e" can also be pronounced, i.e. "tunnie" (/ˈtʌnɪ/).[6] In Australia, it is also pronounced /tɒn/.[7] In the United States, metric ton is the name for this unit used and recommended by NIST;[5] an unqualified mention of a ton almost invariably refers to a short ton of 2,000 pounds (907 kg), and tonne is rarely used in speech or writing. Both terms are acceptable in Canadian usage.
Before metrication in the UK, the unit used for most purposes was the Imperial ton of 2,240 pounds avoirdupois or 20 hundredweight (usually referred to as the long ton in the US), equivalent to approximately 1,016 kg, differing by about 1.6% from the tonne. The UK Weights and Measures Act 1985 explicitly excluded from use for trade certain imperial units, including the ton, unless the item being sold or the weighing equipment being used was weighed or certified prior to 1 December 1980, and even then only if the buyer was made aware that the weight of the item was measured in imperial units.[8][9][10]
Ton and tonne are both derived from a Germanic word in general use in the North Sea area since the Middle Ages (cf. Old English and Old Frisian tunne, Old High German and Medieval Latin tunna, German and French tonne) to designate a large cask, or tun.[11] A full tun, standing about a metre high, could easily weigh a tonne. An English tun (an old wine cask volume measurement equivalent to approximately 954 litres) of wine has a relative mass of approximately 954 kg if full of pure water, a little less for wine.
The spelling tonne pre-dates the introduction of the SI in 1960; it has been used with this meaning in France since 1842,[12] when there were no metric prefixes for multiples of 106 and above, and is now used as the standard spelling for the metric mass measurement in most English-speaking countries.[13][14][15][16] In the United States, the unit was originally referred to using the French words millier or tonneau,[17] but these terms are now obsolete.[2] The Imperial and US customary units comparable to the tonne are both spelled ton in English, though they differ in mass.
Conversions
One tonne is equivalent to:
- In kilograms: 1000 kilograms (kg) by definition.[1]
- In grams: 1000000 grams (g) or 1 megagram (Mg). Megagram is the corresponding official SI unit with the same mass. Mg is distinct from mg, milligram.
- In pounds: Exactly 1000/0.453 592 37 pounds (lb) by definition of the pound,[18] or approximately 2204.622622 lb.
- In short tons: Exactly 1/0.907 184 74 short tons (ST), or approximately 1.102311311 ST.
- One short ton is exactly 0.90718474 t.[19]
- In long tons: Exactly 1/1.016 046 9088 long tons (LT), or approximately 0.9842065276 LT.
- One long ton is exactly 1.0160469088 t.[19]
A tonne is the mass of one cubic metre of pure water: at 4 °C one thousand litres of pure water has an absolute mass of one tonne.[20]
Derived units
For multiples of the tonne, it is more usual to speak of thousands or millions of tonnes. Kilotonne, megatonne, and gigatonne are more usually used for the energy of nuclear explosions and other events in equivalent mass of TNT, often loosely as approximate figures. When used in this context, there is little need to distinguish between metric and other tons, and the unit is spelt either as ton or tonne with the relevant prefix attached.[21]
| Tonnes | Grams | Equivalents* | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Multiple | Name | Symbol | Multiple | Name | Symbol | Tonnes (t) | Kilograms (kg) | Grams (g) | US/short tons (ST)† | Imperial/long tons (LT)† |
| 100 | tonne | t | 106 | megagram | Mg | 1 t | 1,000 kg | 1 million g | 1.1023 ST | 0.98421 LT |
| 103 | kilotonne | ktǂ | 109 | gigagram | Gg | 1,000 t | 1 million kg | 1 billion g | 1,102.3 ST | 984.21 LT |
| 106 | megatonne | Mt | 1012 | teragram | Tg | 1 million t | 1 billion kg | 1 trillion g | 1.1023 million ST | 984,210 LT |
| 109 | gigatonne | Gt | 1015 | petagram | Pg | 1 billion t | 1 trillion kg | 1 quadrillion g | 1.1023 billion ST | 984.21 million LT |
| 1012 | teratonne | Tt | 1018 | exagram | Eg | 1 trillion t | 1 quadrillion kg | 1 quintillion g | 1.1023 trillion ST | 984.21 billion LT |
| 1015 | petatonne | Pt | 1021 | zettagram | Zg | 1 quadrillion t | 1 quintillion kg | 1 sextillion g | 1.1023 quadrillion ST | 984.21 trillion LT |
| 1018 | exatonne | Et | 1024 | yottagram | Yg | 1 quintillion t | 1 sextillion kg | 1 septillion g | 1.1023 quintillion ST | 984.21 quadrillion LT |
*The equivalent units columns use the short scale large-number naming system currently used in most English-language countries, e.g. 1 billion = 1,000 million = 1,000,000,000.
†Values in the equivalent short and long tons columns are rounded to five significant figures. See Conversions for exact values.
ǂThough non-standard, the symbol "kt" is also used for knot, a unit of speed for aircraft and sea-going vessels, and should not be confused with kilotonne.
Alternative usage
A metric ton unit (mtu) can mean 10 kg (approximately 22 lns) within metal (e.g. tungsten, manganese) trading, particularly within the US. It traditionally referred to a metric ton of ore containing 1% (i.e. 10 kg) of metal.[22][23] The following excerpt from a mining geology textbook describes its usage in the particular case of tungsten:
"Tungsten concentrates are usually traded in metric tonne units (originally designating one tonne of ore containing 1% of WO3, today used to measure WO3 quantities in 10 kg units. One metric tonne unit (mtu) of tungsten (VI) contains 7.93 kilograms of tungsten." (Walter L Pohl, Economic Geology: Principles and Practices, English edition, 2011, p 183.)
Tungsten is also known as wolfram and has the atomic symbol W.
In the case of uranium, the acronym MTU is sometimes considered to be metric ton of uranium, meaning 1,000 kg.[24][25][26][27]
A gigatonne is a unit of mass often used by the coal mining industry to assess and define the extent of a coal reserve.
Use of mass as proxy for energy
The tonne of trinitrotoluene (TNT) is used as a proxy for energy, usually of explosions (TNT is a common high explosive). Prefixes are used: kiloton(ne), megaton(ne), gigaton(ne), especially for expressing nuclear weapon yield, based on a specific combustion energy of TNT of about 4.2 MJ/kg (or one thermochemical calorie per milligram). Hence, 1 t TNT = approx. 4.2 GJ, 1 kt TNT = approx. 4.2 TJ, 1 Mt TNT = approx. 4.2 PJ.
The SI unit of energy is the joule. Assuming that a TNT explosion releases 1,000 small (thermochemical) calories per gram (approx. 4.2 kJ/g), one tonne of TNT is approx. equivalent to 4.2 gigajoules.
In the petroleum industry the tonne of oil equivalent (toe) is a unit of energy: the amount of energy released by burning one tonne of crude oil, approx, 42 GJ. There are several slightly different definitions. This is ten times as much as a tonne of TNT because atmospheric oxygen is used.
Unit of force
Like the gram and the kilogram, the tonne gave rise to a (now obsolete) force unit of the same name, the tonne-force, equivalent to about 9.8 kilonewtons: a unit also often called simply "tonne" or "metric ton" without identifying it as a unit of force. In contrast to the tonne as a mass unit, the tonne-force or metric ton-force is not acceptable for use with SI, partly because it is not an exact multiple of the SI unit of force, the newton.
See also
Notes and references
- "The International System of Units (SI), 9th edition" (PDF). 2019. p. 145. Retrieved December 31, 2019.
- "Metric System of Measurement: Interpretation of the International System of Units for the United States" (PDF). Federal Register. 63 (144): 40338. July 28, 1998. 63 FR 40333. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 15, 2011.
- United States National Bureau of Standards (1959-06-25). "Notices "Refinement of values for the yard and the pound"" (PDF). Retrieved 2006-08-12.
- Table 6 Archived 2009-10-01 at the Wayback Machine. BIPM. Retrieved on 2011-07-10.
- Metric System of Measurement: Interpretation of the International System of Units for the United States Archived 2008-04-09 at the Wayback Machine (PDF). See corrections in the Errata section of Archived 2008-04-18 at the Wayback Machine.
- The Oxford English dictionary 2nd ed. lists both /tʌn/ and /ˈtʌnɪ/
- Macquarie Dictionary (fifth ed.). Sydney: Macquarie Dictionary Publishers Pty Ltd. 2009.
- A Dictionary of Weights, Measures, and Units, edited by Donald Fenna, Oxford University Press
- "Weights and Measures Act 1985". Section 8(1), Act No. 72 of 30 October 1985. Retrieved 11 Apr 2016.
- "Weights and Measures Act 1985". Schedule 11(13–14), Act No. 72 of 30 October 1985. Retrieved 11 Apr 2016.
- Harper, Douglas. "tonne". Online Etymology Dictionary.
- "Recherche d'un mot". atilf.atilf.fr.
- "Guidance Note on the use of Metric Units of Measurement by the Public Sector" (PDF). National Measurement Office. 2007. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-02-07. Retrieved 2010-02-13. "Tonne" is listed under "The Principal Metric Units of Measurement" on p. 7.
- "National Measurement Regulations 1999 |". Australian Government. 1999. Retrieved 2010-02-13. "Tonne" is listed under Schedule 1, Part 3 as a non-SI unit of measurement used with SI units of measurement.
- "Appendix 4: Units of Measurement and Conversion Factors". MAF (Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry (New Zealand)). Retrieved 2010-02-13.
- "Canada Gazette". Government of Canada. 1998–2007. Retrieved 2010-02-13.
The Corporation shall pay to producers selling and delivering wheat produced in the designated area to the Corporation the following sums certain per tonne basis...
- Act of July 28, 1866, codified in 15 U.S.C. § 205
- Barbrow, L.E.; Judson, L.V. (1976). Weights and measures standards of the United States – A brief history. Archived from the original on 2008-05-11.
- National Institute of Standards and Technology. Butcher, Tina; Crown, Linda; Harshman, Rick; Williams, Juana, eds. (October 2013). "Appendix C – General Tables of Units of Measurement" (PDF). Specifications, Tolerances, and Other Technical Requirements for Weighing and Measuring Devices. NIST Handbook. 44 (2014 ed.). Washington, D.C.: U.S. Department of Commerce, Technology Administration, National Institute of Standards and Technology. p. C-13. ISSN 0271-4027. OCLC 58927093. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- To within 0.003%.
- The Oxford English Dictionary 2nd ed. gives both megaton and megatonne and adds "The unit may be calculated in either imperial or metric tons; the form megatonne generally implies the metric unit". The use for energy is the first definition; use for mass or weight is the third definition.
- "Platt's Metals Guide to Specifications – Conversion Tables". 8 September 2008. Archived from the original on 8 September 2008.CS1 maint: BOT: original-url status unknown (link)
- How Many? A Dictionary of Units of Measurement. Unc.edu. Retrieved on 2011-07-10.
- Reference.Pdf. (PDF) . Retrieved on 2011-07-10.
- "Glossary". (June 2000). Disposition of Surplus Hanford Site Uranium, Hanford Site, Richland, Washington. US Department of Energy.
- "Acronyms". Y-12 National Security Complex.
- NRC Collection of Abbreviations (NUREG-0544, Rev. 4), United States Nuclear Regulatory Commission. Nrc.gov (2011-03-13). Retrieved on 2011-07-10.
External links
- NIST Special Publication 811, Guide for the Use of the International System of Units (SI)
