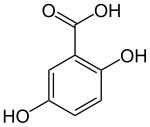
Gentisic acid
Gentisic acid is a dihydroxybenzoic acid. It is a derivative of benzoic acid and a minor (1%) product of the metabolic break down of aspirin, excreted by the kidneys.[2]
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid | |
| Other names
DHB 2,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid 5-Hydroxysalicylic acid Gentianic acid Carboxyhydroquinone 2,5-Dioxybenzoic Acid Hydroquinonecarboxylic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.017 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H6O4 | |
| Molar mass | 154.12 g/mol |
| Appearance | white to yellow powder |
| Melting point | 200 to 205 °C (392 to 401 °F; 473 to 478 K) (Sublimes) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
It is also found in the African tree Alchornea cordifolia and in wine.[3]
Production
Gentisic acid is produced by carboxylation of hydroquinone.[4]
- C6H4(OH)2 + CO2 → C6H3(CO2H)(OH)2
This conversion is an example of a Kolbe–Schmitt reaction.
Alternatively the compound can be synthesized from salicylic acid via Elbs persulfate oxidation.[5][6]
Reactions
In the presence of the enzyme gentisate 1,2-dioxygenase, gentisic acid reacts with oxygen to give maleylpyruvate:
- 2,5-dihydroxybenzoate + O2 maleylpyruvate
Applications
As a hydroquinone, gentisic acid is readily oxidised and is used as an antioxidant excipient in some pharmaceutical preparations.
In the laboratory, it is used as a sample matrix in matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) mass spectrometry,[7] and has been shown to conveniently detect peptides incorporating the boronic acid moiety by MALDI.[8]
References
- Gentisic acid - Compound Summary, PubChem.
- Levy, G; Tsuchiya, T (1972-09-31). "Salicylate accumulation kinetics in man". New England Journal of Medicine. 287 (9): 430–2. doi:10.1056/NEJM197208312870903. PMID 5044917. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - Comparison of Phenolic Acids and Flavan-3-ols During Wine Fermentation of Grapes with Different Harvest Times. Rong-Rong Tian, Qiu-Hong Pan, Ji-Cheng Zhan, Jing-Ming Li, Si-Bao Wan, Qing-Hua Zhang and Wei-Dong Huang, Molecules, 2009, 14, pages 827-838, doi:10.3390/molecules14020827
- Phillip M. Hudnall "Hydroquinone" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2002, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. 2005 Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a13_499.
- Behrman, E.J. (1988). Organic Reactions, Volume 35. New York: John Wiley & Sons Inc. p. 440. ISBN 978-0471832539.
- R. U. Schock Jr.; D. L. Tabern (1951). "The Persulfate Oxidation of Salicylic Acid. 2,3,5-Trihydroxybenzoic Acid". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 16 (11): 1772–1775. doi:10.1021/jo50005a018.
- Strupat K, Karas M, Hillenkamp F (1991). "2,5-Dihidroxybenzoic acid: a new matrix for laser desorption-ionization mass spectrometry". Int. J. Mass Spectrom. Ion Process. 72 (111): 89–102. Bibcode:1991IJMSI.111...89S. doi:10.1016/0168-1176(91)85050-V.
- Crumpton, J.; Zhang, W.; Santos, W. L. (2011). "Facile Analysis and Sequencing of Linear and Branched Peptide Boronic Acids by MALDI Mass Spectrometry". Analytical Chemistry. 83 (9): 3548–3554. doi:10.1021/ac2002565. PMC 3090651. PMID 21449540.