Erythema
Erythema (from the Greek erythros, meaning red) is redness of the skin or mucous membranes, caused by hyperemia (increased blood flow) in superficial capillaries.[1] It occurs with any skin injury, infection, or inflammation. Examples of erythema not associated with pathology include nervous blushes.[2].
| Erythema | |
|---|---|
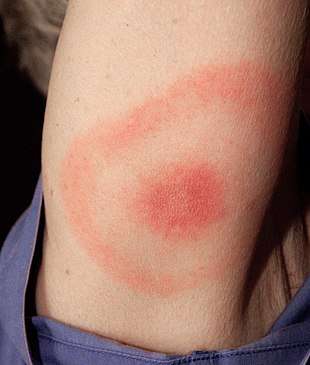 | |
| Characteristic "bull's eye" rash (erythema migrans) of early Lyme disease | |
| Specialty | Dermatology |
Causes
It can be caused by infection, massage, electrical treatment, acne medication, allergies, exercise, solar radiation (sunburn), photosensitization,[3] acute radiation syndrome, mercury toxicity, blister agents,[4] niacin administration,[5] or waxing and tweezing of the hairs—any of which can cause the capillaries to dilate, resulting in redness. Erythema is a common side effect of radiotherapy treatment due to patient exposure to ionizing radiation.
Diagnosis
Erythema disappears on finger pressure (blanching), while purpura or bleeding in the skin and pigmentation do not. There is no temperature elevation, unless it is associated with the dilation of arteries in the deeper layer of the skin.
Types
- Erythema ab igne
- Erythema chronicum migrans
- Erythema induratum
- Erythema infectiosum (or fifth disease)
- Erythema marginatum
- Erythema migrans
- Erythema multiforme (EM)
- Erythema nodosum
- Erythema toxicum
- Erythema elevatum diutinum
- Erythema gyratum repens
- Keratolytic winter erythema
- Palmar erythema
See also
- Flushing (physiology)
- List of cutaneous conditions
References
- Mosby's Medical Dictionary (9th ed.). St. Louis, Missouri: Elsevier. 2013. ISBN 978-0-323-08541-0.
- erythema, Mosby's Medical, Nursing & Allied Health Dictionary, Fourth Edition, Mosby-Year Book 1994, p. 570
- Jane C. Quinn; Yuchi Chen; Belinda Hackney; Muhammad Shoaib Tufail; Leslie A. Weston; Panayiotis Loukopoulos (2018), "Acute-onset high-morbidity primary photosensitisation in sheep associated with consumption of the Casbah and Mauro cultivars of the pasture legume biserrula", BMC Veterinary Research, doi:10.1186/s12917-017-1318-7
- https://fas.org/nuke/guide/usa/doctrine/army/mmcch/Vesicant.htm#CLINICAL Archived 2017-12-12 at the Wayback Machine EFFECTS
- Weterle R, Rybakowski J (Mar–Apr 1990). "Test niacynowy w schizofrenii" [The niacin test in schizophrenia]. Psychiatr Pol. 24 (2): 116–20. PMID 2084715.
External links
| Classification |
|---|
| Look up erythema in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Erythemas. |