Envelope detector
An envelope detector is an electronic circuit that takes a (relatively) high-frequency amplitude modulated signal as input and provides an output which is the envelope of the original signal.
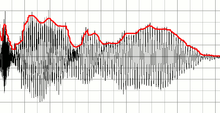
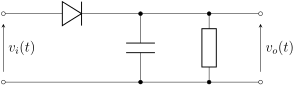
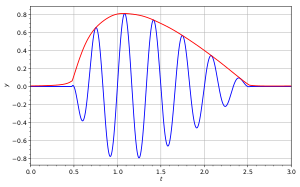
An envelope detector is sometimes called as a peak detector.
Circuit operation
The capacitor in the circuit above stores charge on the rising edge and releases it slowly through the resistor when the input signal amplitude falls. The diode in series rectifies the incoming signal, allowing current flow only when the positive input terminal is at a higher potential than the negative input terminal.
General considerations
Most practical envelope detectors use either half-wave or full-wave rectification of the signal to convert the AC audio input into a pulsed DC signal. Filtering is then used to smooth the final result. This filtering is rarely perfect and some "ripple" is likely to remain on the envelope follower output, particularly for low frequency inputs such as notes from a bass instrument. Reducing the filter cutoff frequency gives a smoother output, but decreases the high frequency response. Therefore, practical designs must reach a compromise.
Definition of the envelope
Any AM or FM signal can be written in the following form
In the case of AM, φ(t) (the phase component of the signal) is constant and can be ignored. In AM, the carrier frequency is also constant. Thus, all the information in the AM signal is in R(t). R(t) is called the envelope of the signal. Hence an AM signal is given by the function
with m(t) representing the original audio frequency message, C the carrier amplitude and R(t) equal to C + m(t). So, if the envelope of the AM signal can be extracted, the original message can be recovered.
In the case of FM, the transmitted has a constant envelope R(t) = R and can be ignored. However, many FM receivers measure the envelope anyway for received signal strength indication.
Diode detector
The simplest form of envelope detector is the diode detector which is shown above. A diode detector is simply a diode between the input and output of a circuit, connected to a resistor and capacitor in parallel from the output of the circuit to the ground. If the resistor and capacitor are correctly chosen, the output of this circuit should approximate a voltage-shifted version of the original (baseband) signal. A simple filter can then be applied to filter out the DC component.
Precision detector
An envelope detector can also be constructed using a precision rectifier feeding into a low-pass filter.
Drawbacks
The envelope detector has several drawbacks:
- The input to the detector must be band-pass filtered around the desired signal, or else the detector will simultaneously demodulate several signals. The filtering can be done with a tunable filter or, more practically, a superheterodyne receiver
- It is more susceptible to noise than a product detector
- If the signal is overmodulated, distortion will occur
Most of these drawbacks are relatively minor and are usually acceptable tradeoffs for the simplicity and low cost of using an envelope detector.
Demodulation of signals
An envelope detector can be used to demodulate a previously modulated signal by removing all high frequency components of the signal. The capacitor and resistor form a low-pass filter to filter out the carrier frequency. Such a device is often used to demodulate AM radio signals because the envelope of the modulated signal is equivalent to the baseband signal.
Audio
An envelope detector is sometimes referred to as an envelope follower in musical environments. It is still used to detect the amplitude variations of an incoming signal to produce a control signal that resembles those variations. However, in this case the input signal is made up of audible frequencies.
Envelope detectors are often a component of other circuits, such as a compressor or an auto-wah or envelope-followed filter. In these circuits, the envelope follower is part of what is known as the "side chain", a circuit which describes some characteristic of the input, in this case its volume.
Both expanders and compressors use the envelope's output voltage to control the gain of an amplifier. Auto-wah uses the voltage to control the cutoff frequency of a filter. The voltage-controlled filter of an analog synthesizer is a similar circuit.
Modern envelope followers can be implemented:
- directly as electronic hardware,
- or as software using either a digital signal processor (DSP) or
- on a general purpose CPU.
See also
- Analytic signal
- Attack-decay-sustain-release envelope