Ferrate
Ferrate loosely refers to a material that can be viewed as containing anionic iron complexes. Examples include tetrachloroferrate ([FeCl4]2−), oxyanions (FeO42-), tetracarbonylferrate ([Fe(CO)4]2-), the organoferrates.[1] The term ferrate derives from the Latin word for iron, ferrum.
- Ferrates
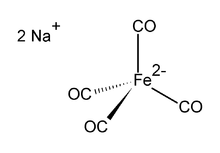 Disodium salt of tetracarbonylferrate.
Disodium salt of tetracarbonylferrate.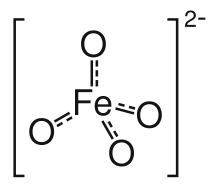 Structure of [FeO4]2-.
Structure of [FeO4]2-.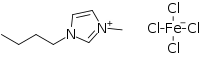 1-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium salt of [FeCl4]−.
1-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium salt of [FeCl4]−.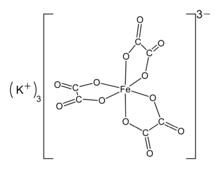 Potassium tris(oxalato)ferrate.
Potassium tris(oxalato)ferrate.
References
- Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.