Fraxinus caroliniana
Fraxinus caroliniana, the pop ash, Florida ash, swamp ash, Carolina ash, or water ash, is a species of ash tree native from Cuba through the subtropical southeastern United States from southern Virginia to Texas. It was originally described by the botanist Philip Miller. It is a small tree about 40 ft. Leaves are compound, opposite, 7–12 in long, leaflets 5–7 in, ovate to oblong, coarsely serrate or entire, 3–6 in long, 2–3 in wide. Fruit is frequently 3-winged (samara) with flat seed portion; seed sometimes a bright violet color. It is the smallest of eastern North American ash species, wood light, soft, weak, 22 lbs./cu.ft. Typical to coastal swamps and subtropical lowlands.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Fraxinus caroliniana. |
| Fraxinus caroliniana | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Asterids |
| Order: | Lamiales |
| Family: | Oleaceae |
| Genus: | Fraxinus |
| Section: | Fraxinus sect. Melioides |
| Species: | F. caroliniana |
| Binomial name | |
| Fraxinus caroliniana | |
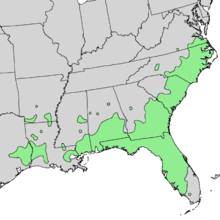 | |
| Natural range of Fraxinus caroliniana | |
References
- Jerome, D., Westwood, M., Oldfield, S. & Romero-Severson (2016). "Fraxinus caroliniana ". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016. Retrieved 14 September 2017.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link) CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
