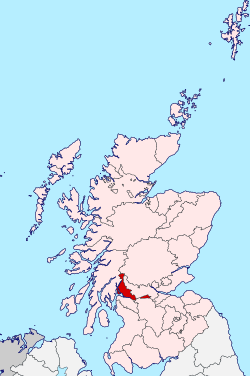
Dunbartonshire
Dunbartonshire (Scottish Gaelic: Siorrachd Dhùn Breatann[1]) or the County of Dumbarton is a historic county, lieutenancy area and registration county in the west central Lowlands of Scotland lying to the north of the River Clyde. Dunbartonshire borders Perthshire to the north, Stirlingshire to the east, Lanarkshire and Renfrewshire to the south, and Argyllshire to the west. The boundaries with Lanarkshire and Stirlingshire are split in two owing to the existence of an exclave around Cumbernauld (see below).
Dumbarton Siorrachd Dhùn Breatann | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Country | Scotland |
| County town | Dumbarton |
| Area | |
| • Total | 241 sq mi (624 km2) |
| Ranked 29th of 34 | |
| Chapman code | DNB |
Prior to 1975, the county was also used for local government with its own county council, its administrative centre being at the town of Dumbarton. Under the 1973 Local Government (Scotland) Act, the county council was abolished and administration was transferred to the newly formed Strathclyde council region. When Strathclyde was itself dissolved in 1996, the term "Dunbartonshire" resurfaced in local administration in the names of the new council areas of East Dunbartonshire and West Dunbartonshire. The two councils do not cover the entire area of the historic county, which also stretches into the Argyll and Bute and North Lanarkshire (which covers the county's large Cumbernauld exclave) council areas. The East Dunbartonshire council area also covers parts of the counties of Stirlingshire and Lanarkshire.
The area had previously been part of the historic district of Lennox, which was a duchy in the Peerage of Scotland related to the Duke of Lennox.
Name

Dumbarton comes from the Scottish Gaelic Dùn Breatainn meaning "fort of the Britons".[2]
Historically, the spelling of the county town and the county were not standardised. By the 18th century the names "County of Dunbarton" and "County of Dumbarton" were used interchangeably.[3]
Different county bodies used the two spellings: the Dunbarton County Constabulary were formed in 1857 by the Commissioners of Supply for the County of Dunbarton.[4]
Dumbartonshire County Council, set up under the Local Government (Scotland) Act 1889, adopted the spelling "Dunbartonshire" by 1914, a fact recognised by the Local Government (Scotland) Act 1947.[5][6]
The correct spelling remains a source of contention.
Council
In modern local government, the county is divided into two council areas of Scotland, namely :
- East Dunbartonshire, with its administrative headquarters at Kirkintilloch
- West Dunbartonshire, with its administrative centre at Dumbarton.
The administrative arm, but not the placename of county used for "local government" purposes was dis-established in 1975 by the Local Government (Scotland) Act 1973, when the Administrative Section became part of the large Council of Strathclyde Region.
Strathclyde was divided into nineteen districts, with the area being divided between Dumbarton, Bearsden and Milngavie, Clydebank, Cumbernauld and Kilsyth and Strathkelvin Districts, the latter also containing a small part of the former Lanarkshire.
The regional identity, the "place-name" was retained for some major functions such as fire service and police at the next reorganisation of local government in 1996.
The county then was administered by three new unitary councils:
- Argyll and Bute Council (which took over the Helensburgh and Lomond part of Dumbarton District)
- East Dunbartonshire Council
- West Dunbartonshire Council
Cumbernauld was not included in either of the new Dunbartonshire councils, instead being placed in the North Lanarkshire area.
Geography

The northern half of the county is sparsely populated and dominated by Loch Lomond, which it shares with Stirlingshire, and the Trossachs (now a national park). There are many islands in the loch which form part of the county, the most notable being Island I Vow, Tarbet Isle, Inchlonaig, Inchconnachan, Inchmoan, Inchtavannach, Fraoch Eilean, Inchgalbraith, Torrinch, Creinch, Inchmurrin and Aber Isle. The much smaller Geal Loch, Lochan Beinn Damhain, Lochan Strath Dubh-uisge and Loch Sloy can also be found here. The area is also home to Ben Vorlich, the highest point of Dunbartonshire at 943 m (3,094 ft) and the 10th tallest mountain in Scotland.

South-western Dunbartonshire has a long coastline along Loch Long, culminating in the Rosneath peninsula which is separated from the main body of the county by Gare Loch. Both of these lead into the Firth of Clyde which forms the southern border. The area east of the river Leven is dominated geographically by the Kilpatrick Hills which also contains a number of small lochs and reservoirs. In the far south-east the county encompasses a portion of the Greater Glasgow conurbation.

The Cumbernauld exclave is largely flat and heavily urbanised.
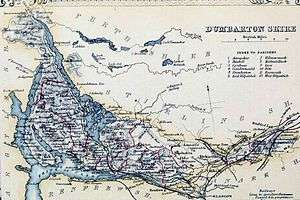
Boundaries and the Cumbernauld exclave
The county retained a large exclave situated 5 miles to the east of the main part of the county despite the boundary changes in the 1890s elsewhere in Scotland, consisting of the civil parishes of Kirkintilloch and Cumbernauld, between Stirlingshire and Lanarkshire. This area had originally been part of Stirlingshire, but had been annexed to Dunbarton in the reign of David II at the request of Malcolm Fleming, Earl of Wigtown, the owner of the land, who was also Sheriff of Dumbarton.[7]
The exclave was dealt with in 19th century legislation as greater administrative duties were given to the counties.
The Police (Scotland) Act 1857 established police forces throughout Scotland. A section of the act allowed for the parishes to be transferred to the jurisdiction of either Stirlingshire or Lanarkshire Constabulary on resolution of two-thirds of the Commissioners of Supply for the County of Dumbarton.[8]
Similar provisions allowing for the transfer of the area for all purposes were included in the County General Assessment (Scotland) Act 1868.[9] No such resolution was made, and the two parishes remained in Dunbartonshire.
The Roads and Bridges (Scotland) Act 1878 provided that for the purposes of that act all detached parts of counties should be placed in the county by which they were surrounded, or with which they had the longest boundary.[10] Accordingly, Cumbernauld and Kirkintilloch came under the control of the Stirlingshire Road Board. It was originally anticipated that the area would be transferred to Stirlingshire for all other purposes by the boundary commissioners proposed by the Local Government Bill of 1889[11] However, a clause was inserted in the bill that stated "the parishes of Cumbernauld and Kirkintilloch, including the burghs and police burghs situate therein, shall for the purposes of this Act, be considered as forming part of the county of Dumbarton". The clause was vigorously opposed by the Stirlingshire Commissioners of Supply as they had incurred considerable expense in maintaining the roads of the two parishes. The Act as passed provided that the Dunbartonshire County Council was to financially compensate Stirlingshire on the transfer of road powers.[12]
Transport

The West Highland Line runs through the county connecting Glasgow to Oban and Fort William and is popular with tourist due to its scenic view of the Highlands. The North Clyde line serves the towns of the Vale of Leven, and many suburban and commuter lines serve those parts of Dunbartonshire that form part of the Glasgow conurbation. Two lines run west-east through the Cumbernauld exclave, linking this area to Glasgow and Falkirk.
Various ferries criss-cross Loch Lomond, linking some of the towns along its banks. The Rosneath peninsula is connected by a ferry from Kilcreggan to Gourock in Renfrewshire.
Settlements
Villages and hamlets
- Aldochlay
- Ardlui
- Ardpeaton
- Arrochar
- Auchenvennel
- Bellsmyre
- Blairglas
- Blairvadach
- Bonhill
- Bowling
- Caldarvan
- Cardross
- Clynder
- Cove
- Craigendoran
- Croftamie
- Dalreoch
- Dumfin
- Edentaggart
- Garelochhead
- Gartocharn
- Hardgate
- Inverbeg
- Inveruglas
- Jamestown
- Kilcreggan
- Luss
- Milton
- Old Kilpatrick
- Portincaple
- Portkil
- Rahane
- Renton
- Rhu
- Rosneath
- Shandon
- Shantron
- Stuckgowan
- Tarbet
 Bonhill
Bonhill Kilcreggan
Kilcreggan Luss
Luss Rhu
Rhu
Glasgow conurbation
 Clyebank Town Hall
Clyebank Town Hall- New Kilpatrick Parish Church, Bearsden
 Yoker
Yoker
Cumbernauld exclave
 Carbrain
Carbrain Cumbernauld
Cumbernauld Kirkintilloch
Kirkintilloch
Civil Parishes
- Arrochar
- Bonhill
- Cardross
- Craigrownie
- Cumbernauld
- Dalreoch
- Dumbarton
- Kilmaronock
- Kirkintilloch
- Luss
- New Kilpatrick
- Old Kilpatrick
- Renton
- Rhu
- Rosneath
- Rossdhu
Military Connections
During the rise of the Volunteer Force, the military in Dunbartonshire was widely expanded. See: Militia and Volunteer of Dunbartonshire.
References
- "Dunbartonshire". www.ainmean-aite.scot. Retrieved 22 February 2020.
- "Visions of Britain".
- See for instance Crown Lands - Forfeited Estates Act, 1784 (1784 c. 57) and Manning of the Navy Act, 1795 (1795 c. 29)
- Edinburgh Gazette, Issue 6736, published 15 September 1857
- Edinburgh Gazette, Issue 12743, published 24 November 1914
- Local Government (Scotland) Act 1947 (1947 c. 43)
- Cumbernauld, A Topographical Dictionary of Scotland (1846)(British History Online)
- Police (Scotland) Act 1857 (C.72) s.70
- 1868 (C.82) s.6
- Roads and Bridges (Scotland) Act 1878 C.51, S.40
- "Local Government (Scotland) Bill No.179 (HL Deb 06 August 1889 vol 339 cc447-531)". Hansard, Lords Sitting. 6 August 1889. Retrieved 30 June 2008.
- Local Government (Scotland) Act 1889 1889 (c. 50) s.40
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Dumbartonshire. |
Bibliography
- "The Book of Dumbartonshire", J. Scott Keltie in Macmillan's Magazine, Vol. LXII, May to Oct., 1880, pp. 33–42
- A Short History of Dumbartonshire I.M.M. MacPhail

