Georgia State Route 332
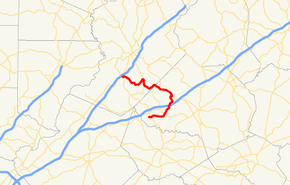
State Route 332 (SR 332) is a 23.2-mile (37.3 km) state highway in the northeastern part of the U.S. state of Georgia. It travels from SR 53 in Hoschton in Jackson County to SR 13 in Oakwood in Hall County. The route physically travels in a backwards "C" shape.
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 | ||||
| Route information | ||||
| Maintained by GDOT | ||||
| Length | 24.0 mi[1] (38.6 km) | |||
| Existed | June 1, 1963[2][3]–present | |||
| Major junctions | ||||
| South end | ||||
| North end | ||||
| Location | ||||
| Counties | Jackson, Hall | |||
| Highway system | ||||
| ||||
Route description
SR 332 begins at an intersection with SR 53 (Main Street) in Hoschton in Jackson County. It travels to the east on Pendergrass Road, and leaves the city limits of town before crossing over Indian Creek. It curves to the north-northeast, passes northwest of the Traditions of Braselton Golf Club, and intersects SR 124. It continues to the north-northeast, where it crosses over, but does not have an interchange with, Interstate 85 (I-85). After a northeast curve and a crossing of Holders Creek, the highway enters Pendergrass. Almost immediately, SR 332 curves to the north-northwest until it intersects North Old Gainesville Highway. Here, the route turns to the southeast and curves to the east to an intersection with US 129/SR 11 (Civil War Hearland Leaders Trail). The three highway travel concurrently northwest to an intersection with Main Street just east of Talmo. It travels to the southwest and enters Talmo. Almost immediately, it curves to the northwest. It passes the Talmo Cemetery and the Talmo Public Library. SR 332 then begins a zigzag route to the northwest, entering Hall County and alternating to the southwest and the north. Southeast of Belmont, SR 332 begins a concurrency with SR 60 (Candler Road). In Belmont, they intersect the eastern terminus of SR 211 (Tanners Mill Road). In Candler, SR 332 splits off to the west-southwest, following Poplar Springs Road. The route crosses Walnut Creek again and continues in a general northwest direction to meet its northern terminus, an intersection with SR 13 (Atlanta Highway) in the southeast part of Oakwood. The route's northern terminus is about 0.1 miles (0.16 km) from having a second intersection with SR 53.[1]
The only part of SR 332 that is part of the National Highway System, a system of roadways important to the nation's economy, defense, and mobility, is the segment that is concurrent with US 129/SR 11 in the Pendergrass–Talmo area.[4][5]
History
The roadway that would eventually be designated as SR 332 was established at least as far back as 1919 as a part of SR 11, which traveled from Jefferson to Gainesville.[6] By the end of 1926, US 129 had been designated along this highway.[7][8] In 1942, this entire length of US 129/SR 11 was paved.[9][10] By the middle of 1955, an unnumbered roadway was constructed between the Braselton area and Gainesville.[11][12] By the middle of 1960, this roadway was designated as SR 60.[13][14] By the middle of 1963, SR 332 was built, and paved, from its southern terminus to its current southern intersection with SR 60.[2][3] Prior to 1966, SR 332 was extended to its northern terminus in Oakwood, with the segment from the intersection with Weaver Road, southwest of Candler, to Oakwood, paved.[15][16] Later that year, the remaining segment, from Weaver Road to Candler, was paved.[16][17]
Major intersections
| County | Location | mi[1] | km | Destinations | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jackson | Hoschton | 0.0 | 0.0 | Southern terminus | |
| | 4.0 | 6.4 | |||
| Pendergrass | 9.0 | 14.5 | Southern end of US 129/SR 11 concurrency | ||
| | 11.9 | 19.2 | Northern end of US 129/SR 11 concurrency | ||
| Hall | | 15.4 | 24.8 | Southern end of SR 60 concurrency | |
| Belmont | 16.5 | 26.6 | Eastern terminus of SR 211 | ||
| Candler | 18.1 | 29.1 | Northern end of SR 60 concurrency | ||
| Oakwood | 24.0 | 38.6 | |||
1.000 mi = 1.609 km; 1.000 km = 0.621 mi
| |||||
See also
.svg.png)

References
- Google (June 11, 2014). "Route of SR 332" (Map). Google Maps. Google. Retrieved June 11, 2014.
- State Highway Department of Georgia (1960). State Highway System and Other Principal Connecting Roads (PDF) (Map) (1960–1961 ed.). Scale not given. Atlanta: State Highway Department of Georgia. OCLC 5673161. Retrieved August 19, 2015. (Corrected to June 1, 1960.)
- State Highway Department of Georgia (1963). State Highway System and Other Principal Connecting Roads (PDF) (Map). Scale not given. Atlanta: State Highway Department of Georgia. OCLC 5673161. Retrieved August 19, 2015. (Corrected to June 1, 1963.)
- National Highway System: (Draft) Georgia (PDF) (Map). Federal Highway Administration. November 15, 2013. Retrieved June 11, 2014.
- National Highway System: Gainesville, GA (PDF) (Map). Federal Highway Administration. October 1, 2012. Retrieved June 11, 2014.
- State Highway Department of Georgia (1920). System of State Aid Roads as Approved Representing 4800 Miles of State Aid Roads Outside the Limits of the Incorporated Towns (PDF) (Map). Scale not given. Atlanta: State Highway Department of Georgia. Retrieved August 19, 2015.
- State Highway Department of Georgia (1921). System of State Roads (PDF) (Map). Scale not given. Atlanta: State Highway Department of Georgia. Retrieved August 19, 2015.
- State Highway Department of Georgia (October 1926). System of State Roads (PDF) (Map). Scale not given. Atlanta: State Highway Department of Georgia. Retrieved August 19, 2015.
- State Highway Department of Georgia (January 1, 1942). System of State Roads (PDF) (Map). Scale not given. Atlanta: State Highway Department of Georgia. OCLC 5673161. Retrieved August 19, 2015.
- State Highway Department of Georgia (January 1, 1943). System of State Roads (PDF) (Map). Scale not given. Atlanta: State Highway Department of Georgia. OCLC 5673161. Retrieved August 19, 2015.
- State Highway Department of Georgia (1954). State Highway System and Other Principal Connecting Roads (PDF) (Map). Scale not given. Atlanta: State Highway Department of Georgia. OCLC 5673161. Retrieved August 19, 2015. (Corrected to June 1, 1954.)
- State Highway Department of Georgia (1955). State Highway System and Other Principal Connecting Roads (PDF) (Map). Scale not given. Atlanta: State Highway Department of Georgia. OCLC 5673161. Retrieved August 19, 2015. (Corrected to June 1, 1955.)
- State Highway Department of Georgia (1957). State Highway System and Other Principal Connecting Roads (PDF) (Map). Scale not given. Atlanta: State Highway Department of Georgia. OCLC 5673161. Retrieved August 19, 2015. (Corrected to July 1, 1957.)
- State Highway Department of Georgia (1960). State Highway System and Other Principal Connecting Roads (PDF) (Map) (1960–1961 ed.). Scale not given. Atlanta: State Highway Department of Georgia. OCLC 5673161. Retrieved August 19, 2015. (Corrected to June 1, 1960.)
- State Highway Department of Georgia (1964). State Highway System (PDF) (Map). Scale not given. Atlanta: State Highway Department of Georgia. Archived from the original (PDF) on March 4, 2016. Retrieved August 19, 2015. (Corrected to June 1, 1963.)
- State Highway Department of Georgia (January 1966). Official Highway Map (PDF) (Map). Scale not given. Atlanta: State Highway Department of Georgia. Retrieved August 19, 2015.
- State Highway Department of Georgia (January 1967). Official Highway Map (PDF) (Map). Scale not given. Atlanta: State Highway Department of Georgia. Retrieved August 19, 2015.
