Ethionine
Ethionine is a non-proteinogenic amino acid structurally related to methionine, with an ethyl group in place of the methyl group.
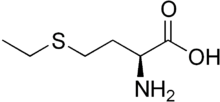 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-Amino-4-ethylsulfanylbutyric acid | |
| Other names
S-Ethyl-L-homocysteine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.588 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H13NO2S | |
| Molar mass | 163.239 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Ethionine is an antimetabolite and methionine antagonist. It prevents amino acid incorporation into proteins and interferes with cellular use of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Because of these pharmacological effects, ethionine is highly toxic and is a potent carcinogen.[1]
Ethionine has been found to naturally occur in the edible pulp of the durian fruit, and postulated to be a biosynthetic precursor for ethanethiol and other strong odorants found in the fruit.[2]
References
- Narayan Shivapurkar, Mary J. Wilson and Lionel A. Poirier (1984). "Hypomethylation of DNA in ethionine-fed rats". Carcinogenesis. 5 (8): 989–992. doi:10.1093/carcin/5.8.989. PMID 6744518.
- Nadine S. Fischer and Martin Steinhaus. "Identification of an Important Odorant Precursor in Durian: First Evidence of Ethionine in Plants". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.9b07065.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.