French ship Algésiras (1855)
Algésiras was a second-rank, 90-gun, steam-powered ship of the line built for the French Navy in the 1850s, lead ship of her class of five ships. The ship participated in the Second Italian War of Independence in 1859.
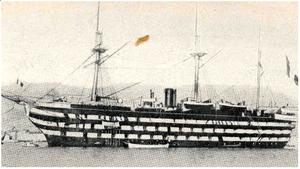 Algésiras used as a school ship | |
| History | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Algésiras |
| Namesake: | Battle of Algeciras |
| Ordered: | 13 November 1852 |
| Builder: | Arsenal de Toulon |
| Laid down: | April 1853 |
| Launched: | 4 October 1855 |
| Completed: | May 1856 |
| Commissioned: | 10 April 1856 |
| Decommissioned: | 10 February 1865 |
| Reclassified: |
|
| Stricken: | 20 November 1901 |
| Fate: | Destroyed by fire, 25 November 1906 |
| General characteristics (as built) | |
| Class and type: | Algésiras-class ship of the line |
| Displacement: | 5,121 t (5,040 long tons) |
| Length: | 71.23 m (233 ft 8 in) (waterline) |
| Beam: | 16.8 m (55 ft 1 in) |
| Draught: | 8.45 m (27 ft 9 in) (full load) |
| Depth of hold: | 8.16 m (26 ft 9 in) |
| Installed power: | 8 boilers; 2,057 ihp (1,534 kW) |
| Propulsion: | 1 screw; 2 horizontal-return connecting-rod steam engines |
| Sail plan: | Ship rigged |
| Speed: | 12 knots (22 km/h; 14 mph) |
| Complement: | 913 |
| Armament: |
|
Description
The Algésiras-class ships were repeats of the pioneering ship of the line Napoléon and were also designed by naval architect Henri Dupuy de Lôme. They had a length at the waterline of 71.23 metres (233 ft 8 in), a beam of 16.8 metres (55 ft 1 in) and a depth of hold of 8.16 metres (26 ft 9 in). The ships displaced 5,121 tonnes (5,040 long tons) and had a draught of 8.45 metres (27 ft 9 in) at deep load. Their crew numbered 913 officers and ratings.[1]
The primary difference between Napoléon and the Algésiras class was that the boilers of the latter ships were moved forward of the engines. They were powered by a pair of two-cylinder horizontal-return connecting-rod steam engines, also designed by Dupuy de Lôme, that drove the single propeller shaft using steam provided by eight boilers. The engines were rated at 900 nominal horsepower and produced 2,057 indicated horsepower (2,086 PS; 1,534 kW). During her sea trials, Algésiras reached a sustained speed of 13 knots (24 km/h; 15 mph). The ships were fitted with three masts and ship rigged.[1]
The armament of the Algésiras-class ships consisted of eighteen 36-pounder (174.8 mm (6.9 in)) smoothbore cannon and sixteen 223.3 mm (8.8 in) Paixhans guns on the lower gundeck and thirty-four 30-pounder 164.7 mm (6.5 in) cannon on the upper gundeck. On the quarterdeck and forecastle were twenty 163 mm (6.4 in) Paixhans guns and a pair of 163 mm rifled muzzle-loading guns.[1]
Career
In 1859, she took part in the blockade of Venice and various operations in the Mediterranean during the Second Italian War of Independence.[2]
She was decommissioned in 1865 and used as a transport. She was later used as a school ship.[2]
On 25 November 1906, she was destroyed in Toulon by an accidental fire.[2]
Citations
- Winfield & Roberts, p. 70
- Roche, I, p. 34
References
- Roche, Jean-Michel (2005). Dictionnaire des bâtiments de la flotte de guerre française de Colbert à nos jours. Tome I: 1671–1870. ISBN 978-2-9525917-0-6. OCLC 165892922.
- Winfield, Rif & Roberts, Stephen S. (2015). French Warships in the Age of Sail 1786–1861: Design, Construction, Careers and Fates. Barnsley, UK: Seaforth Publishing. ISBN 978-1-84832-204-2.