Firmicus (crater)
Firmicus is a lunar impact crater that lies in the eastern part of the Moon's near side, so that from Earth it appears oval in shape due to foreshortening. It is, however, very nearly circular. The crater is located to the west of the Mare Undarum, and northeast of the similar-sized crater Apollonius. To the north of Firmicus are the craters van Albada and Auzout. Attached to its northwest rim is the Lacus Perseverantiae, a miniature lunar mare.
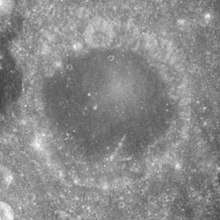 The Firmicus crater as seen from the Apollo 17 CSM | |
| Coordinates | 7.3°N 63.4°E |
|---|---|
| Diameter | 56 km |
| Depth | 1.5 km |
| Colongitude | 297° at sunrise |
| Eponym | Julius Firmicus Maternus |
The crater is named after 4th century Roman astrologer Julius Firmicus Maternus.[1] The name was formally adopted by the IAU in 1935.
The most notable aspect of Firmicus is the dark, flat floor. It has a similar albedo to the surface of Mare Crisium to the north, making it stand out somewhat from its surroundings. The floor has suffered no significant impacts since it was created, although there are undoubtedly many minor impacts across its surface. The outer rim of Firmicus has undergone some erosion, particularly along the northern rim where it is overlain by a pair of small craterlets.
Satellite craters

By convention these features are identified on lunar maps by placing the letter on the side of the crater midpoint that is closest to Firmicus.

| Firmicus | Latitude | Longitude | Diameter |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 6.4° N | 65.1° E | 8 km |
| B | 7.3° N | 65.8° E | 14 km |
| C | 7.7° N | 66.5° E | 13 km |
| D | 5.9° N | 64.4° E | 11 km |
| E | 8.0° N | 63.6° E | 9 km |
| F | 6.5° N | 61.8° E | 9 km |
| G | 6.9° N | 61.9° E | 9 km |
| H | 7.5° N | 60.3° E | 7 km |
| M | 4.1° N | 67.2° E | 42 km |
_2.png) Firmicus C is a concentric crater
Firmicus C is a concentric crater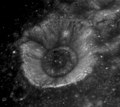 Oblique view of Firmicus C from Apollo 17
Oblique view of Firmicus C from Apollo 17
References
- "Firmicus (crater)". Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature. USGS Astrogeology Research Program.
- Andersson, L. E.; Whitaker, E. A. (1982). NASA Catalogue of Lunar Nomenclature. NASA RP-1097.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Bussey, B.; Spudis, P. (2004). The Clementine Atlas of the Moon. New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-81528-4.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Cocks, Elijah E.; Cocks, Josiah C. (1995). Who's Who on the Moon: A Biographical Dictionary of Lunar Nomenclature. Tudor Publishers. ISBN 978-0-936389-27-1.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- McDowell, Jonathan (July 15, 2007). "Lunar Nomenclature". Jonathan's Space Report. Retrieved 2007-10-24.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Menzel, D. H.; Minnaert, M.; Levin, B.; Dollfus, A.; Bell, B. (1971). "Report on Lunar Nomenclature by the Working Group of Commission 17 of the IAU". Space Science Reviews. 12 (2): 136–186. Bibcode:1971SSRv...12..136M. doi:10.1007/BF00171763.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Moore, Patrick (2001). On the Moon. Sterling Publishing Co. ISBN 978-0-304-35469-6.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Price, Fred W. (1988). The Moon Observer's Handbook. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-33500-3.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Rükl, Antonín (1990). Atlas of the Moon. Kalmbach Books. ISBN 978-0-913135-17-4.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Webb, Rev. T. W. (1962). Celestial Objects for Common Telescopes (6th revised ed.). Dover. ISBN 978-0-486-20917-3.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Whitaker, Ewen A. (1999). Mapping and Naming the Moon. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-62248-6.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Wlasuk, Peter T. (2000). Observing the Moon. Springer. ISBN 978-1-85233-193-1.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Firmicus (crater). |
- LTO-62C1 Firmicus — L&PI topographic map
