Deadhorse, Alaska
Deadhorse is an unincorporated community located within the CDP of Prudhoe Bay in North Slope Borough, Alaska, United States, along the North Slope near the Arctic Ocean. The town consists mainly of facilities for the workers and companies that operate at the nearby Prudhoe Bay Oil Field. Deadhorse is accessible via the Dalton Highway from Fairbanks, 495 mi (797 km) south, or Deadhorse Airport. Limited accommodation is also available for tourists.
Deadhorse, Alaska | |
|---|---|
 Aerial view of Deadhorse, March 2007 | |
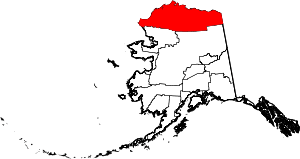
 Deadhorse, Alaska Location in the United States of America | |
| Coordinates: 70°12′20″N 148°30′42″W | |
| Country | United States |
| State | Alaska |
| Borough | North Slope |
| Government | |
| • Borough mayor | Harry K. Brower, Jr. |
| • State senator | Donny Olson (D) |
| • State rep. | Dean Westlake (D) |
| Elevation | 49 ft (15 m) |
| Time zone | UTC-9 (Alaska (AKST)) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-8 (AKDT) |
| GNIS ID | 2419433[1] |
The permanent population is variously listed as being between 25 and 50 residents. Temporary residents (employed by various firms with local interests) can range as high as 3,000.
Companies with facilities in Deadhorse service Prudhoe Bay, nearby oil fields, and the Trans-Alaska Pipeline System (TAPS), which brings oil from Prudhoe Bay to Valdez on the south-central Alaska coast. Facilities in Deadhorse are built entirely on man-made gravel pads and usually consist of pre-fabricated modules shipped to Deadhorse via barge or air cargo.
History
The Prudhoe Bay, Alaska area was developed to house personnel, provide support for drilling operations, and transport oil to the Alaskan pipeline.[2] Prior to 1977, oil seeps (small pores or fissure networks through which liquid petroleum emerges at the surface of the land)[3] on the Arctic coastal plain had caught the attention of the U.S. petroleum interests.[2] The U.S. Navy drilled for oil between 1944 and 1953 with little success.[2] However, in 1967, after several attempts at drilling for oil, oil company mergers, and competitive bidding for state lease sales, the Prudhoe Bay oil field was discovered.[2]
Sources conflict on the origin of the area's name.[4] The most cited theory appears to be that the area takes its name from a local business prominent in the late 1960s and 1970s, the "Dead Horse Haulers" trucking company.[4][5] How the trucking company got its name remains in dispute.[4][5]
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1970 | 163 | — | |
| 1980 | 64 | −60.7% | |
| 1990 | 26 | −59.4% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census[6] | |||
Deadhorse first appeared on the 1970 U.S. Census as an unincorporated village. It was made a census-designated place (CDP) in 1980. It appeared last on the 1990 census. After 2000, it was merged into the Prudhoe Bay CDP.
Tourism and wildlife

Tourists traveling to Deadhorse and Prudhoe Bay typically take tour buses from Fairbanks via the James Dalton Highway, a two-day journey with an overnight stop in Coldfoot. During the summer months, visitors can arrange for tours to the Arctic Ocean via a guided tour only. There is no longer any public Arctic Ocean access from Deadhorse. All tours must be booked 24 hours in advance to allow time for background checks on all passengers going through the oilfield check point. Tourists can also experience the midnight sun due to Deadhorse's location above the Arctic Circle. In winter, the opposite phenomenon, polar night, occurs.
The area often features large herds of caribou and over 200 bird and waterfowl species, including geese, swans, gulls and eagles.[7] Other indigenous wildlife include Arctic foxes, Arctic ground squirrels, grizzly bears, polar bears, musk oxen, and Arctic hares.[7]
Because alcoholic beverages are not sold in Deadhorse, a humorous slogan for the town is "All that far and still no bar."[8]
This is the beginning or end of an Iron Butt Association motorcycle rider challenge called "The Ultimate Coast to Coast". This ride starts from Key West, Florida, and gives riders 30 days to reach Deadhorse, Alaska. It is also the midpoint of the "Haul Road 1000" and the beginning or end of the "Alaska Insanity Gold" challenge (riders allotted 24 hours for those two challenges).[9]
Climate
Deadhorse features a borderline semi-arid-tundra climate (Köppen ET), as even the warmest month, July, has a daily average temperature of only 47 °F (8.3 °C) [Although Deadhorse reaches 80 °F (26.7 °C) an average of every 4 years, and there has never been a year where it didn't reach 70 °F (21.1 °C)]. The mean annual temperature is 12 °F (−11 °C), with daytime temperatures reliably remaining below freezing from early/mid October to late April. As the area is located in USDA Plant Hardiness Zone 2,[10] temperatures below −40 °F/°C can be expected during the height of winter.
- Longest day: 63 days, 23 hours, 40 minutes (12:09 a.m. on May 20 to 11:18 p.m. on July 22)
- Shortest day: 45 min (11:42 a.m. to 12:27 p.m. on November 24)
- Longest night: 54 days, 22 hours, 51 min (12:27 p.m. on November 24 to 11:18 a.m. on January 18)
- Shortest night: 26 min (11:43 p.m. on May 19 to 12:09 a.m. on May 20)
- Highest recorded temperature: 85 °F (29 °C) on 13 July 2016
- Lowest recorded temperature: −62 °F (−52 °C) on 27 January 1989
- Highest wind speed recorded: 95 knots (109 mph; 176 km/h) on 25 February 1989
- Official lowest wind chill: −102 °F (−74 °C) on 28 January 1989 (air temperature of −54 °F or −48 °C) and wind speed of 31 kn (36 mph; 57 km/h)
| Climate data for Deadhorse, Alaska | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 40 (4) |
40 (4) |
42 (6) |
43 (6) |
55 (13) |
83 (28) |
85 (29) |
82 (28) |
70 (21) |
50 (10) |
37 (3) |
39 (4) |
85 (29) |
| Mean maximum °F (°C) | 21.2 (−6.0) |
16.5 (−8.6) |
14.3 (−9.8) |
29.9 (−1.2) |
41.3 (5.2) |
69.2 (20.7) |
73.6 (23.1) |
70.6 (21.4) |
58.9 (14.9) |
35.8 (2.1) |
24.5 (−4.2) |
21.2 (−6.0) |
76.9 (24.9) |
| Average high °F (°C) | −9 (−23) |
−12 (−24) |
−8 (−22) |
8 (−13) |
27 (−3) |
46 (8) |
53 (12) |
48 (9) |
37 (3) |
21 (−6) |
5 (−15) |
−4 (−20) |
18 (−8) |
| Daily mean °F (°C) | −16 (−27) |
−18 (−28) |
−16 (−27) |
1 (−17) |
22 (−6) |
39 (4) |
46 (8) |
42 (6) |
33 (1) |
17 (−8) |
−2 (−19) |
−11 (−24) |
11 (−11) |
| Average low °F (°C) | −23.1 (−30.6) |
−23.6 (−30.9) |
−23.1 (−30.6) |
−7.9 (−22.2) |
16.1 (−8.8) |
32.8 (0.4) |
38.3 (3.5) |
35.8 (2.1) |
27.7 (−2.4) |
12.5 (−10.8) |
−8.1 (−22.3) |
−17.2 (−27.3) |
5.0 (−15.0) |
| Mean minimum °F (°C) | −43.1 (−41.7) |
−44.1 (−42.3) |
−41.4 (−40.8) |
−27.8 (−33.2) |
−4.9 (−20.5) |
25.9 (−3.4) |
31.9 (−0.1) |
28.6 (−1.9) |
17.1 (−8.3) |
−10.1 (−23.4) |
−25.6 (−32.0) |
−38.7 (−39.3) |
−47.3 (−44.1) |
| Record low °F (°C) | −62 (−52) |
−57 (−49) |
−54 (−48) |
−47 (−44) |
−19 (−28) |
18 (−8) |
28 (−2) |
23 (−5) |
1 (−17) |
−30 (−34) |
−45 (−43) |
−52 (−47) |
−62 (−52) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 0.15 (3.8) |
0.13 (3.3) |
0.14 (3.6) |
0.10 (2.5) |
0.08 (2.0) |
0.37 (9.4) |
0.72 (18) |
0.95 (24) |
0.65 (17) |
0.40 (10) |
0.14 (3.6) |
0.19 (4.8) |
4.02 (102) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 1.42 (3.6) |
2.09 (5.3) |
0.98 (2.5) |
0.79 (2.0) |
2.21 (5.6) |
0.79 (2.0) |
0 (0) |
0.12 (0.30) |
3.11 (7.9) |
8.12 (20.6) |
2.01 (5.1) |
2.09 (5.3) |
23.73 (60.2) |
| Source: NOAA (temperature normals 1981–2010),[11] weather.com (precipitation and extremes)[12] | |||||||||||||
Health care
Deadhorse (including Prudhoe Bay) is classified as an isolated town/Sub-Regional Center. It is found in EMS Region 6A in the North Slope Region. Emergency Services have limited highway, coastal, and airport access. Emergency service is provided by paid EMS service and Fairweather Deadhorse Medical Clinic (open daily and on call 24 hours a day [907-685-1800] for emergencies and urgent care). Auxiliary health care is provided by oil company medical staff and the Greater Prudhoe Bay Fire Dept. Individuals requiring hospital care are usually transported to the nearest hospital/medical center, Sammuel Simmonds Memorial Hospital, in Utqiagvik, Alaska. Because no roads connect Deadhorse to Utqiagvik, individuals are transported by plane or helicopter (an approximately 45 minute flight).[13]
In popular culture
Comic books
Television
- Deadhorse is the subject of the second episode of America's Toughest Jobs
- Deadhorse is featured on the third through sixth seasons of Ice Road Truckers, a reality television series airing on the History Channel;[16] it dramatizes trucking on the Dalton Highway and often features truckers transporting equipment to the oil companies located in or around the Prudhoe Bay area.[16]
- It is briefly featured in the first, second, and third seasons of the BBC's Life Below Zero.
- It is featured in the first episode of the BBC's World's Most Dangerous Roads
- It is featured in the X-Files, season 2, episode 17: "End Game".
Image gallery
- Sign at General Store, Deadhorse, Alaska (January 2008)
.jpg) Deadhorse General Store (2003)
Deadhorse General Store (2003) The Dalton Highway at Deadhorse (July 2010)
The Dalton Highway at Deadhorse (July 2010)
References
- U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: Deadhorse, Alaska
- "Prudhoe Bay - Visit Alaska". Myalaskan.com. 2012-04-17. Archived from the original on 2013-03-15. Retrieved 2013-05-16.
- "oil seep definition of oil seep in the Free Online Encyclopedia". Encyclopedia2.thefreedictionary.com. Retrieved 2013-05-16.
- Archived May 9, 2008, at the Wayback Machine
- http://uaf-db.uaf.edu/Jukebox/haul_road_07/assets/docs/bc_deadhorse.pdf%5B%5D
- "U.S. Decennial Census". Census.gov. Retrieved June 6, 2013.
- http://www.prudhoebay.com/communities_Deadhorse.htm Deadhorse, Alaska website
- "Life in Deadhorse, Alaska: It's all about the oil". Independent Record. 2006-08-10. Retrieved 2017-09-11.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2013-04-02. Retrieved 2013-05-25.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- The Arbor Day Foundation. "The Arbor Day Foundation". Arborday.org. Retrieved 2013-05-16.
- "Station Name: AK DEADHORSE AP". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 2013-03-11.
- "Average weather for Deadhorse". weather.com. Retrieved July 27, 2016.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2014-10-30. Retrieved 2014-10-22.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) Far North - Prudhoe Bay Information
- Grissom, Eric & Sloan, Phil & Louise, Marissa & Halvorson, David. "Deadhorse". deadhorsecomic.com. Frankenstein's Daughter.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
- Grissom, Eric & Sloan, Phil & Louise, Marissa & Halvorson, David (2013). Dead Birds (Deadhorse #1). Frankenstein's Daughter.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
- "Ice Road Truckers Episode Guide - Season 6". History.com. Archived from the original on 2010-02-09. Retrieved 2013-05-16.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Deadhorse, Alaska. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Deadhorse. |
See also
- Dead horse (disambiguation)