Dellia Battery
Dellia Battery (Maltese: Batterija tad-Dellija), also known as Vendôme Battery (Maltese: Batterija ta' Vendôme) or Pwales Right Battery (Maltese: Batterija tal-Lemin tal-Pwales), was an artillery battery[lower-alpha 1] in Xemxija Bay, limits of St. Paul's Bay, Malta. It was built by the Order of Saint John in 1715 as one of a series of coastal fortifications around the coasts of the Maltese Islands. It was demolished in 1924, but the coats of arms and inscription which were located above the main entrance still exist and are now a monument.
| Dellia Battery | |
|---|---|
Batterija tad-Dellija | |
| St. Paul's Bay, Malta | |
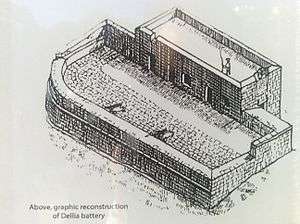 Graphic reconstruction of Dellia Battery | |
 Map of Dellia Battery | |
| Coordinates | 35°56′42.1″N 14°23′7.9″E |
| Type | Artillery battery[lower-alpha 1] |
| Site information | |
| Condition | Coats of arms and inscription preserved as a monument Foundations possibly buried beneath modern road |
| Site history | |
| Built | 1715 |
| Built by | Order of Saint John |
| Materials | Limestone |
| Fate | Demolished, 1924 |
History
Dellia Battery was built in 1715 as part of the Order of Saint John's first building program of batteries and redoubts around the coasts of Malta. It was one of two batteries defending Xemxija Bay, the other one being Arrias Battery, which is still in existence.[1]
The battery consisted of a mostly rectangular gun platform with a rounded end, ringed by a low parapet. Its gorge was closed off by a rectangular blockhouse. The doorway was surmounted by the coats of arms of the Order, Grand Master Ramon Perellos y Roccaful and the Langue of France. The latter represented Philippe de Vendôme, who had a leading role in the construction of batteries in Malta.
In 1770, the battery was armed with six 6-pounder iron guns, and was supplied with 420 rounds of roundshot and 90 rounds of grapeshot. Three of its guns were removed by 1785.[2]
In the early 20th century, the battery was a summer residence for the consul-general of Austria-Hungary, Antonio Muscat Fenech. At this point, an extension was added to the battery, and it flew the Union jack and Austro-Hungarian ensign.[2]
Most of Dellia Battery was demolished in 1924 to make way for a new road, but the three escutcheons with coats of arms and a commemorative marble plaque which stood on the doorway were retained. The parapet was also retained, but it was eventually demolished after World War II when a roundabout was built in its place.[3]

Today, the only remains of the battery are the coats of arms and plaque which formerly stood on the doorway. These are mounted on a plinth on the side of the road.[4] In addition, the foundations possibly still exist, buried under the modern road.[3]
The plinth containing the coats of arms and inscription is listed on the National Inventory of the Cultural Property of the Maltese Islands.[3]
Further reading
- Spiteri, Stepehen C. (1994). Fortresses of the Cross: Hospitaller Military Architecture (1136-1798). Heritage Interpretation Services. p. 519. ISBN 9789990996531.
References
- "San Pawl il-Baħar". lc.gov.mt. Archived from the original on 7 March 2016.
- Mizzi, John A. (4 June 2012). "The Dellija redoubt". Times of Malta. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016.
- "Vendôme Battery – Pwales" (PDF). National Inventory of the Cultural Property of the Maltese Islands. 28 June 2013. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 January 2016.
- Mallia, Oliver (30 January 2012). "Delija coat of arms". Times of Malta. Archived from the original on 3 March 2016.
Notes
- Sometimes described as a redoubt.