Extreme weather events in Melbourne
Extreme weather events in Melbourne, Australia have occurred on multiple occasions. The city has experienced a number of highly unusual weather events and extremes of weather. An increase in heat waves and record breaking temperatures in the 21st century has led to much discussion over the effects of climate change in the country.[1][2]
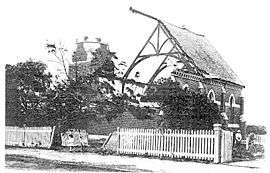
A church destroyed by the 1918 Brighton tornado

Flash flooding in the intersection of Flinders and Spencer Streets during the 2010 Melbourne thunderstorm.
List of weather events
- 31 August 1849 – A snowstorm blankets Melbourne for the first and last time in history (with accumulation on the streets).[3]
- 1863 – A major flood puts Port Melbourne underwater leaving thousands homeless across the city and drowning one man at Princes Bridge.[4]
- 26 July 1882 – Snow falls for half an hour in Melbourne.[5]
- 1882 – Elizabeth Street in Melbourne is flooded.
- 1880 – The great flood causes the Yarra River to swell to 305 metres (1,001 ft) in width.[6] The most significant flood in Melbourne's recorded history, it forces thousands to vacate their homes and causes at least one death.
- 1908 – A heatwave strikes Melbourne.[7][8]
- 2 February 1918 – The Brighton tornado, an F3 class and the most intense tornado to hit a major Australian city, strikes the bayside suburb of Brighton.[9]
- 29 November to 1 December 1934 – Torrential rainfall of up to 350 mm causes the Yarra River to become a raging torrent. Extensive damage with 35 dead, 250 injured, and 3,000 homeless.[10][11][12][13]
- 13 January 1939 – Melbourne experiences its second-hottest temperature on record, 45.6 °C (114.1 °F), during a four-day nationwide heat wave in which the Black Friday bushfires destroy townships that are now Melbourne suburbs.[14]
- 1951 – A moderate cover of snow blankets the central business district (CBD) and suburbs.[15][16]
- 3 December 1954 – Record rainfall causes flooding in Elwood and Flemington with homes evacuated. Train lines are closed by landslides, basement level shops are flooded, and events are cancelled.[17]
- February 1972 – Elizabeth Street is flooded after 75mm of rain in 17 minutes, with dramatic pictures of cars floating and underwater in the central city.[18][19]
- 7 April 1977 – Laverton smashed by 12 hour thunderstorm and breaks several Victorian rainfall records including most rainfall; in 2 hours (105mm), in 3 hours (137mm) and in 4 hours (153mm).[20][21]
- 8 February 1983 – The city is enveloped by a massive dust storm that "turned day into night".
- 16 February 1983 – Melbourne is encircled by an arc of fire as the Ash Wednesday fires encroach on the city.
- 18 September 1984 – Storm causes flooding of 100 homes in the eastern suburbs.[22]
- December 1990 – Heatwave causes 4 deaths.[23]
- 26 December 1999 – Flash flooding damages 300 homes with the worst effect on Broadmeadows.
- December 2003 – Freak storms
- February 2005 – Freak storms[24][25][26]
- January 2009 – A heatwave results in a record three successive days over 43 °C (109 °F).[27] This is closely followed by Melbourne's hottest day on record on 7 February, when the temperature reaches 46.4 °C (115.5 °F) in the CBD. This same heatwave triggers the Black Saturday bushfires, the worst in Australian history.[28]
- 6 March 2010 – Storms pass directly over Melbourne bringing large hail, flash flooding and high winds, causing widespread damage across western and central Victoria, stopping all modes of transportation in Melbourne. CBD streets of Flinders, Spencer and Elizabeth are spectacularly flash flooded.
- 4 February 2011 – Severe rainstorm causes flash flooding in parts of Melbourne.[29]
- 10 November 2011 – Severe storm causes flash flooding in Croydon and Frankston.[30]
- 25 December 2011 – Severe thunderstorms, large hailstones, flash flooding, and reports of tornadoes cause major damage to houses and vehicles in the worst-hit areas of Fiskville, Melton, Taylors Lakes, and Keilor Downs.[31]
- 4–12 March 2013 – Melbourne faces a 10-day heatwave.[32]
- 31 May 2013 – Melbourne faces heavy rain and thunderstorms; Melbourne Airport records 10mm of rain in 10 minutes just after 9 p.m.
- 18 July 2013 – Melbourne records the highest July temperature ever, reaching 23.3 °C (73.9 °F).
- 14–17 January 2014 – Melbourne records four consecutive days of temperatures exceeding 41 °C (106 °F), two of which exceed 43 °C (109 °F).[33][34]
- 21 November 2016 – Thunderstorm asthma kills 9 and hospitalises hundreds, high heat and humidity cause thunderstorms to form northwest of the city, due to excessive grass growth in the north and west of Melbourne these storms send pollen into Melbourne and its suburbs raising pollen counts and triggering thousands of severe asthma attacks. The massive number of attacks overloaded emergency services and contributed to the fatalities.[35][36][37]
- 14 December 2018 - Flash flooding with roughly 30 mm of rain falling within 15 minutes before 5:45 p.m, during rush hour, flooding roads in inner Melbourne along with other various suburbs while shutting down most tram lines and train lines in Melbourne's East[38][39]
- 4 August 2020 - A cold front brings snow down to as low as 150 meters above sea level around midday, resulting in rare light dustings in many of Melbourne's suburbs, most noteably in its north western suburbs Craigieburn, Sunbury, Wallan (amongst others). These suburbs had not received snow in decades. Snow was also recorded on the higher levels of Melbourne CBD highrises. [40]
Highest and lowest temperatures
Candles suffering the effects of Melbourne's hottest recorded temperature of 46.4 °C (115.5 °F) on 7 February 2009
Many of the hottest days recorded in Melbourne occurred during major heatwaves which precipitated large firestorms:
- 47.2 °C (117.0 °F) (Anecdotal) – 6 February 1851 (Black Thursday)[41]
- 46.4 °C (115.5 °F) – 7 February 2009 (Black Saturday)
- 45.6 °C (114.1 °F) – 13 January 1939 (Black Friday)
Melbourne's coldest temperature ever was −2.8 °C (27.0 °F) on 21 July 1869.[42]
gollark: Great!
gollark: I "note" things by having an open tab for it.
gollark: 20 tabs? Weak.
gollark: I don't think they can actually void the warranty for using custom firmware, in good™ countries.
gollark: Redesign it better.
See also
References
- "Melbourne: City of woes". The Age. 2 September 2003. Retrieved 2009-03-19.
- "Australia's 2014 summer breaks 156 heat records with climate change". IndyMedia. Retrieved 31 March 2014.
- "Climate – Entry – eMelbourne – The Encyclopedia of Melbourne Online". emelbourne.net.au.
- The Argus. 28 December 1863
- "The Weather. Snow Storms". The Argus (Melbourne, Vic. : 1848 – 1956). Melbourne, Vic.: National Library of Australia. 27 July 1882. p. 9. Retrieved 13 January 2016.
- "Melbourne: City of woes". theage.com.au.
- "Melbourne faces worst hot spell in 100 years". The Age.
- "The Age – Google News Archive Search". google.com.
- Wallace, Catherine (21 June 2018). "The Brighton Cyclone: A Century On". Brighton Historical Society Journal (183). Retrieved 4 July 2019.
- National Climate Centre. "BOM – Australian Climate Extremes-Flood". nla.gov.au. Archived from the original on 2009-03-17.
- "Southern Vic: Floods (incl Yarra River)". Ema.gov.au. 25 July 2003. Archived from the original on 27 May 2012. Retrieved 5 October 2010.
- "Is this our gift to future generations?". theage.com.au.
- On the edge of a cyclone
- "Record heat and stupidity as Melbourne swelters". The Age. 25 January 2003. Retrieved 2009-03-19.
- Low-level Snow, Bureau of Meteorology, archived from the original on 17 March 2009, retrieved 2010-11-28
- The day it snowed in Burwood, Burwood Bulletin, retrieved 2010-11-28
- "Heaviest Deluge in City's History". The Age (Melbourne, Vic. : 1854 – 1954). Melbourne, Vic.: National Library of Australia. 4 December 1954. p. 1. Retrieved 30 October 2015.
- "Melbourne: City of woes". The Age. Melbourne. 2 September 2003.
- "Melbourne Awash!!", TMSV Running Journal, archived from the original on 2011-02-20, retrieved 2010-11-28
- "BOM – Australia's Record Rainfall".
- "BOM – The Estimation of Probable Maximum Precipitation in Australia" (PDF).
- Melbourne floods hit 100 homes, The Sydney Morning Herald – Sep 19, 1984
- "Melbourne, Vic: Heatwave" Archived February 5, 2012, at the Wayback Machine. Ema.gov.au. 25 July 2003. Retrieved 5 October 2010.
- "Wild weather hits". theage.com.au.
- "Melbourne has never seen anything like it". theage.com.au.
- "Storm damage bill could be $100m". theage.com.au.
- "Melbourne braces for heatwave". The Guardian. 17 December 2015. Retrieved 2016-01-13.
- Hamish Townsend (7 February 2009). "City Swelters, records tumble in heat". The Age. Melbourne. Retrieved 2009-03-19.
- "Severe Storm – Melbourne, Victoria Feb 2011". Australian Emergency Management Knowledge Hub.
- "Emergency services clean up after storms lash Victoria, South Australia". AAP. 10 November 2011.
- "Tornado, hail as storms lash Melbourne". The Age. Melbourne. 25 December 2011.
- "Melbourne faces 10-day heatwave". The Age. Melbourne. March 6, 2013.
- "Melbourne records heatwave not seen for 100 years". ABC. Retrieved 19 January 2014.
- "Melbourne, Victoria January 2014 Daily Weather Observations". Bureau of Meteorology. Archived from the original on 2014-01-06.
- Wood, Stephanie (2017-03-10). "Thunderstorm asthma: the night a deadly storm took Melbourne's breath away". The Sydney Morning Herald. Retrieved 2017-03-19.
- "Emergency chiefs did not understand Melbourne's asthma storm, review finds". ABC News. 2017-02-01. Retrieved 2017-03-19.
- "Explainer: What is thunderstorm asthma?". News. Retrieved 2017-03-19.
- Oaten, James (15 Dec 2018). "Melbourne weather brings flash flooding to CBD and eastern suburbs as deluge dumped on city". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. Archived from the original on 28 April 2019.
- Travers, Brianna; Rose, Tasmin; Hosking, Wes (15 Dec 2018). "Melbourne and surrounding suburbs cop a soaking in peak-hour downpour". Herald Sun.
- https://www.theage.com.au/national/victoria/snow-in-melbourne-s-cbd-as-antarctic-blast-hits-victoria-20200805-p55in0.html
- "Black Thursday". The Argus (Melbourne, Vic. : 1848 – 1957). Melbourne, Vic.: National Library of Australia. 17 January 1857. p. 4. Retrieved 13 January 2016.
- "Climate statistics for Australian locations — Melbourne". Bureau of Meteorology. Retrieved 13 January 2016.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.