Elamipretide
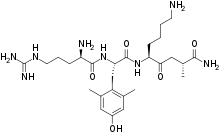
Elamipretide (also known as SS-31, , MTP-131 and Bendavia)[1][2] is a small mitochondrially-targeted tetrapeptide (D-Arg-dimethylTyr-Lys-Phe-NH2) that appears to reduce the production of toxic reactive oxygen species and stabilize cardiolipin.[3]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | H-D-Arg-Tyr(2,6-diMe)-Lys-Phe-NH2; D-Arginyl-2,6-dimethyl-L-tyrosyl-L-lysyl-L-phenylalaninamide |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C32H49N9O5 |
| Molar mass | 639.802 g·mol−1 |
| |
Stealth Peptides, a privately held company, was founded in 2006 to develop intellectual property licensed from several universities including elamipretide; it subsequently changed its name to Stealth BioTherapeutics.[4][5]
As of November 2017 Stealth had obtained an orphan designation in the US for use in mitochondrial myopathy and had started a Phase III trial in that indication.[2] As of January 2020, trial expectations were not met.[6]
References
- "Recommended INN List 75" (PDF). WHO Drug Information. 30 (1): 111. 2016.
- "Elamipretide". AdisInsight. Retrieved 29 November 2017.
- Kloner RA, Shi J, Dai W (February 2015). "New therapies for reducing post-myocardial left ventricular remodeling". Annals of Translational Medicine. 3 (2): 20. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2305-5839.2015.01.13. PMC 4322169. PMID 25738140.
- Valigra L (April 9, 2012). "Stealth Peptides sees positive results from Bendavia". Boston Business Journal.
- Dolgin E (11 February 2016). "New drugs offer hope for mitochondrial disease". STAT.
- PhD, Alberto Molano (2020-01-10). "Elamipretide Failed to Meet Promise of Earlier Trial Results for..." Mitochondrial Disease News. Retrieved 2020-02-24.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.