Dolby 3D
Dolby 3D (formerly known as Dolby 3D Digital Cinema) is a marketing name for a system from Dolby Laboratories, Inc. to show three-dimensional motion pictures in a digital cinema.

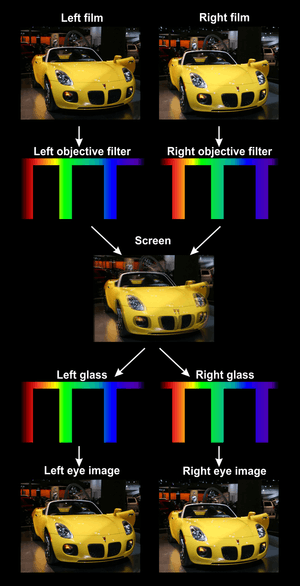
Technology
Dolby 3D uses a Dolby Digital Cinema projector that can show both 2D and 3D films. For 3D presentations, an alternate color wheel is placed in the projector. This contains one more set of red, green, and blue filters in addition to the red, green, and blue filters found on a typical color wheel. The additional set of three filters are able to produce the same color gamut as the original three filters, but transmit light at different wavelengths. Glasses with complementary dichroic filters in the lenses are worn, which filter out either one or the other set of three light wavelengths. In this way, one projector can display the left and right stereoscopic images simultaneously.[1] This method of stereoscopic projection is called wavelength multiplex visualization, and was created by Infitec.[2][3] The dichroic filters in the Dolby 3D glasses are more expensive and fragile than the glasses technology used in circular polarization systems like RealD Cinema or linear polarization systems like Digital IMAX and are not considered disposable.[4] However, an important benefit of Dolby 3D in comparison with RealD is that Dolby 3D works with conventional projection screens.[5] Dolby 3D also produces a brighter and sharper 3D image than RealD and is able to be comfortably viewed on outdoor cinema screens and drive-in cinemas.[6][4]
Gallery
- Dolby 3D glasses
- Dichroic lenses
 Color filter design of the Dolby3D system
Color filter design of the Dolby3D system
References
- Kooptech. "Dolby 3D glasses - how it works". kooptech-cinema.com. Retrieved 2018-11-11.
- Sokol, John (June 3, 2009). "Video Technology: Dolby 3D Digital Cinema". Retrieved 2018-11-11.
- Design, dimensions Web. "stereoscopy.com - FAQ". www.stereoscopy.com. Retrieved 2018-11-11.
- "FAQs - Galaxy Drive-In Theatre". www.galaxydriveintheatre.com. Retrieved 2018-11-11.
- "Dolby 3D Cinema Bundle". www.dolby.com. Retrieved 2018-11-11.
- "Q&A: Which is the Best 3D Format? – Page 2 of 3 – /Film". /Film. February 3, 2012. Retrieved 2018-11-11.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Dolby 3D. |