Eysturoy
Eysturoy (pronounced ['estroi]) (Danish: Østerø) meaning 'East Island' is a region and the second-largest of the Faroe Islands in the North Atlantic, both in size and population.
Eysturoy Østerø | |
|---|---|
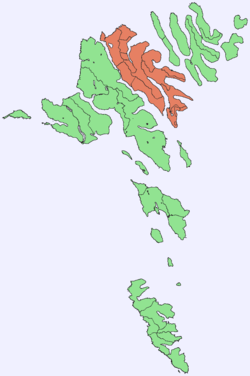 Location within the Faroe Islands | |
| Coordinates: 62°13′N 6°53′W | |
| State | Kingdom of Denmark |
| Constituent country | Faroe Islands |
| Region | Eysturoy |
| Area | |
| • Total | 286.3 km2 (110.5 sq mi) |
| Area rank | 2 |
| Population (12-2018) | |
| • Total | 11,490[1] |
| • Rank | 2 |
| Time zone | UTC+0 (GMT) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+1 (EST) |
| Calling code | 298590683 |
Description
Eysturoy is separated by a narrow sound from the main island of Streymoy. Eysturoy is extremely rugged, with some 66 separate mountain peaks, including Slættaratindur, the highest peak in the archipelago at 2,890 feet (880 metres). Important settlements on Eysturoy are Fuglafjørður in the north and the densely populated area of the municipalities of Runavík and Nes in the south.
Eysturoy is connected with Streymoy by the Streymin Bridge over the sound. The islanders humorously refer to this bridge as the only bridge over the Atlantic. (The natives of the Scottish island of Seil make the same claim, as do the people of Great Bernera in Na h-Eileanan Siar). Leirvík on the east coast of the island is the gateway for transport connections to the north-eastern islands, particularly Klaksvík on the island of Borðoy, which is the Faroes' second-largest town. In December 2020, the sub-sea Eysturoy Tunnel is due to open, creating a direct link between Runavík, Strendur and Tórshavn, and making southern Eysturoy a central place on the Tórshavn-Klaksvík axis.
Sites of interest on Eysturoy include the villages of Eiði and Gjógv, the latter having a small natural port in a rock column; the Blásastova historical museum in the village of Gøta; and the varmakelda (thermal springs) of Fuglafjørður, which indicate the volcanic origin of the archipelago. Off the northern tip of the island are the basalt sea stacks Risin og Kellingin.
The town of Glyvrar on the eastern coast of Eysturoy is the home-base for Bakkafrost, the largest company in the Faeroe Islands. Bakkafrost is the eighth-largest fishing company worldwide.[2]
Important Bird Area
The north, north-east, and south-east coasts of the island have been identified as an Important Bird Area by BirdLife International because of their significance as seabird breeding sites, especially for Manx shearwaters (2500 pairs), European storm petrels (500 pairs) and black guillemots (300 pairs).[3]
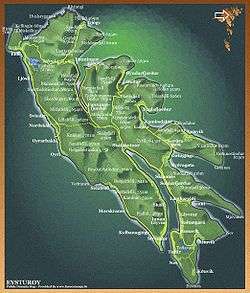 Map of Eysturoy |
 Gjógv harbour |
References
- Statistical Database
- "portal.fo - Føroysk alifyritøka er áttinda størst í heiminum". Archived from the original on 2015-10-29. Retrieved 2018-11-23.
- BirdLife International. (2012). Important Bird Areas factsheet: Eysturoy. Downloaded from "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2007-07-10. Retrieved 2012-11-14.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) on 2012-02-22.
Further reading
- Viderö, Kristian Osvald. Saga Eysturoyar. Tórshavn: Bókagarður, 1994.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Eysturoy. |
| Look up Eysturoy in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |

- Personal website with 15 aerial photos of Eysturoy
