Endolymphatic duct
From the posterior wall of the saccule a canal, the endolymphatic duct, is given off; this duct is joined by the ductus utriculosaccularis, and then passes along the aquaeductus vestibuli and ends in a blind pouch (endolymphatic sac) on the posterior surface of the petrous portion of the temporal bone, where it is in contact with the dura mater.
| Endolymphatic duct | |
|---|---|
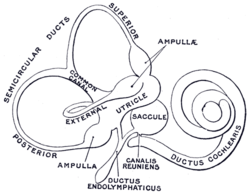 The membranous labyrinth. (Ductus endolymphaticus labeled at bottom center.) | |
 Endolymphatic duct is #6, and is labeled at top center. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | ductus endolymphaticus |
| MeSH | D004711 |
| TA | A15.3.03.079 |
| FMA | 61246 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Disorders of the endolymphatic duct include Meniere's Disease and Enlarged Vestibular Aqueduct.
Additional images
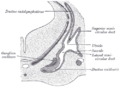 Transverse section through head of fetal sheep, in the region of the labyrinth. X 30.
Transverse section through head of fetal sheep, in the region of the labyrinth. X 30.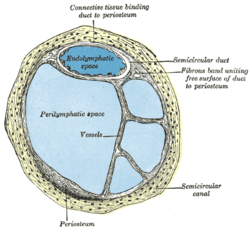 Transverse section of a human semicircular canal and duct
Transverse section of a human semicircular canal and duct
gollark: Binary search trees of (codepoint, index in string).
gollark: Heat-death-of-the-universe terminated strings?
gollark: That would work, I can reuse the LTS code.
gollark: Yes.
gollark: I do have this, although I'm not convinced that vectorized bubblesort and 32-way mergesort was the right way to go.
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1052 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.