Furfuryl alcohol
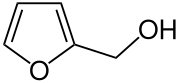
Furfuryl alcohol is an organic compound containing a furan substituted with a hydroxymethyl group. It is a colorless liquid, but aged samples appear amber. It possesses a faint odor of burning and a bitter taste. It is miscible with but unstable in water. It is soluble in common organic solvents.[4]
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(Furan-2-yl)methanol | |
| Other names
Furan-2-ylmethanol Furfuryl alcohol 2-Furanmethanol 2-Furancarbinol 2-(Hydroxymethyl)furan | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.388 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H6O2 | |
| Molar mass | 98.10 g/mol |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| Odor | burning odor[2] |
| Density | 1.128 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −29 °C (−20 °F; 244 K) |
| Boiling point | 170 °C (338 °F; 443 K) |
| miscible | |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | External MSDS |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | 65 °C; 149 °F; 338 K [2] |
| Explosive limits | 1.8% - 16.3%[2] |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LC50 (median concentration) |
397 ppm (mouse, 6 hr) 85 ppm (rat, 6 hr) 592 ppm (rat, 1 hr)[3] |
LCLo (lowest published) |
597 ppm (mouse, 6 hr)[3] |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible) |
TWA 50 ppm (200 mg/m3)[2] |
REL (Recommended) |
TWA 10 ppm (40 mg/m3) ST 15 ppm (60 mg/m3) [skin][2] |
IDLH (Immediate danger) |
75 ppm[2] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Synthesis
Furfuryl alcohol is manufactured industrially by hydrogenation of furfural, which is itself typically produced from waste bio-mass such as corncobs or sugar cane bagasse. As such furfuryl alcohol may be considered a green chemical.[5]
Reactions
It undergoes many reactions including Diels-Alder additions to electrophilic alkenes and alkynes. Hydroxymethylation gives 1,5-bis(hydroxymethyl)furan. Hydrolysis gives levulinic acid. Upon treatment with acids, heat and/or catalysts, furfuryl alcohol can be made to polymerize into a resin, poly(furfuryl alcohol). Hydrogenation of furfuryl alcohol can proceed to give hydroxymethyl derivative of tetrahydrofuran and 1,5-pentanediol. The etherification reaction of furfuryl alcohol with alkyl or aryl halide (e.g. benzyl chloride) in the liquid-liquid-liquid triphase system with the help of a phase transfer catalyst also reported. [6]
Applications
The primary use of furfuryl alcohol is as a monomer for the synthesis of furan resins.[4][7] These polymers are used in thermoset polymer matrix composites, cements, adhesives, coatings and casting/foundry resins. Polymerization involves an acid-catalyzed polycondensation, usually giving a black cross-linked product. A highly simplified representation is shown below.
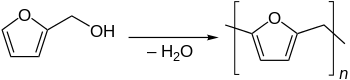
Craft uses
Furfuryl alcohol has been used in rocketry as a fuel which ignites hypergolically (immediately and energetically in contact) with white fuming nitric acid or red fuming nitric acid oxidizer.[8] The use of hypergolics avoids the need for an igniter. In late 2012, Spectra, a concept liquid rocket engine using white fuming nitric acid as the oxidizer to furfuryl alcohol fuel was static tested by Copenhagen Suborbitals.[9][10]
Because of its low molecular weight, furfuryl alcohol can impregnate the cells of wood, where it can be polymerized and bonded with the wood by heat, radiation, and/or catalysts or additional reactants. The treated wood has improved moisture-dimensional stability, hardness, and decay and insect resistance; catalysts can include zinc chloride, citric, and formic acid, as well as borates.[11][12]
Safety
The median lethal dose for furfuryl alcohol ranges from 160 to 400 mg/kg (mouse or rabbit, oral).
See also
- Furfurylamine - corresponding amine
- 2-Furonitrile - corresponding nitrile
- Furan-2-ylmethanethiol - corresponding thiol
- 2-Furoic acid - corresponding carboxylic acid
Further reading
- Choura, Mekki; Belgacem, Naceur M.; Gandini, Alessandro (January 1996). "Acid-Catalyzed Polycondensation of Furfuryl Alcohol: Mechanisms of Chromophore Formation and Cross-Linking". Macromolecules. 29 (11): 3839–3850. doi:10.1021/ma951522f.
References
- Merck Index, 11th Edition, 4215.
- NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0298". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- "Furfuryl alcohol". Immediately Dangerous to Life and Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- Hoydonckx, H. E.; Van Rhijn, W. M.; Van Rhijn, W.; De Vos, D. E.; Jacobs, P. A. "Furfural and Derivatives". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a12_119.pub2.
- Mariscal, R.; Maireles-Torres, P.; Ojeda, M.; Sádaba, I.; López Granados, M. (2016). "Furfural: a renewable and versatile platform molecule for the synthesis of chemicals and fuels" (PDF). Energy Environ. Sci. 9 (4): 1144–1189. doi:10.1039/C5EE02666K. hdl:10261/184700. ISSN 1754-5692.
- Katole DO, Yadav GD. Process intensification and waste minimization using liquid-liquid-liquid triphase transfer catalysis for the synthesis of 2-((benzyloxy)methyl)furan. Molecular Catalysis 2019;466:112–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcat.2019.01.004
- Brydson, J. A. (1999). "Furan Resins". In J. A. Brydson (ed.). Plastics Materials (Seventh Edition). Oxford: Butterworth-Heinemann. pp. 810–813. doi:10.1016/B978-075064132-6/50069-3. ISBN 9780750641326.
- MUNJAL, N. L. (May 1970). "Ignition catalysts for furfuryl alcohol - Red fuming nitric acid bipropellant". AIAA Journal. 8 (5): 980–981. doi:10.2514/3.5816.
- Madsen, Peter. "Spectra-testen". Archived from the original on September 12, 2012. Retrieved September 10, 2012.
- "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-03-17. Retrieved 2013-05-01.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) The Spectra engine test report pdf
- Alfred J., Stamm (1977). "Chapter 9". Wood Technology: Chemical Aspects. ACS Symposium Series. 43. Washington: American Chemical Society. pp. 141–149. doi:10.1021/bk-1977-0043.ch009. ISBN 9780841203730.
- Baysal, Ergun; Ozaki, S.Kiyoka; Yalinkilic, MustafaKemal (21 August 2004). "Dimensional stabilization of wood treated with furfuryl alcohol catalysed by borates". Wood Science and Technology. doi:10.1007/s00226-004-0248-2.
