Duchy of Opole
Duchy of Opole (German: Herzogtum Oppeln; Czech: Opolské knížectví) was one of the duchies of Silesia ruled by the Piast dynasty. Its capital was Opole (Oppeln, Opolí) in Upper Silesia.
.jpg)
Duchy of Opole | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1172–1202 1281–1532 | |||||||||
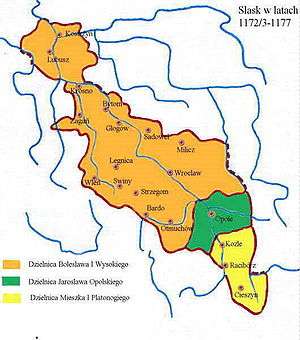 Silesia 1172-77: Bolesław I the Tall at Wrocław (orange), Mieszko I Tanglefoot at Racibórz (yellow), Jarosław at Opole (green) | |||||||||
| Status | Silesian duchy Fiefdom of Bohemia (1291–1306; 1327–1348) Fiefdom of the Bohemian Crown (until 1742) Part of Prussia (1742–1919) | ||||||||
| Capital | Opole | ||||||||
| Historical era | Middle Ages | ||||||||
| 1172 | |||||||||
• United with Racibórz | 1202 | ||||||||
• Split off Racibórz | 1281 | ||||||||
• Vassalized (finally) by Bohemia | 1327 | ||||||||
• Inherited Racibórz | 1521 | ||||||||
• Fell to Bohemia | 1532 | ||||||||
• Annexed by Prussia | 1742 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Duke Boleslaw III 'the Wrymouth' (r.1102-38; who died a feudatory of the German Emperor) had restored Polish fortunes to some extent but having endured terrific internal strife, he decreed in his Will that the 'kingdom' would be better divided into four hereditary principalities for each of his four sons. A kind of family federation. One became Duke of Great Poland (around Gniezno), another Silesia, another Cracow, another, half-heathen Masovia. The rising local magnates, dowered with estates, preferred provincial princes. But the division of loyalties among these princes brought on a long period of dynastic struggle, intrigue, and national weakness. By this time Silesia, under strong German influence, had been divided into sixteen minuscule principalities and was finally annexed by Bohemia. Civil Wars followed which encouraged foreign intervention. Boleslav IV (1146–73) submitted (1157) as vassal of the German Emperor, Frederick I Barbarossa, and the Piast Dukes in Silesia ultimately grew wholly Germanized. The disputes, however, continued.[1]
Duke Bolesław I the Tall and his younger brother Mieszko I Tanglefoot divided the territory among themselves into the two duchies of Wrocław and Racibórz. Bolesław originally had the intention to bequest the Duchy of Wrocław as a whole to his son of his second marriage Henry I the Bearded, which caused the protest of his eldest son Jarosław. After a long-term dispute in 1172 the Duchy of Opole was formed with Jarosław becoming the first duke. In turn he was obliged to an ecclesiastical career and became Bishop of Wrocław in 1198.
When Duke Jarosław died in 1201, the Opole lands reverted to his still living father Bolesław and were briefly incorporated into the Duchy of Wrocław. Bolesław himself however died shortly afterwards and in 1202 Opole was taken by his brother Duke Mieszko I Tanglefoot of Racibórz, who merged it with his duchy, creating the united Upper Silesian Duchy of Opole and Racibórz.
After the death of Mieszko's grandson Duke Władysław Opolski in 1281, his sons again divided the Duchy of Opole and Racibórz and the Duchy of Opole was recreated for Casimir and his brother Bolko I, contemporaneously with the establishment of the duchies of Cziesyn and Bytom on former Racibórz territory. In 1327 King John the Blind of Bohemia reasserted his influence over the Duchy of Opole in an attempt to stabilise the situation.
The Duchy underwent various future territorial changes, becoming increasingly small until the mid-15th century, when it would start to expand again, resulting in the recreation of the Duchy of Opole and Racibórz under Duke Jan II the Good in 1521. Jan however died without issue in 1532 and the Opole line of the Piasts became extinct, whereafter Opole and Racibórz as feudal fiefdoms reverted to the sovereignty of the Bohemian Crown. It would then fall to Margrave George of Brandenburg-Ansbach from the House of Hohenzollern, who had signed his inheritance treaty with Duke Jan in 1522 with the consent of the Bohemian king Ferdinand I of Habsburg. Between 1645 - 1666 Opole was held in feu by the Polish House of Vasa, reverting to the Habsburg Kings of Bohemia. In 1742 it was annexed and incorporated into the Kingdom of Prussia.
See also
- Dukes of Opole
- Dukes of Silesia
- Opole Voivodeship
References
- Previté-Orton, C.W., The Shorter Cambridge Medieval History, Cambridge University Press, U.K., 1952, vol.2, p.743, et al


