Egleston station
Egleston was a rapid transit station in Boston, Massachusetts. It served the Washington Street Elevated, part of the MBTA's Orange Line. It was located over Egleston Square at the intersection of Washington Street and Columbus Avenue in the Roxbury neighborhood. The station opened in November 1909, and was closed in April 1987 when the Orange Line was rerouted to the west along the Southwest Corridor.
Egleston | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Egleston station in October 1908, a year before opening | |||||||||||
| Location | Washington Street at Columbus Avenue Boston, Massachusetts | ||||||||||
| Coordinates | 42°18′57.26″N 71°5′53.53″W | ||||||||||
| Owned by | Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority | ||||||||||
| Line(s) | Washington Street Elevated | ||||||||||
| Platforms | 2 side platforms | ||||||||||
| Tracks | 2 | ||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||
| Opened | November 22, 1909[1]:291 | ||||||||||
| Closed | April 30, 1987[1]:326 | ||||||||||
| Services | |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
History
Construction

The Boston Elevated Railway constructed the Washington Street Elevated from downtown Boston to Dudley Square in 1901; an extension to Forest Hills was approved on January 4, 1904 and began construction on May 2, 1906.[2]:A1-A2 Construction of the elevated structure proceeded southbound and reached Egleston Square on August 20, 1906, although construction on the station did not start until 1907 because of delays in the design.[2]:34, A2 The extension opened on November 22, 1909 with Egleston as the sole new intermediate station; Green Street to the south was added as an infill station in 1912.[1]:291
Architecture
The architectural design of the station was similar to the earlier stations designed by A.W. Longfellow Jr. at Dover and Northampton, with most exterior surfaces sheathed in copper, although it is not believed that Longfellow designed the station.[2]:45–46 Its structural design incorporated improvements over the older stations, including the first use of reinforced concrete on the Elevated. The waiting room was suspended below the steel elevated structure, which allowed it to be larger than the between-the-tracks waiting rooms at Dover and Northampton. Anticipating use of eight-car trains due to higher than expected ridership, the station was built with 350-foot (110 m) side platforms rather than a 160-foot (49 m) island platform.[2]:45–46
Transfer station
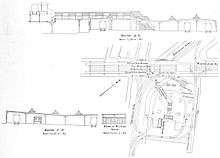
Egleston was intended to serve as a transfer point for surface streetcar lines from Jamaica Plain and Dorchester in order to divert traffic from overcrowded Dudley station.[2]:37 The staircases from the station waiting room originally led directly into Egleston Square itself (on the northwest side of Washington Street between Columbus Avenue and Atherton Street) and into the median of Washington Street, which required many streetcar passengers to cross lanes of traffic to reach the station.[2]:37 In response to continued streetcar crowding at Dudley, the BERy built an off-street prepayment transfer station on the east side of the intersection, with an escalator and connecting bridge directly to the waiting room.[3][4] The transfer station and bridge were constructed in 1916 and opened on January 20, 1918.[2]:A2[5]
Closure
%2C_circa_1940s.jpg)
Streetcar service continued for several decades before bustitution; route 42 to Dudley was converted in September 1949, route 29 to Mattapan in September 1955, and route 40 to Arborway in December 1955.[1]:34, 42 Route 43 – the last streetcar route into the Tremont Street subway via the Pleasant Street incline – was cut back from Egleston to Lenox Street in June 1956, although bustitution of the remaining section did not occur until 1961 and 1962.[1]:43
From 1979 to 1987, the Southwest Corridor was reconstructed to include the Orange Line as well as commuter rail and intercity service. Egleston station and the rest of the Washington Street Elevated closed on April 30, 1987; the relocated Orange Line opened on May 4, 1987.[1]:326
References
- Belcher, Jonathan. "Changes to Transit Service in the MBTA district" (PDF). NETransit. Page numbers are accurate to the April 21, 2018 version.
- Zaitzevsky, Cynthia R. (July 1986). "Written Historical and Descriptive Data" (PDF). National Park Service / Historic American Engineering Record. Retrieved 26 June 2015.
- Cheney, Frank; Sammarco, Anthony M. (2000). When Boston Rode The El. Arcadia Publishing. pp. 109–118. ISBN 9780738504629.
- "Boston Profits By Elevated Railway Station Improvements". Electric Railway Journal. McGraw-Hill. 48 (7): 258–263. 12 August 1916 – via Internet Archive.
- Annual report of the directors of the Boston Elevated Railway Company. 2. Boston Elevated Railway. 1919. p. 14 – via Internet Archive.
External links
![]()